Abstract
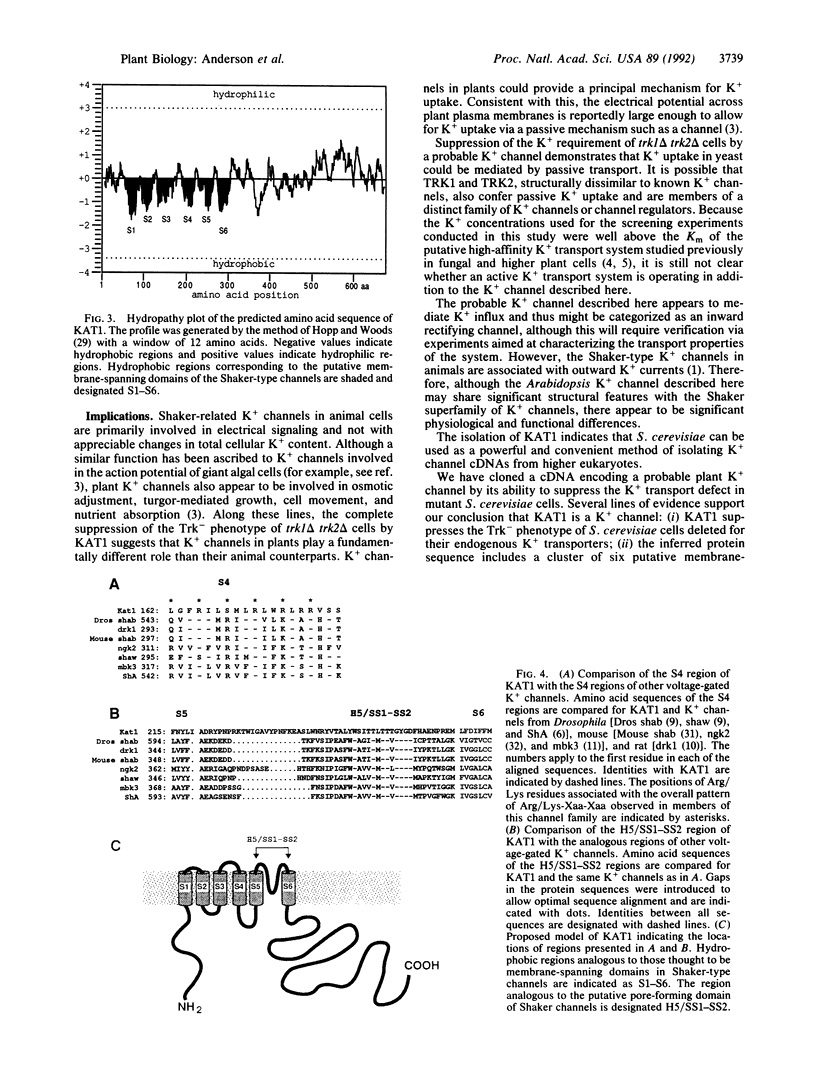
We report the isolation of a cDNA (KAT1) from Arabidopsis thaliana that encodes a probable K+ channel. KAT1 was cloned by its ability to suppress a K+ transport-defective phenotype in mutant Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. This suppression is sensitive to known K+ channel blockers, including tetraethylammonium and Ba2+ ions. The KAT1 cDNA contains an open reading frame capable of encoding a 78-kDa protein that shares structural features found in the Shaker superfamily of K+ channels. These include a cluster of six putative membrane-spanning helices (S1-S6) at the amino terminus of the protein, a presumed voltage-sensing region containing Arg/Lys-Xaa-Xaa-Arg/Lys repeats within S4, and the highly conserved pore-forming region (known as H5 or SS1-SS2). Our results suggest that the structural motif for K+ channels has been conserved between plants and animals.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. A., Best L. A., Gaber R. F. Structural and functional conservation between the high-affinity K+ transporters of Saccharomyces uvarum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1991 Mar 1;99(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Interaction of tetraethylammonium ion derivatives with the potassium channels of giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Oct;58(4):413–437. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker D. M., Guarente L. High-efficiency transformation of yeast by electroporation. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:182–187. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler A., Wei A. G., Baker K., Salkoff L. A family of putative potassium channel genes in Drosophila. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):943–947. doi: 10.1126/science.2493160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandy K. G., Williams C. B., Spencer R. H., Aguilar B. A., Ghanshani S., Tempel B. L., Gutman G. A. A family of three mouse potassium channel genes with intronless coding regions. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):973–975. doi: 10.1126/science.2305265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Mulligan J. T., Ramer S. W., Spottswood M., Davis R. W. Lambda YES: a multifunctional cDNA expression vector for the isolation of genes by complementation of yeast and Escherichia coli mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1731–1735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frech G. C., VanDongen A. M., Schuster G., Brown A. M., Joho R. H. A novel potassium channel with delayed rectifier properties isolated from rat brain by expression cloning. Nature. 1989 Aug 24;340(6235):642–645. doi: 10.1038/340642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaber R. F., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. TRK1 encodes a plasma membrane protein required for high-affinity potassium transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2848–2859. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt R. E., Blatt Y., Montal M. The structure of the voltage-sensitive sodium channel. Inferences derived from computer-aided analysis of the Electrophorus electricus channel primary structure. FEBS Lett. 1985 Dec 2;193(2):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustin M. C., Martinac B., Saimi Y., Culbertson M. R., Kung C. Ion channels in yeast. Science. 1986 Sep 12;233(4769):1195–1197. doi: 10.1126/science.2426783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy H. R., Seetharamulu P. Molecular model of the action potential sodium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):508–512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The selective inhibition of delayed potassium currents in nerve by tetraethylammonium ion. J Gen Physiol. 1967 May;50(5):1287–1302. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.5.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Zagotta W. N., Aldrich R. W. Biophysical and molecular mechanisms of Shaker potassium channel inactivation. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):533–538. doi: 10.1126/science.2122519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Voltage-sensitive ion channels. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90979-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko C. H., Gaber R. F. TRK1 and TRK2 encode structurally related K+ transporters in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4266–4273. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochian L. V., Shaff J. E., Lucas W. J. High affinity k uptake in maize roots: a lack of coupling with h efflux. Plant Physiol. 1989 Nov;91(3):1202–1211. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.3.1202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Yellen G. Mutations affecting TEA blockade and ion permeation in voltage-activated K+ channels. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):276–279. doi: 10.1126/science.2218530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Shimizu S., Tanabe T., Takai T., Kayano T., Ikeda T., Takahashi H., Nakayama H., Kanaoka Y., Minamino N. Primary structure of Electrophorus electricus sodium channel deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):121–127. doi: 10.1038/312121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Navarro A., Blatt M. R., Slayman C. L. A potassium-proton symport in Neurospora crassa. J Gen Physiol. 1986 May;87(5):649–674. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.5.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder J. I., Hedrich R. Involvement of ion channels and active transport in osmoregulation and signaling of higher plant cells. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 May;14(5):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz T. L., Tempel B. L., Papazian D. M., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Multiple potassium-channel components are produced by alternative splicing at the Shaker locus in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):137–142. doi: 10.1038/331137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Takeshima H., Mikami A., Flockerzi V., Takahashi H., Kangawa K., Kojima M., Matsuo H., Hirose T., Numa S. Primary structure of the receptor for calcium channel blockers from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):313–318. doi: 10.1038/328313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempel B. L., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Cloning of a probable potassium channel gene from mouse brain. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):837–839. doi: 10.1038/332837a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempel B. L., Papazian D. M., Schwarz T. L., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Sequence of a probable potassium channel component encoded at Shaker locus of Drosophila. Science. 1987 Aug 14;237(4816):770–775. doi: 10.1126/science.2441471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warmke J., Drysdale R., Ganetzky B. A distinct potassium channel polypeptide encoded by the Drosophila eag locus. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1560–1562. doi: 10.1126/science.1840699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G., Jurman M. E., Abramson T., MacKinnon R. Mutations affecting internal TEA blockade identify the probable pore-forming region of a K+ channel. Science. 1991 Feb 22;251(4996):939–942. doi: 10.1126/science.2000494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yool A. J., Schwarz T. L. Alteration of ionic selectivity of a K+ channel by mutation of the H5 region. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):700–704. doi: 10.1038/349700a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagotta W. N., Hoshi T., Aldrich R. W. Restoration of inactivation in mutants of Shaker potassium channels by a peptide derived from ShB. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):568–571. doi: 10.1126/science.2122520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]