Abstract
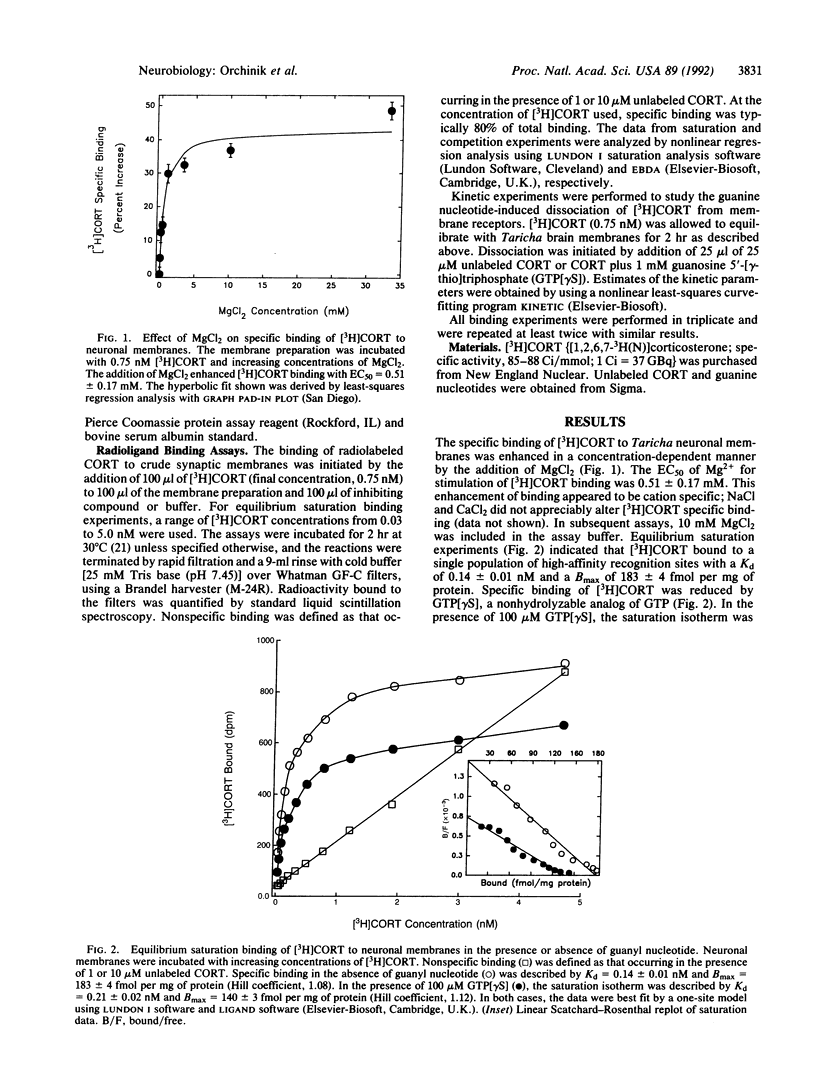
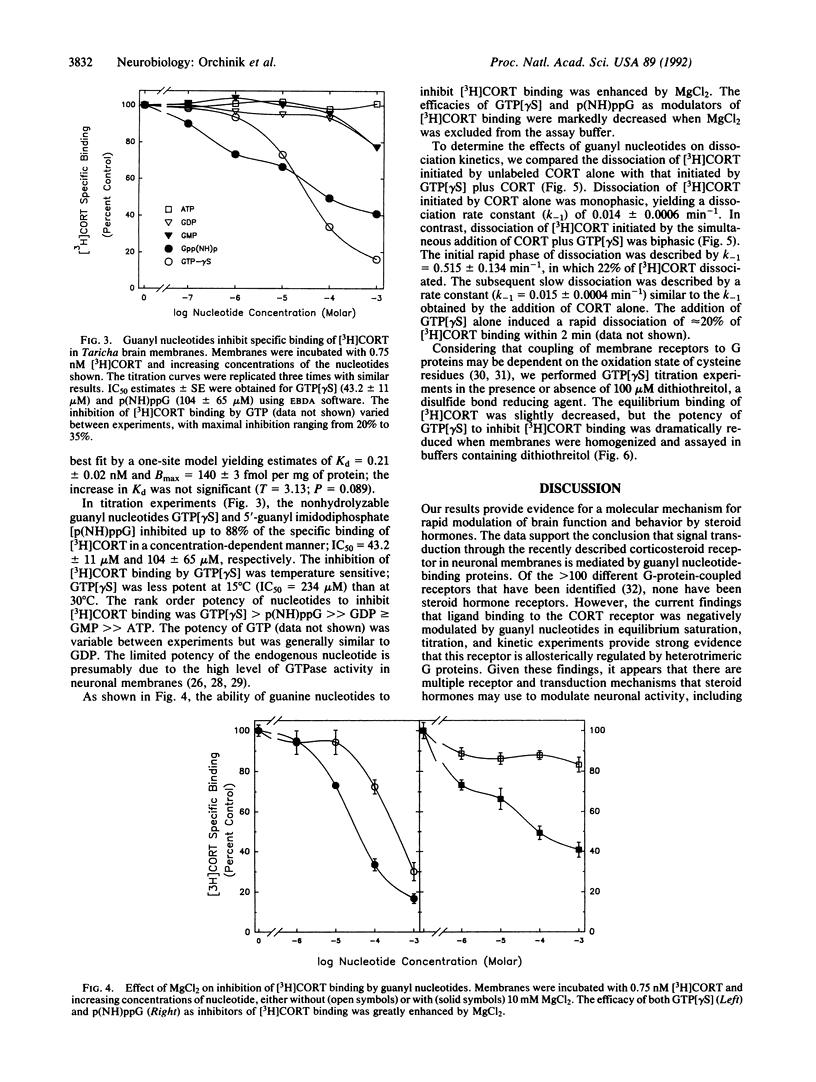
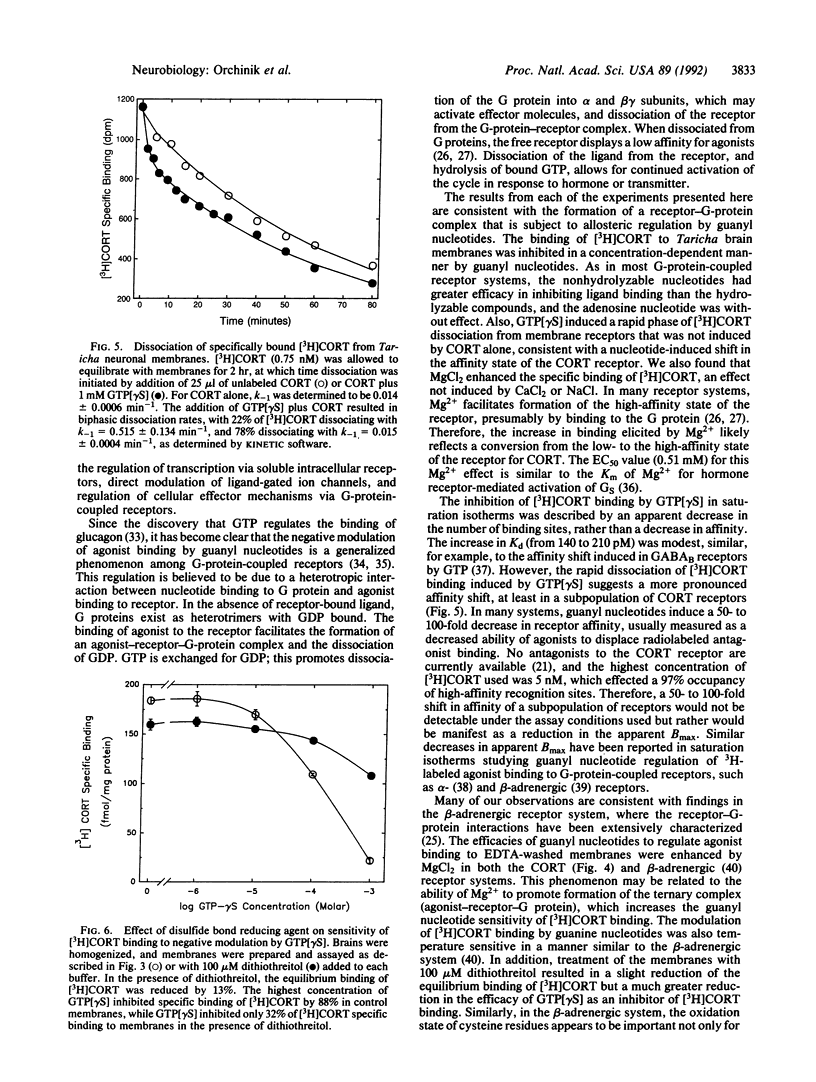
The recently characterized corticosteroid receptor on amphibian neuronal membranes appears to mediate rapid, stress-induced changes in male reproductive behaviors. Because the transduction mechanisms associated with this receptor are unknown, we performed radioligand binding studies to determine whether this steroid receptor is negatively modulated by guanyl nucleotides. The binding of [3H]corticosterone to neuronal membranes was inhibited by nonhydrolyzable guanyl nucleotides in both equilibrium saturation binding and titration studies. The addition of guanyl nucleotide plus unlabeled corticosterone induced a rapid phase of [3H]corticosterone dissociation from membranes that was not induced by addition of unlabeled ligand alone. Furthermore, the equilibrium binding of [3H]corticosterone and the sensitivity of the receptor to modulation by guanyl nucleotides were both enhanced by Mg2+. These results are consistent with the formation of a ternary complex of steroid, receptor, and guanine nucleotide-binding protein that is subject to regulation by guanyl nucleotides. Therefore, rapid signal transduction through corticosteroid receptors on neuronal membranes appears to be mediated by guanine nucleotide-binding proteins.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnbaumer L., Abramowitz J., Brown A. M. Receptor-effector coupling by G proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 7;1031(2):163–224. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(90)90007-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blondeau J. P., Baulieu E. E. Progesterone receptor characterized by photoaffinity labelling in the plasma membrane of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Biochem J. 1984 May 1;219(3):785–792. doi: 10.1042/bj2190785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boege F., Neumann E., Helmreich E. J. Structural heterogeneity of membrane receptors and GTP-binding proteins and its functional consequences for signal transduction. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jul 1;199(1):1–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16085.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd S. K., Moore F. L. Evidence for GABA involvement in stress-induced inhibition of male amphibian sexual behavior. Horm Behav. 1990 Mar;24(1):128–138. doi: 10.1016/0018-506x(90)90032-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson-Jurica M. A., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. Steroid receptor family: structure and functions. Endocr Rev. 1990 May;11(2):201–220. doi: 10.1210/edrv-11-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lean A., Stadel J. M., Lefkowitz R. J. A ternary complex model explains the agonist-specific binding properties of the adenylate cyclase-coupled beta-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7108–7117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devane W. A., Dysarz F. A., 3rd, Johnson M. R., Melvin L. S., Howlett A. C. Determination and characterization of a cannabinoid receptor in rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;34(5):605–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubrovsky B., Filipini D., Gijsbers K., Birmingham M. K. Early and late effects of steroid hormones on the central