Abstract
Chylomicron catabolism is known to be initiated by the enzyme lipoprotein lipase (triacylglycero-protein acylhydrolase, EC 3.1.1.34). Chylomicron remnants, produced by lipolysis, are rapidly taken up by the liver via an apolipoprotein E (apoE)-mediated, receptor-dependent process. The low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor-related protein (LRP) has been suggested as the potential apoE receptor. We have analyzed the binding of human chylomicrons to HepG2 cells in the absence and presence of lipoprotein lipase. Bovine and human lipoprotein lipases were able to increase the specific binding of the chylomicrons by up to 30-fold. This effect was not dependent on lipolysis but appeared to be due to the lipase protein itself. It was not found when a structurally unrelated, bacterial lipase was used. Using beta-migrating very low density lipoproteins (beta-VLDLs), known as a good ligand for LRP, binding studies were performed on LDL receptor-negative human fibroblasts. The binding was increased 40-fold by addition of lipoprotein lipase. Crosslinking experiments on cells with 125I-labeled apoE liposomes or lipoprotein lipase showed that both proteins were able to bind to LRP on the cell surface. The binding of apoE to LRP was highly increased by the addition of lipase. We conclude that lipoprotein lipase strongly enhances the binding of apoE-containing lipoproteins to LRP and therefore might play an important role in chylomicron catabolism not only because of its lipolytic activity but also because of its structural properties.
Full text
PDF


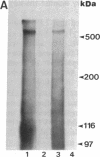
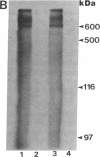
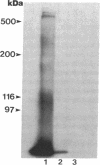
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbeeny C. M., Rifici V. A. The uptake of chylomicron remnants and very low density lipoprotein remnants by the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9662–9666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auwerx J. H., Babirak S. P., Fujimoto W. Y., Iverius P. H., Brunzell J. D. Defective enzyme protein in lipoprotein lipase deficiency. Eur J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;19(5):433–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1989.tb00255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babirak S. P., Iverius P. H., Fujimoto W. Y., Brunzell J. D. Detection and characterization of the heterozygote state for lipoprotein lipase deficiency. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 May-Jun;9(3):326–334. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.3.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisiegel U., Weber W., Havinga J. R., Ihrke G., Hui D. Y., Wernette-Hammond M. E., Turck C. W., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Apolipoprotein E-binding proteins isolated from dog and human liver. Arteriosclerosis. 1988 May-Jun;8(3):288–297. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.8.3.288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisiegel U., Weber W., Ihrke G., Herz J., Stanley K. K. The LDL-receptor-related protein, LRP, is an apolipoprotein E-binding protein. Nature. 1989 Sep 14;341(6238):162–164. doi: 10.1038/341162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Olivecrona T. Phospholipase activity of milk lipoprotein lipase. Methods Enzymol. 1991;197:345–356. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)97160-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson G., Olivecrona T. Lipoprotein lipase. Mechanism of product inhibition. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(2):557–562. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04603.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borensztajn J., Getz G. S., Padley R. J., Kotlar T. J. The apoprotein B-independent hepatic uptake of chylomicron remnants. Biochem J. 1982 May 15;204(2):609–612. doi: 10.1042/bj2040609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Lipoprotein receptors in the liver. Control signals for plasma cholesterol traffic. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):743–747. doi: 10.1172/JCI111044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrella M., Cooper A. D. High affinity binding of chylomicron remnants to rat liver plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):338–342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chajek-Shaul T., Friedman G., Stein O., Olivecrona T., Stein Y. Binding of lipoprotein lipase to the cell surface is essential for the transmembrane transport of chylomicron cholesteryl ester. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jul 20;712(1):200–210. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. D., Yu P. Y. Rates of removal and degradation of chylomicron remnants by isolated perfused rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1978 Jul;19(5):635–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckel R. H. Lipoprotein lipase. A multifunctional enzyme relevant to common metabolic diseases. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 20;320(16):1060–1068. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904203201607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felts J. M., Itakura H., Crane R. T. The mechanism of assimilation of constituents of chylomicrons, very low density lipoproteins and remnants - a new theory. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 27;66(4):1467–1475. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90524-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florén C. H. Hepatic binding of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in humans. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1985 Oct;45(6):531–537. doi: 10.3109/00365518509155255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I. J., Kandel J. J., Blum C. B., Ginsberg H. N. Association of plasma lipoproteins with postheparin lipase activities. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1523–1528. doi: 10.1172/JCI112744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz J., Hamann U., Rogne S., Myklebost O., Gausepohl H., Stanley K. K. Surface location and high affinity for calcium of a 500-kd liver membrane protein closely related to the LDL-receptor suggest a physiological role as lipoprotein receptor. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4119–4127. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz J., Kowal R. C., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Proteolytic processing of the 600 kd low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) occurs in a trans-Golgi compartment. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1769–1776. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08301.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs H. H., Brown M. S., Russell D. W., Davignon J., Goldstein J. L. Deletion in the gene for the low-density-lipoprotein receptor in a majority of French Canadians with familial hypercholesterolemia. N Engl J Med. 1987 Sep 17;317(12):734–737. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198709173171204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeg J. M., Demosky S. J., Jr, Gregg R. E., Schaefer E. J., Brewer H. B., Jr Distinct hepatic receptors for low density lipoprotein and apolipoprotein E in humans. Science. 