Abstract
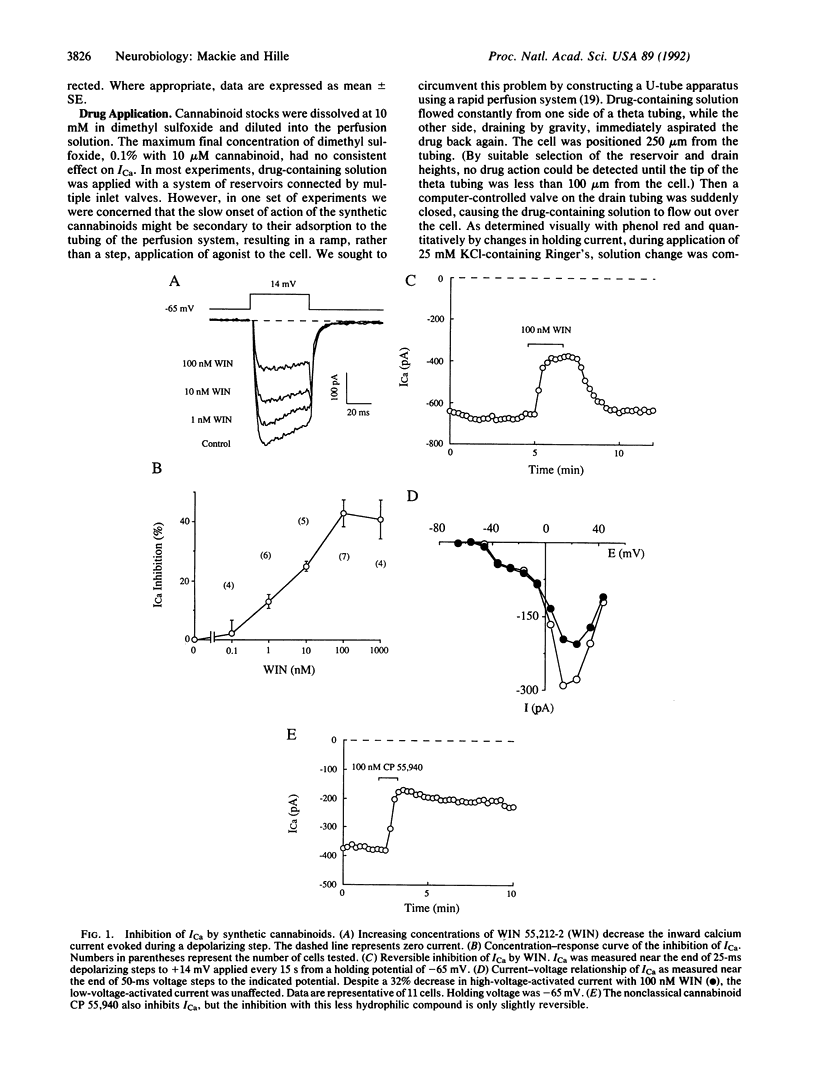
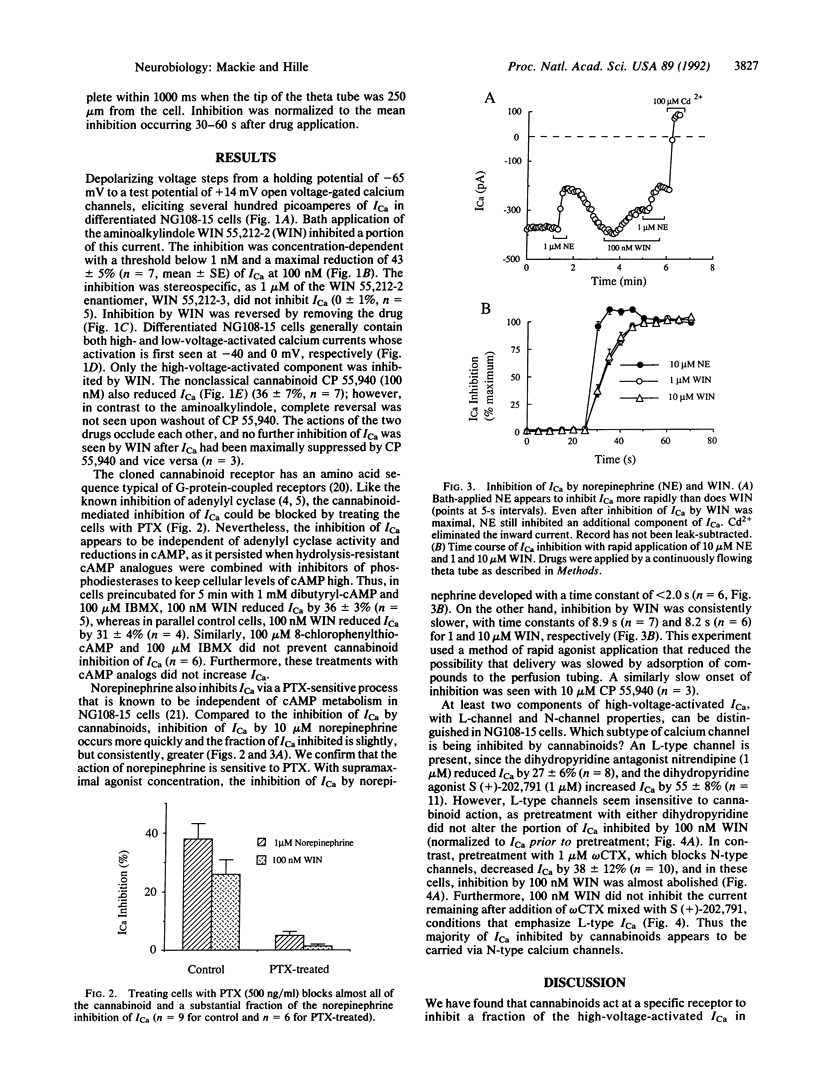
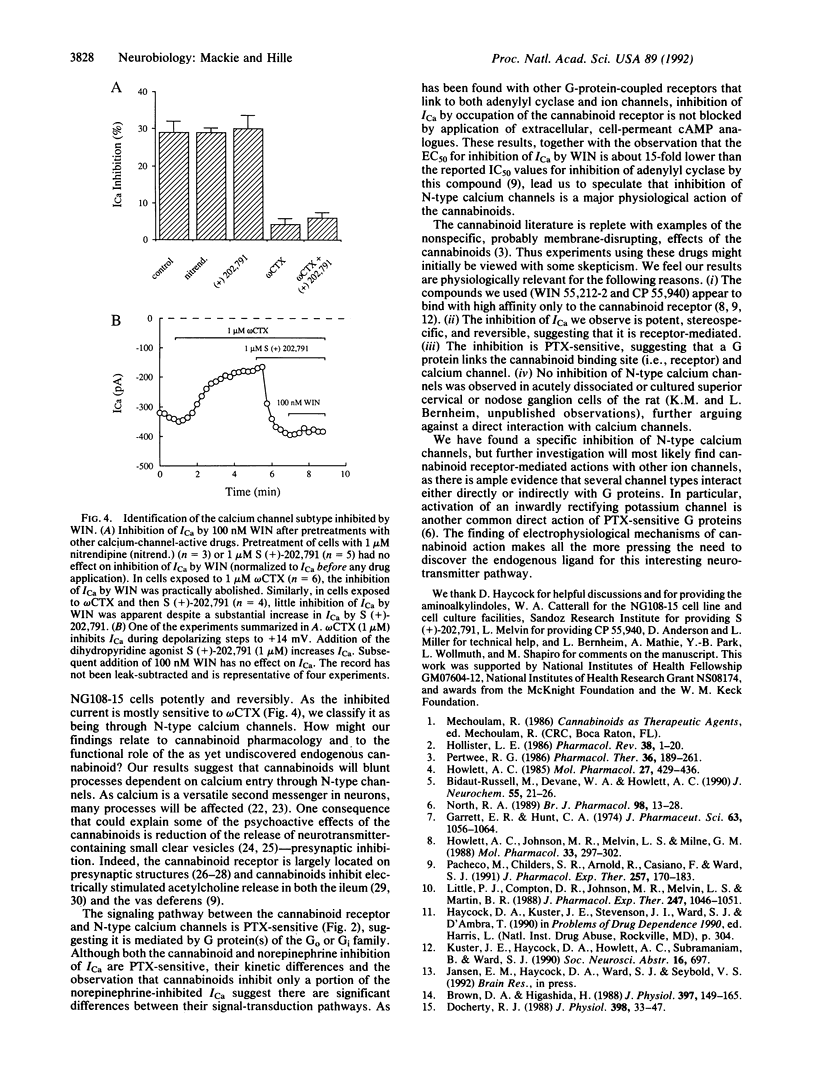
The psychoactive properties of Cannabis sativa and its major biologically active constituent, delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol, have been known for years. The recent identification and cloning of a specific cannabinoid receptor suggest that cannabinoids mimic endogenous compounds affecting neural signals for mood, memory, movement, and pain. Using whole-cell voltage clamp and the cannabinomimetic aminoalkylindole WIN 55,212-2, we have found that cannabinoid receptor activation reduces the amplitude of voltage-gated calcium currents in the neuroblastoma-glioma cell line NG108-15. The inhibition is potent, being half-maximal at less than 10 nM, and reversible. The inactive enantiomer, WIN 55,212-3, does not reduce calcium currents even at 1 microM. Of the several types of calcium currents in NG108-15 cells, cannabinoids predominantly inhibit an omega-conotoxin-sensitive, high-voltage-activated calcium current. Inhibition was blocked by incubation with pertussis toxin but was not altered by prior treatment with hydrolysis-resistant cAMP analogues together with a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, suggesting that the transduction pathway between the cannabinoid receptor and calcium channel involves a pertussis toxin-sensitive GTP-binding protein and is independent of cAMP metabolism. However, the development of inhibition is considerably slower than a pharmacologically similar pathway used by an alpha 2-adrenergic receptor in these cells. Our results suggest that inhibition of N-type calcium channels, which could decrease excitability and neurotransmitter release, may underlie some of the psychoactive effects of cannabinoids.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernheim L., Beech D. J., Hille B. A diffusible second messenger mediates one of the pathways coupling receptors to calcium channels in rat sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1991 Jun;6(6):859–867. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90226-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidaut-Russell M., Devane W. A., Howlett A. C. Cannabinoid receptors and modulation of cyclic AMP accumulation in the rat brain. J Neurochem. 1990 Jul;55(1):21–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb08815.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Higashida H. Voltage- and calcium-activated potassium currents in mouse neuroblastoma x rat glioma hybrid cells. J Physiol. 1988 Mar;397:149–165. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty R. J. Gadolinium selectively blocks a component of calcium current in rodent neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid (NG108-15) cells. J Physiol. 1988 Apr;398:33–47. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett E. R., Hunt C. A. Physiochemical properties, solubility, and protein binding of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol. J Pharm Sci. 1974 Jul;63(7):1056–1064. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600630705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haycock D. A., Kuster J. E., Stevenson J. I., Ward S. J., D'Ambra T. Characterization of aminoalkylindole binding: selective displacement by cannabinoids. NIDA Res Monogr. 1990;105:304–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham M., Groen B. G., Lynn A. B., De Costa B. R., Richfield E. K. Neuronal localization of cannabinoid receptors and second messengers in mutant mouse cerebellum. Brain Res. 1991 Jun 28;552(2):301–310. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90096-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham M., Lynn A. B., Johnson M. R., Melvin L. S., de Costa B. R., Rice K. C. Characterization and localization of cannabinoid receptors in rat brain: a quantitative in vitro autoradiographic study. J Neurosci. 1991 Feb;11(2):563–583. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-02-00563.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham M., Lynn A. B., de Costa B. R., Richfield E. K. Neuronal localization of cannabinoid receptors in the basal ganglia of the rat. Brain Res. 1991 May 3;547(2):267–274. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90970-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollister L. E. Health aspects of cannabis. Pharmacol Rev. 1986 Mar;38(1):1–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Marty A. Muscarinic activation of ionic currents measured by a new whole-cell recording method. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Aug;92(2):145–159. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlett A. C. Cannabinoid inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Biochemistry of the response in neuroblastoma cell membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Apr;27(4):429–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlett A. C., Johnson M. R., Melvin L. S., Milne G. M. Nonclassical cannabinoid analgetics inhibit adenylate cyclase: development of a cannabinoid receptor model. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;33(3):297–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little P. J., Compton D. R., Johnson M. R., Melvin L. S., Martin B. R. Pharmacology and stereoselectivity of structurally novel cannabinoids in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Dec;247(3):1046–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucero M. T., Pappone P. A. Membrane responses to norepinephrine in cultured brown fat cells. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Mar;95(3):523–544. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.3.