Abstract
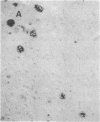
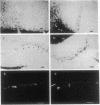
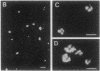
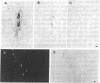
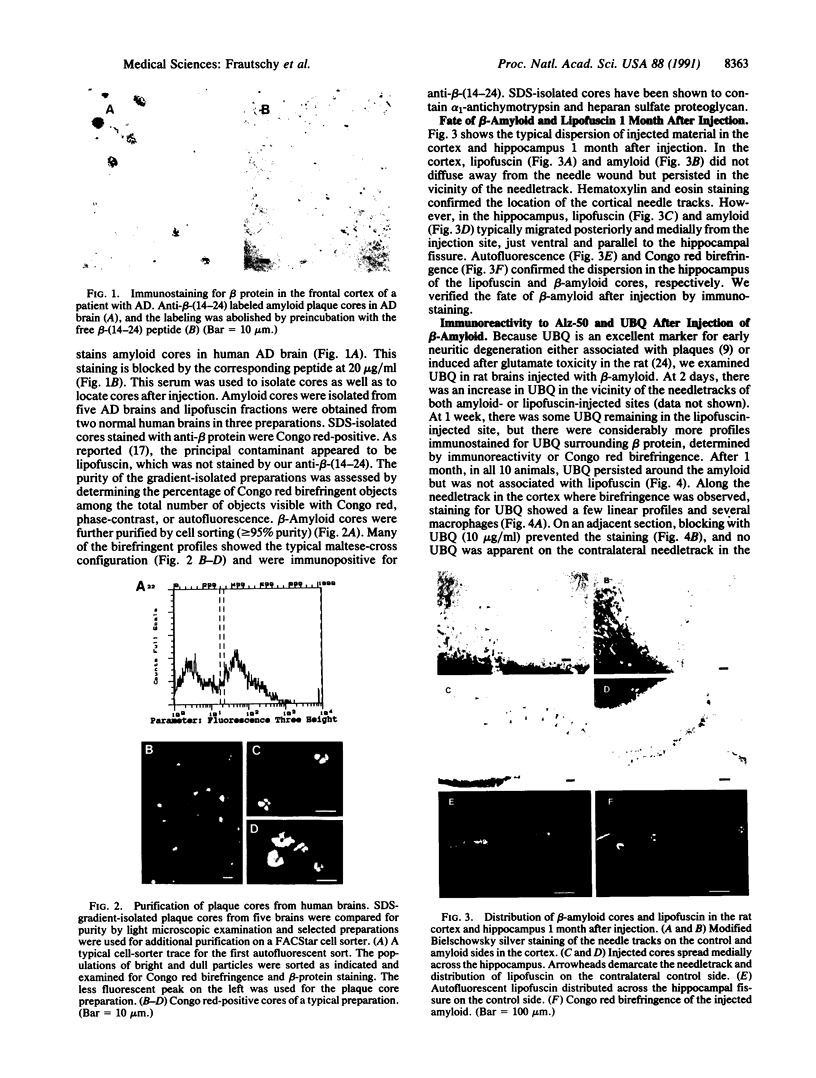
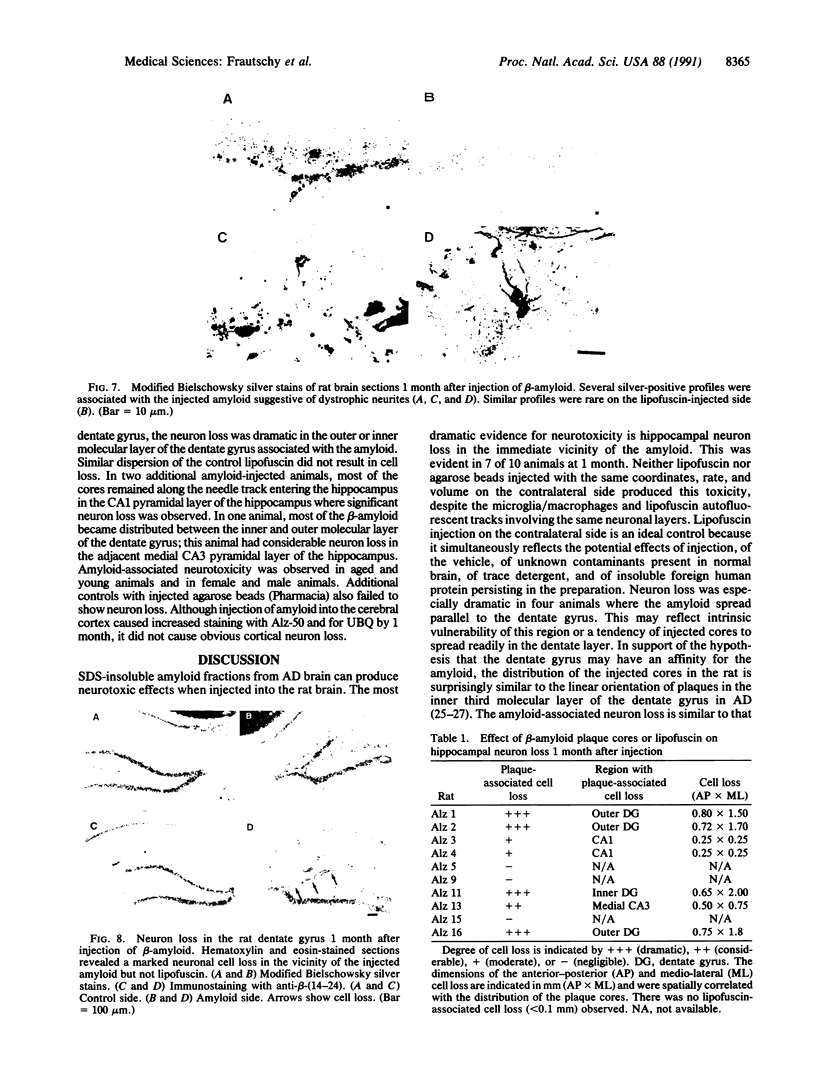
Although amyloid deposits have long been known to accumulate in Alzheimer disease (AD) brain, their origin and significance remain speculative. Because of the lack of an in vivo model where amyloid deposits can be induced, the relationship of the extracellular beta-amyloid deposits to other AD pathology has never been directly investigated. Therefore, we injected SDS-isolated amyloid cores into rat cortex and hippocampus. Similarly isolated lipofuscin fractions from control human brains were injected on the contralateral side. Rats were perfused and brains were examined immunohistochemically at 2 days, 7 days, and 1 month after injection. Alz-50, a monoclonal antibody against abnormally phosphorylated tau proteins, stained neurons along the cortical needle track at 2 but not 7 days after injection of either amyloid or lipofuscin. At 1 month, however, ubiquitin, Alz-50 antigen, and silver-positive structures were observed only in response to amyloid. In 7 of 10 animals, there was considerable neuronal loss in the hippocampal layers. In each instance, these effects were in the immediate vicinity of beta-protein immunoreactive material. Marked neuronal loss was never observed at any time after lipofuscin injection. These results indicate a neuronal response to amyloid. When preparations of mature plaque amyloid isolated from the AD brain are injected into the rat brain, they exert neurotoxic effects and induce antigens found in the AD brain.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham C. R., Selkoe D. J., Potter H. Immunochemical identification of the serine protease inhibitor alpha 1-antichymotrypsin in the brain amyloid deposits of Alzheimer's disease. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):487–501. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90462-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. M., Timiras P. S. Ubiquitin-protein conjugates in Alzheimer's lesions. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Aug 18;79(1-2):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90698-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G., Masliah E., Huynh T. V., DeTeresa R., Terry R. D., Okuda C., Saitoh T. An antiserum against amyloid beta-protein precursor detects a unique peptide in Alzheimer brain. Neurosci Lett. 1989 May 22;100(1-3):340–346. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90710-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crain B. J., Burger P. C. Neuritic plaques in the human fascia dentata: a model system for the study of plaque formation in Alzheimer's disease. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;317:523–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson D. W., Farlo J., Davies P., Crystal H., Fuld P., Yen S. H. Alzheimer's disease. A double-labeling immunohistochemical study of senile plaques. Am J Pathol. 1988 Jul;132(1):86–101. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):885–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgaber D., Lerman M. I., McBride O. W., Saffiotti U., Gajdusek D. C. Characterization and chromosomal localization of a cDNA encoding brain amyloid of Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):877–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3810169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman B. T., Van Hoesen G. W., Damasio A. R., Barnes C. L. Alzheimer's disease: cell-specific pathology isolates the hippocampal formation. Science. 