1985 Feb 15;227(4688):759–761. doi: 10.1126/science.2982214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui D. Y., Brecht W. J., Hall E. A., Friedman G., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Isolation and characterization of the apolipoprotein E receptor from canine and human liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4256–4267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi S., Yamada N., Shimano H., Mori N., Mokuno H., Gotohda T., Kawakami M., Murase T., Takaku F. Apolipoprotein E and lipoprotein lipase secreted from human monocyte-derived macrophages modulate very low density lipoprotein uptake. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3040–3047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern P. A., Martin R. A., Carty J., Goldberg I. J., Ong J. M. Identification of lipoprotein lipase immunoreactive protein in pre- and postheparin plasma from normal subjects and patients with type I hyperlipoproteinemia. J Lipid Res. 1990 Jan;31(1):17–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Brown M. S., Basu S. K., Bilheimer D. W., Goldstein J. L. Saturation and suppression of hepatic lipoprotein receptors: a mechanism for the hypercholesterolemia of cholesterol-fed rabbits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1396–1400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal R. C., Herz J., Goldstein J. L., Esser V., Brown M. S. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein mediates uptake of cholesteryl esters derived from apoprotein E-enriched lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5810–5814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal R. C., Herz J., Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Opposing effects of apolipoproteins E and C on lipoprotein binding to low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10771–10779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen T., Moestrup S. K., Gliemann J., Bendtsen L., Sand O., Sottrup-Jensen L. Evidence that the newly cloned low-density-lipoprotein receptor related protein (LRP) is the alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor. FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 10;276(1-2):151–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80530-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund H., Takahashi K., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Lipoprotein binding and endosomal itinerary of the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9318–9322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFARLANE A. S. Efficient trace-labelling of proteins with iodine. Nature. 1958 Jul 5;182(4627):53–53. doi: 10.1038/182053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mjos O. D., Faergeman O., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Characterization of remnants produced during the metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins of blood plasma and intestinal lymph in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):603–615. doi: 10.1172/JCI108130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder M., de Wit E., Havekes L. M. The binding of human lipoprotein lipase treated VLDL by the human hepatoma cell line HepG2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Feb 5;1081(3):308–314. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(91)90287-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel S. P., Dolphin P. J., Rubinstein D. An in vitro model for the catabolism of rat chylomicrons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 7;63(3):764–772. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80449-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redgrave T. G., Fidge N. H., Yin J. Specific, saturable binding and uptake of rat chylomicron remnants by rat skin fibroblasts. J Lipid Res. 1982 May;23(4):638–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Jenkins L. L., Brewer H. B., Jr Human chylomicron apolipoprotein metabolism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jan 30;80(2):405–412. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90691-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrill B. C., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Rapid hepatic clearance of the canine lipoproteins containing only the E apoprotein by a high affinity receptor. Identity with the chylomicron remnant transport process. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1804–1807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein O., Halperin G., Leitersdorf E., Olivecrona T., Stein Y. Lipoprotein lipase mediated uptake of non-degradable ether analogues of phosphatidylcholine and cholesteryl ester by cultured cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Aug 15;795(1):47–59. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland D. K., Ashcom J. D., Williams S., Burgess W. H., Migliorini M., Argraves W. S. Sequence identity between the alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor and low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein suggests that this molecule is a multifunctional receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17401–17404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber M. G., Olivecrona T., Kayden H. J. Bovine milk lipoprotein lipase transfers tocopherol to human fibroblasts during triglyceride hydrolysis in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1729–1734. doi: 10.1172/JCI111883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilaró S., Llobera M., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Olivecrona T. Lipoprotein lipase uptake by the liver: localization, turnover, and metabolic role. Am J Physiol. 1988 May;254(5 Pt 1):G711–G722. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.254.5.G711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallinder L., Peterson J., Olivecrona T., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G. Hepatic and extrahepatic uptake of intravenously injected lipoprotein lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Oct 4;795(3):513–524. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E. E., Greeve J., Daerr W. H., Greten H. Binding of rat chylomicrons and their remnants to the hepatic low-density-lipoprotein receptor and its role in remnant removal. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 1;252(2):553–561. doi: 10.1042/bj2520553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E., Chao Y., Havel R. J. Regulation of the hepatic uptake of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in the rat. Opposing effects of homologous apolipoprotein E and individual C apoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8303–8307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaidan H., Dhanireddy R., Hamosh M., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Hamosh P. Lipid clearing in premature infants during continuous heparin infusion: role of circulating lipases. Pediatr Res. 1985 Jan;19(1):23–25. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198501000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]