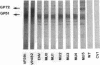
Abstract
Modified bovine leukemia virus (BLV) glycoproteins were expressed by using vaccinia virus recombinants, and their fusogenic capacities were examined by a syncytia-formation assay. This analysis indicates that (i) both BLV envelope glycoproteins gp51 and gp30 are necessary for cell fusion; (ii) insertion of the N-terminal segment of gp30 (fusion peptide) into the lipid bilayer in an oblique orientation, as predicted by computer conformational analysis, results in fusogenic capacities higher than insertion in a perpendicular or parallel orientation; and (iii) replacement of the BLV fusion peptide with its simian immunodeficiency virus counterpart does not modify the fusogenic capacity of the BLV glycoprotein.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bosch M. L., Earl P. L., Fargnoli K., Picciafuoco S., Giombini F., Wong-Staal F., Franchini G. Identification of the fusion peptide of primate immunodeficiency viruses. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):694–697. doi: 10.1126/science.2541505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasseur R., Cornet B., Burny A., Vandenbranden M., Ruysschaert J. M. Mode of insertion into a lipid membrane of the N-terminal HIV gp41 peptide segment. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1988 Apr;4(2):83–90. doi: 10.1089/aid.1988.4.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasseur R. Differentiation of lipid-associating helices by use of three-dimensional molecular hydrophobicity potential calculations. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):16120–16127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasseur R., Goormaghtigh E., Ruysschaert J. M. Theoretical conformational analysis of phospholipids bilayers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Nov 16;103(1):301–310. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91693-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasseur R., Lorge P., Goormaghtigh E., Ruysschaert J. M., Espion D., Burny A. The mode of insertion of the paramyxovirus F1 N-terminus into lipid matrix, an initial step in host cell/virus fusion. Virus Genes. 1988 Jul;1(4):325–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00257096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasseur R., Ruysschaert J. M. Conformation and mode of organization of amphiphilic membrane components: a conformational analysis. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 15;238(1):1–11. doi: 10.1042/bj2380001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasseur R., Vandenbranden M., Cornet B., Burny A., Ruysschaert J. M. Orientation into the lipid bilayer of an asymmetric amphipathic helical peptide located at the N-terminus of viral fusion proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Nov 16;1029(2):267–273. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90163-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruck C., Mathot S., Portetelle D., Berte C., Franssen J. D., Herion P., Burny A. Monoclonal antibodies define eight independent antigenic regions on the bovine leukemia virus (BLV) envelope glycoprotein gp51. Virology. 1982 Oct 30;122(2):342–352. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90234-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burny A., Cleuter Y., Kettmann R., Mammerickx M., Marbaix G., Portetelle D., Van den Broeke A., Willems L., Thomas R. Bovine leukemia: facts and hypotheses derived from the study of an infectious cancer. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1988;32:149–170. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-039232-2.50010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Brechling K., Moss B. Vaccinia virus expression vector: coexpression of beta-galactosidase provides visual screening of recombinant virus plaques. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3403–3409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Schwarz E., Komaromy M., Wall R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Weiss R. M., Terwilliger T. C. The helical hydrophobic moment: a measure of the amphiphilicity of a helix. Nature. 1982 Sep 23;299(5881):371–374. doi: 10.1038/299371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed E. O., Myers D. J., Risser R. Characterization of the fusion domain of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein gp41. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4650–4654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallaher W. R. Detection of a fusion peptide sequence in the transmembrane protein of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):327–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90485-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Doms R. W., York D., White J. Studies on the mechanism of membrane fusion: site-specific mutagenesis of the hemagglutinin of influenza virus. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):11–23. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves D. C., Jones L. V. Early syncytium formation by bovine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):1055–1063. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.1055-1063.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter C., James P., Bächi T., Semenza G., Brunner J. Hydrophobic binding of the ectodomain of influenza hemagglutinin to membranes occurs through the "fusion peptide". J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6459–6464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horth M., Lambrecht B., Khim M. C., Bex F., Thiriart C., Ruysschaert J. M., Burny A., Brasseur R. Theoretical and functional analysis of the SIV fusion peptide. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2747–2755. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07823.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski M., Potz J., Basiripour L., Dorfman T., Goh W. C., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Rosen C., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Functional regions of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.3629244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackett M., Smith G. L., Moss B. General method for production and selection of infectious vaccinia virus recombinants expressing foreign genes. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):857–864. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.857-864.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin I., Defrise-Quertain F., Mandieau V., Nielsen N. M., Saermark T., Burny A., Brasseur R., Ruysschaert J. M., Vandenbranden M. Fusogenic activity of SIV (simian immunodeficiency virus) peptides located in the GP32 NH2 terminal domain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 29;175(3):872–879. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91646-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M., Rabin L. B., Feinberg M. B., Lieberman M., Kosek J. C., Reyes G. R., Weissman I. L. Endoproteolytic cleavage of gp160 is required for the activation of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portetelle D., Couez D., Bruck C., Kettmann R., Mammerickx M., Van der Maaten M., Brasseur R., Burny A. Antigenic variants of bovine leukemia virus (BLV) are defined by amino acid substitutions in the NH2 part of the envelope glycoprotein gp51. Virology. 1989 Mar;169(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portetelle D., Limbach K., Burny A., Mammerickx M., Desmettre P., Riviere M., Zavada J., Paoletti E. Recombinant vaccinia virus expression of the bovine leukaemia virus envelope gene and protection of immunized sheep against infection. Vaccine. 1991 Mar;9(3):194–200. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(91)90153-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portetelle D., Mammerickx M., Burny A. Use of two monoclonal antibodies in an ELISA test for the detection of antibodies to bovine leukaemia virus envelope protein gp51. J Virol Methods. 1989 Feb;23(2):211–222. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(89)90135-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayers J. R., Schmidt W., Eckstein F. 5'-3' exonucleases in phosphorothioate-based oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):791–802. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Ott J., Eckstein F. The rapid generation of oligonucleotide-directed mutations at high frequency using phosphorothioate-modified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8765–8785. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems L., Bruck C., Portetelle D., Burny A., Kettmann R. Expression of a cDNA clone corresponding to the long open reading frame (XBL-I) of the bovine leukemia virus. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):55–59. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]