Abstract
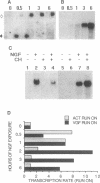
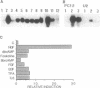
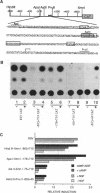
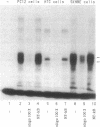
vgf, a gene coding for a protein secreted through the regulated pathway, is rapidly up-modulated by nerve growth factor in PC12 cells and is expressed in vivo only in cell subpopulations of neuronal and endocrine origin. Here we demonstrate the following: (i) the nerve growth factor-dependent induction of vgf mRNA occurs at the transcriptional level and requires ongoing protein synthesis, (ii) lack of vgf expression in the nonneuronal cell line HTC is in part mediated by the presence of a repressor, (iii) a 110-base-pair sequence in the vgf promoter region contains positive and negative regulatory elements that partially account for its regulated expression, and (iv) a 47-base-pair oligonucleotide within this sequence specifically binds nuclear proteins that differ between vgf-expressing and non-expressing cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barde Y. A. The nerve growth factor family. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1990;2(4):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(90)90021-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein D. E., Greene L. A. Nerve growth factor has both mitogenic and antimitogenic activity. Dev Biol. 1982 Dec;94(2):477–482. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90364-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X., Rosenfeld M. G. Mechanisms of complex transcriptional regulation: implications for brain development. Neuron. 1991 Aug;7(2):183–196. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90257-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Kaplan D. R., Parada L. F., Chao M. V. High-affinity NGF binding requires coexpression of the trk proto-oncogene and the low-affinity NGF receptor. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):678–683. doi: 10.1038/350678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Jing S. Q., Nanduri V., O'Rourke E., Barbacid M. The trk proto-oncogene encodes a receptor for nerve growth factor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90419-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Fan C. M., Maniatis T., Baltimore D. The involvement of NF-kappa B in beta-interferon gene regulation reveals its role as widely inducible mediator of signal transduction. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90966-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor 35 years later. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1154–1162. doi: 10.1126/science.3306916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi A., Alemà S. The mechanism of action of nerve growth factor. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1991;31:205–228. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.31.040191.001225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi A., Eldridge J. D., Paterson B. M. Molecular cloning of a gene sequence regulated by nerve growth factor. Science. 1985 Jul 26;229(4711):393–395. doi: 10.1126/science.3839317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machida C. M., Rodland K. D., Matrisian L., Magun B. E., Ciment G. NGF induction of the gene encoding the protease transin accompanies neuronal differentiation in PC12 cells. Neuron. 1989 Jun;2(6):1587–1596. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori N., Stein R., Sigmund O., Anderson D. J. A cell type-preferred silencer element that controls the neural-specific expression of the SCG10 gene. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):583–594. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90116-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Sandgren E. P., Avarbock M. R., Allen D. D., Brinster R. L. Heterologous introns can enhance expression of transgenes in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):478–482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Possenti R., Eldridge J. D., Paterson B. M., Grasso A., Levi A. A protein induced by NGF in PC12 cells is stored in secretory vesicles and released through the regulated pathway. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2217–2223. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08345.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salton S. R., Fischberg D. J., Dong K. W. Structure of the gene encoding VGF, a nervous system-specific mRNA that is rapidly and selectively induced by nerve growth factor in PC12 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2335–2349. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Nakamura S., Taga T., Matsuda T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Kaziro Y. Induction of neuronal differentiation in PC12 cells by B-cell stimulatory factor 2/interleukin 6. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3546–3549. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6419–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Greenberg M. E. The regulation and function of c-fos and other immediate early genes in the nervous system. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):477–485. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90106-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Togari A., Dickens G., Kuzuya H., Guroff G. The effect of fibroblast growth factor on PC12 cells. J Neurosci. 1985 Feb;5(2):307–316. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-02-00307.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Pol A. N., Decavel C., Levi A., Paterson B. Hypothalamic expression of a novel gene product, VGF: immunocytochemical analysis. J Neurosci. 1989 Dec;9(12):4122–4137. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-12-04122.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]