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A. The physiological role of calcium-dependent channels. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Nov;12(11):420–424. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda L. A., Lolait S. J., Brownstein M. J., Young A. C., Bonner T. I. Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):561–564. doi: 10.1038/346561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadzean I., Docherty R. J. Noradrenaline- and Enkephalin-Induced Inhibition of Voltage-Sensitive Calcium Currents in NG108-15 Hybrid Cells. Eur J Neurosci. 1989 Mar;1(2):141–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1989.tb00781.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A. Twelfth Gaddum memorial lecture. Drug receptors and the inhibition of nerve cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;98(1):13–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb16855.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye J. S., Seltzman H. H., Pitt C. G., Snyder S. H. High-affinity cannabinoid binding sites in brain membranes labeled with [3H]-5'-trimethylammonium delta 8-tetrahydrocannabinol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Sep;234(3):784–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco M., Childers S. R., Arnold R., Casiano F., Ward S. J. Aminoalkylindoles: actions on specific G-protein-linked receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Apr;257(1):170–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pertwee R. G. The central neuropharmacology of psychotropic cannabinoids. Pharmacol Ther. 1988;36(2-3):189–261. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(88)90106-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds I. J., Wagner J. A., Snyder S. H., Thayer S. A., Olivera B. M., Miller R. J. Brain voltage-sensitive calcium channel subtypes differentiated by omega-conotoxin fraction GVIA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8804–8807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S. H. Stereospecific presynaptic inhibitory effect of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol on cholinergic transmission in the myenteric plexus of the guinea pig. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1978 Dec;56(6):968–975. doi: 10.1139/y78-154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Greenberg M. E. The regulation and function of c-fos and other immediate early genes in the nervous system. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):477–485. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90106-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. J., Augustine G. J. Calcium ions, active zones and synaptic transmitter release. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):458–464. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90199-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