nervous system. Ciba Found Symp. 1990;153:240–260. doi: 10.1002/9780470513989.ch14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finidori-Lepicard J., Schorderet-Slatkine S., Hanoune J., Baulieu E. E. Progesterone inhibits membrane-bound adenylate cyclase in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):255–257. doi: 10.1038/292255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis G. S., Cohn J. N. Heart failure: mechanisms of cardiac and vascular dysfunction and the rationale for pharmacologic intervention. FASEB J. 1990 Oct;4(13):3068–3075. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.13.2210153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser C. M. Site-directed mutagenesis of beta-adrenergic receptors. Identification of conserved cysteine residues that independently affect ligand binding and receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9266–9270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gametchu B. Glucocorticoid receptor-like antigen in lymphoma cell membranes: correlation to cell lysis. Science. 1987 Apr 24;236(4800):456–461. doi: 10.1126/science.3563523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godeau J. F., Schorderet-Slatkine S., Hubert P., Baulieu E. E. Induction of maturation in Xenopus laevis oocytes by a steroid linked to a polymer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2353–2357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. R., Bowery N. G., Hudson A. L. Inhibition of GABAB receptor binding by guanyl nucleotides. J Neurochem. 1984 Mar;42(3):652–657. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg M. D. Structure-activity relationships for transmembrane signaling: the receptor's turn. FASEB J. 1991 Feb;5(2):178–186. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.2.1848518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlett A. C., Qualy J. M., Khachatrian L. L. Involvement of Gi in the inhibition of adenylate cyclase by cannabimimetic drugs. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Mar;29(3):307–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua S. Y., Chen Y. Z. Membrane receptor-mediated electrophysiological effects of glucocorticoid on mammalian neurons. Endocrinology. 1989 Feb;124(2):687–691. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-2-687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar R., Birnbaumer L. Hormone receptor modulates the regulatory component of adenylyl cyclase by reducing its requirement for Mg2+ and enhancing its extent of activation by guanine nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5179–5183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ke F. C., Ramirez V. D. Binding of progesterone to nerve cell membranes of rat brain using progesterone conjugated to 125I-bovine serum albumin as a ligand. J Neurochem. 1990 Feb;54(2):467–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01895.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen M., Kelly E., MacDermot J. Guanine nucleotide sensitivity of [3H]iloprost binding to prostacyclin receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun 19;207(2):111–117. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(91)90085-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. J., Moss R. L., Dudley C. A. The effects of microelectrophoretically applied estrogen, cortisol and acetylcholine on medial preoptic-septal unit activity throughout the estrous cycle of the female rat. Exp Brain Res. 1977 Oct 24;30(1):53–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00237858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch B., Lutz-Bucher B., Briaud B., Mialhe C. Specific interaction of corticosteroids with binding sites in the plasma membranes of the rat anterior pituitary gland. J Endocrinol. 1978 Nov;79(2):215–222. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0790215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan N. C., Chen J. S., Belelli D., Pritchett D. B., Seeburg P. H., Gee K. W. A steroid recognition site is functionally coupled to an expressed GABA(A)-benzodiazepine receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun 12;188(6):403–406. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(90)90201-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Schimerlik M. I., Murray T. F. Characterization of agonist radioligand interactions with porcine atrial A1 adenosine receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;34(3):334–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewska M. D., Harrison N. L., Schwartz R. D., Barker J. L., Paul S. M. Steroid hormone metabolites are barbiturate-like modulators of the GABA receptor. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):1004–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.2422758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda L. A., Lolait S. J., Brownstein M. J., Young A. C., Bonner T. I. Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):561–564. doi: 10.1038/346561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami T., Oomura Y., Nabekura J., Fukuda A. 17 beta-estradiol depolarization of hypothalamic neurons is mediated by cyclic AMP. Brain Res. 1990 Jun 11;519(1-2):301–307. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90092-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore F. L., Miller L. J. Stress-induced inhibition of sexual behavior: corticosterone inhibits courtship behaviors of a male amphibian (Taricha granulosa). Horm Behav. 1984 Dec;18(4):400–410. doi: 10.1016/0018-506x(84)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabekura J., Oomura Y., Minami T., Mizuno Y., Fukuda A. Mechanism of the rapid effect of 17 beta-estradiol on medial amygdala neurons. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):226–228. doi: 10.1126/science.3726531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell J. M., Wolfe B. B., Frazer A. Agonist interactions with beta adrenergic receptors in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Mar;228(3):640–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orchinik M., Murray T. F., Moore F. L. A corticosteroid receptor in neuronal membranes. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1848–1851. doi: 10.1126/science.2063198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patiño R., Thomas P. Characterization of membrane receptor activity for 17 alpha, 20 beta, 21-trihydroxy-4-pregnen-3-one in ovaries of spotted seatrout (Cynoscion nebulosus). Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1990 May;78(2):204–217. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(90)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietras R. J., Szego C. M. Estrogen receptors in uterine plasma membrane. J Steroid Biochem. 1979 Oct;11(4):1471–1483. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(79)90124-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Krans H. M., Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. IV. Effects of guanylnucleotides on binding of 125I-glucagon. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1872–1876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouot B. M., U'Prichard D. C., Snyder S. H. Multiple alpha 2-noradrenergic receptor sites in rat brain: selective regulation of high-affinity [3H]clonidine binding by guanine nucleotides and divalent cations. J Neurochem. 1980 Feb;34(2):374–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb06607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler S. E., Maller J. L., Cooper D. M. Progesterone inhibition of Xenopus oocyte adenylate cyclase is not mediated via the Bordetella pertussis toxin substrate. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;26(3):526–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler S. E., Maller J. L. Identification of a steroid receptor on the surface of Xenopus oocytes by photoaffinity labeling. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):355–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler S. E., Maller J. L. Progesterone inhibits adenylate cyclase in Xenopus oocytes. Action on the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6368–6373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher M., Coirini H., Pfaff D. W., McEwen B. S. Behavioral effects of progesterone associated with rapid modulation of oxytocin receptors. Science. 1990 Nov 2;250(4981):691–694. doi: 10.1126/science.2173139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher M. Rapid membrane effects of steroid hormones: an emerging concept in neuroendocrinology. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Sep;13(9):359–362. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. I., Strathmann M. P., Gautam N. Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):802–808. doi: 10.1126/science.1902986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. D. The induction of oocyte maturation: transmembrane signaling events and regulation of the cell cycle. Development. 1989 Dec;107(4):685–699. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.4.685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. S., Waterhouse B. D., Woodward D. J. Sex steroid effects on extrahypothalamic CNS. I. Estrogen augments neuronal responsiveness to iontophoretically applied glutamate in the cerebellum. Brain Res. 1987 Sep 29;422(1):40–51. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90538-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suyemitsu T., Terayama H. Specific binding sites for natural glucocorticoids in plasma membranes of rat liver. Endocrinology. 1975 Jun;96(6):1499–1508. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-6-1499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towle A. C., Sze P. Y. Steroid binding to synaptic plasma membrane: differential binding of glucocorticoids and gonadal steroids. J Steroid Biochem. 1983 Feb;18(2):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(83)90079-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Lefkowitz R. J. Slowly reversible binding of catecholamine to a nucleotide-sensitive state of the beta-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7207–7213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


