Abstract
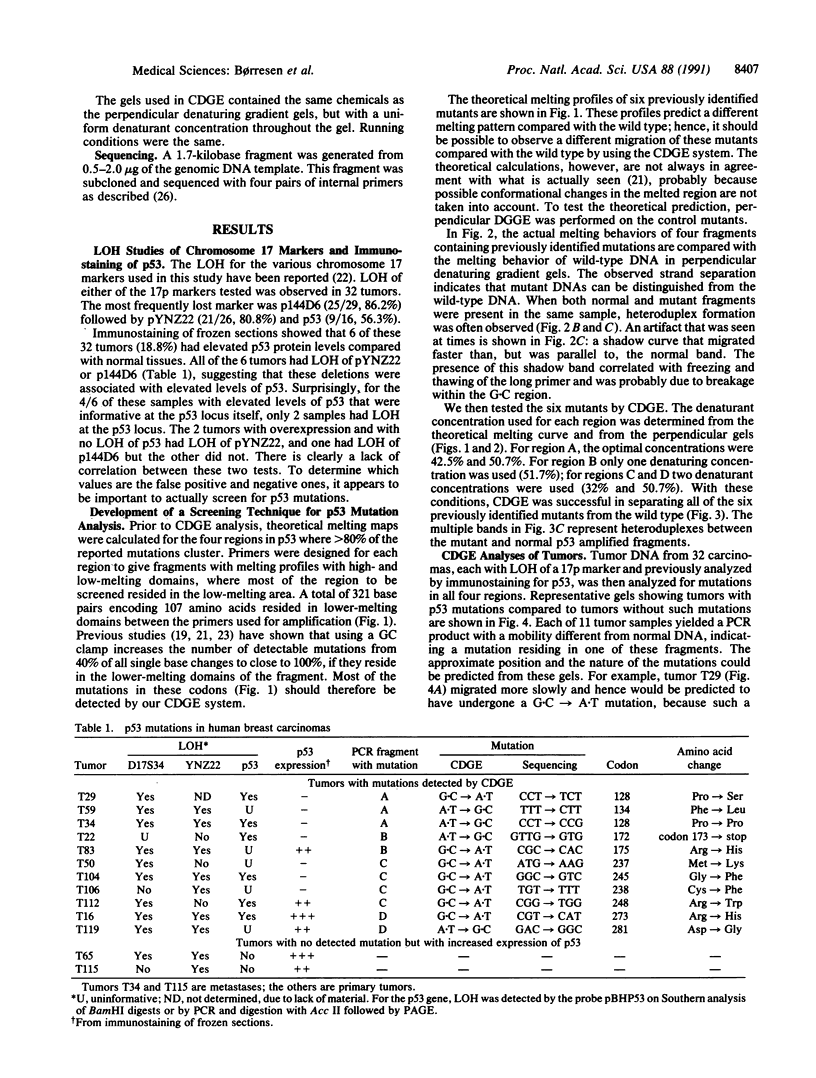
At present, mutation of the p53 gene appears to be the most common genetic alteration found in human cancers. These mutations can occur within many different regions of the gene. We have developed a modification of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis termed "constant denaturant gel electrophoresis" (CDGE), which provides a rapid and sensitive method to screen the four conserved regions within the p53 gene where the majority of p53 mutations have been reported. The sensitivity of CDGE was first tested with known p53 mutations in all four conserved regions. The CDGE technique was then used to screen 32 breast carcinomas that had been analyzed by immunohistochemical methods for altered p53 protein levels and whose DNA had already been shown to have loss of heterozygosity for a chromosome 17p marker. By immunostaining techniques, only 6 of the 32 tumors had elevated p53 expression. However, CDGE detected p53 mutations in 11 of the 32 tumors. DNA sequence analysis was performed to determine the nucleotide positions of these mutations in all 11 samples. Loss of heterozygosity for the pYNZ22 or p144D6 markers did not associate with either the loss of heterozygosity at the p53 locus or the mutations detected by CDGE. We conclude that CDGE is a rapid and effective technique to screen for p53 mutations.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahuja H., Bar-Eli M., Advani S. H., Benchimol S., Cline M. J. Alterations in the p53 gene and the clonal evolution of the blast crisis of chronic myelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6783–6787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. J., Fearon E. R., Nigro J. M., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., vanTuinen P., Ledbetter D. H., Barker D. F., Nakamura Y. Chromosome 17 deletions and p53 gene mutations in colorectal carcinomas. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):217–221. doi: 10.1126/science.2649981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartek J., Iggo R., Gannon J., Lane D. P. Genetic and immunochemical analysis of mutant p53 in human breast cancer cell lines. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):893–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressac B., Galvin K. M., Liang T. J., Isselbacher K. J., Wands J. R., Ozturk M. Abnormal structure and expression of p53 gene in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1973–1977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattoretti G., Rilke F., Andreola S., D'Amato L., Delia D. P53 expression in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1988 Feb 15;41(2):178–183. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles C., Thompson A. M., Elder P. A., Cohen B. B., Mackenzie I. M., Cranston G., Chetty U., Mackay J., Macdonald M., Nakamura Y. Evidence implicating at least two genes on chromosome 17p in breast carcinogenesis. Lancet. 1990 Sep 29;336(8718):761–763. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93236-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton R. G., Rodrigues N. R., Campbell R. D. Reactivity of cytosine and thymine in single-base-pair mismatches with hydroxylamine and osmium tetroxide and its application to the study of mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4397–4401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devilee P., Cornelisse C. J., Kuipers-Dijkshoorn N., Jonker C., Pearson P. L. Loss of heterozygosity on 17p in human breast carcinomas: defining the smallest common region of deletion. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1990;53(1):52–54. doi: 10.1159/000132893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer S. G., Lerman L. S. DNA fragments differing by single base-pair substitutions are separated in denaturing gradient gels: correspondence with melting theory. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1579–1583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fults D., Tippets R. H., Thomas G. A., Nakamura Y., White R. Loss of heterozygosity for loci on chromosome 17p in human malignant astrocytoma. Cancer Res. 1989 Dec 1;49(23):6572–6577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs R. A., Caskey C. T. Identification and localization of mutations at the Lesch-Nyhan locus by ribonuclease A cleavage. Science. 1987 Apr 17;236(4799):303–305. doi: 10.1126/science.3563511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovig E., Smith-Sørensen B., Brøgger A., Børresen A. L. Constant denaturant gel electrophoresis, a modification of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis, in mutation detection. Mutat Res. 1991 Jan;262(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(91)90108-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iggo R., Gatter K., Bartek J., Lane D., Harris A. L. Increased expression of mutant forms of p53 oncogene in primary lung cancer. Lancet. 