1984 Sep 14;225(4667):1168–1170. doi: 10.1126/science.6474172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itagaki S., McGeer P. L., Akiyama H., Zhu S., Selkoe D. Relationship of microglia and astrocytes to amyloid deposits of Alzheimer disease. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Oct;24(3):173–182. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh J. Y., Yang L. L., Cotman C. W. Beta-amyloid protein increases the vulnerability of cultured cortical neurons to excitotoxic damage. Brain Res. 1990 Nov 19;533(2):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91355-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Simms G., Weinman N. A., Multhaup G., McDonald B. L., Beyreuther K. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson M. P. Antigenic changes similar to those seen in neurofibrillary tangles are elicited by glutamate and Ca2+ influx in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 1990 Jan;4(1):105–117. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90447-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., McGeer E., Rogers J., Sibley J. Anti-inflammatory drugs and Alzheimer disease. Lancet. 1990 Apr 28;335(8696):1037–1037. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91101-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mundy W. R., Tilson H. A. Neurotoxic effects of colchicine. Neurotoxicology. 1990 Fall;11(3):539–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst A., Brunnschweiler H., Lautenschlager C., Ulrich J. A special type of senile plaque, possibly an initial stage. Acta Neuropathol. 1987;74(2):133–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00692843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Luber-Narod J., Styren S. D., Civin W. H. Expression of immune system-associated antigens by cells of the human central nervous system: relationship to the pathology of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(4):339–349. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(88)80079-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt D. E., Geula C., Mesulam M. M. Protease nexin I immunostaining in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1989 Nov;26(5):628–634. doi: 10.1002/ana.410260507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., LaCorbiere M., Saitoh T., Cole G. Characterization of an amyloid beta precursor protein that binds heparin and contains tyrosine sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):2066–2069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.2066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Abraham C. R. Isolation of paired helical filaments and amyloid fibers from human brain. Methods Enzymol. 1986;134:388–404. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)34105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seubert P., Nakagawa Y., Ivy G., Vanderklish P., Baudry M., Lynch G. Intrahippocampal colchicine injection results in spectrin proteolysis. Neuroscience. 1989;31(1):195–202. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloviter R. S., Valiquette G., Abrams G. M., Ronk E. C., Sollas A. L., Paul L. A., Neubort S. Selective loss of hippocampal granule cells in the mature rat brain after adrenalectomy. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):535–538. doi: 10.1126/science.2911756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow A. D., Mar H., Nochlin D., Kimata K., Kato M., Suzuki S., Hassell J., Wight T. N. The presence of heparan sulfate proteoglycans in the neuritic plaques and congophilic angiopathy in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1988 Dec;133(3):456–463. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stopa E. G., Gonzalez A. M., Chorsky R., Corona R. J., Alvarez J., Bird E. D., Baird A. Basic fibroblast growth factor in Alzheimer's disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 14;171(2):690–696. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91201-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suenaga T., Hirano A., Llena J. F., Yen S. H., Dickson D. W. Modified Bielschowsky stain and immunohistochemical studies on striatal plaques in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;80(3):280–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00294646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRY R. D., GONATAS N. K., WEISS M. ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDIES IN ALZHEIMER'S PRESENILE DEMENTIA. Am J Pathol. 1964 Feb;44:269–297. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida Y., Ihara Y., Tomonaga M. Alzheimer's disease brain extract stimulates the survival of cerebral cortical neurons from neonatal rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 15;150(3):1263–1267. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90765-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vietje B. P., Wells J. Selective lesions of granule cells by fluid injections into the dentate gyrus. Exp Neurol. 1989 Dec;106(3):275–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(89)90160-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walicke P., Cowan W. M., Ueno N., Baird A., Guillemin R. Fibroblast growth factor promotes survival of dissociated hippocampal neurons and enhances neurite extension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):3012–3016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.3012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitson J. S., Glabe C. G., Shintani E., Abcar A., Cotman C. W. Beta-amyloid protein promotes neuritic branching in hippocampal cultures. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Mar 14;110(3):319–324. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90867-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitson J. S., Selkoe D. J., Cotman C. W. Amyloid beta protein enhances the survival of hippocampal neurons in vitro. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1488–1490. doi: 10.1126/science.2928783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. M., Iqbal K., Bancher C., Miller D., Currie J. Cytoskeletal protein pathology and the formation of beta-amyloid fibers in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1989 Sep-Oct;10(5):409–414. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(89)90079-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Nakazato Y., Hirai S., Shoji M. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of amyloid beta protein in the diffuse plaques of Alzheimer-type dementia. Brain Res. 1990 Feb 5;508(2):320–324. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90416-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamano M., Luiten P. G. Direct synaptic contacts of medial septal efferents with somatostatin immunoreactive neurons in the rat hippocampus. Brain Res Bull. 1989 Jun;22(6):993–1001. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(89)90011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yankner B. A., Dawes L. R., Fisher S., Villa-Komaroff L., Oster-Granite M. L., Neve R. L. Neurotoxicity of a fragment of the amyloid precursor associated with Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):417–420. doi: 10.1126/science.2474201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yankner B. A., Duffy L. K., Kirschner D. A. Neurotrophic and neurotoxic effects of amyloid beta protein: reversal by tachykinin neuropeptides. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):279–282. doi: 10.1126/science.2218531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]