1990 Mar 24;335(8691):675–679. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90801-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerman L. S., Fischer S. G., Hurley I., Silverstein K., Lumelsky N. Sequence-determined DNA separations. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1984;13:399–423. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.13.060184.002151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay J., Steel C. M., Elder P. A., Forrest A. P., Evans H. J. Allele loss on short arm of chromosome 17 in breast cancers. Lancet. 1988 Dec 17;2(8625):1384–1385. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90584-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin D., Li F. P., Strong L. C., Fraumeni J. F., Jr, Nelson C. E., Kim D. H., Kassel J., Gryka M. A., Bischoff F. Z., Tainsky M. A. Germ line p53 mutations in a familial syndrome of breast cancer, sarcomas, and other neoplasms. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1233–1238. doi: 10.1126/science.1978757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda H., Miller C., Koeffler H. P., Battifora H., Cline M. J. Rearrangement of the p53 gene in human osteogenic sarcomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7716–7719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan L. M., Matlashewski G. J., Scrable H. J., Cavenee W. K. Mechanisms of p53 loss in human sarcomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5863–5867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro J. M., Baker S. J., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., Hostetter R., Cleary K., Bigner S. H., Davidson N., Baylin S., Devilee P. Mutations in the p53 gene occur in diverse human tumour types. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):705–708. doi: 10.1038/342705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita M., Iwahana H., Kanazawa H., Hayashi K., Sekiya T. Detection of polymorphisms of human DNA by gel electrophoresis as single-strand conformation polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2766–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita M., Suzuki Y., Sekiya T., Hayashi K. Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):874–879. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland D. Recursion relation generation of probability profiles for specific-sequence macromolecules with long-range correlations. Biopolymers. 1974;13(9):1859–1871. doi: 10.1002/bip.1974.360130916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. E., Hickey G. I., Lowry W. S., White P., Atkinson R. J. Allele loss from chromosome 17 in ovarian cancer. Oncogene. 1990 Oct;5(10):1581–1583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Tanigami A., Yamakawa K., Akiyama F., Kasumi F., Sakamoto G., Nakamura Y. Allelotype of breast cancer: cumulative allele losses promote tumor progression in primary breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1990 Nov 15;50(22):7184–7189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott N., Sagar P., Stewart J., Blair G. E., Dixon M. F., Quirke P. p53 in colorectal cancer: clinicopathological correlation and prognostic significance. Br J Cancer. 1991 Feb;63(2):317–319. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield V. C., Cox D. R., Lerman L. S., Myers R. M. Attachment of a 40-base-pair G + C-rich sequence (GC-clamp) to genomic DNA fragments by the polymerase chain reaction results in improved detection of single-base changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):232–236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soussi T., Caron de Fromentel C., May P. Structural aspects of the p53 protein in relation to gene evolution. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):945–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Nau M. M., Chiba I., Birrer M. J., Rosenberg R. K., Vinocour M., Levitt M., Pass H., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D. p53: a frequent target for genetic abnormalities in lung cancer. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):491–494. doi: 10.1126/science.2554494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson A. M., Steel C. M., Chetty U., Hawkins R. A., Miller W. R., Carter D. C., Forrest A. P., Evans H. J. p53 gene mRNA expression and chromosome 17p allele loss in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1990 Jan;61(1):74–78. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1990.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









