Abstract
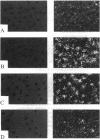
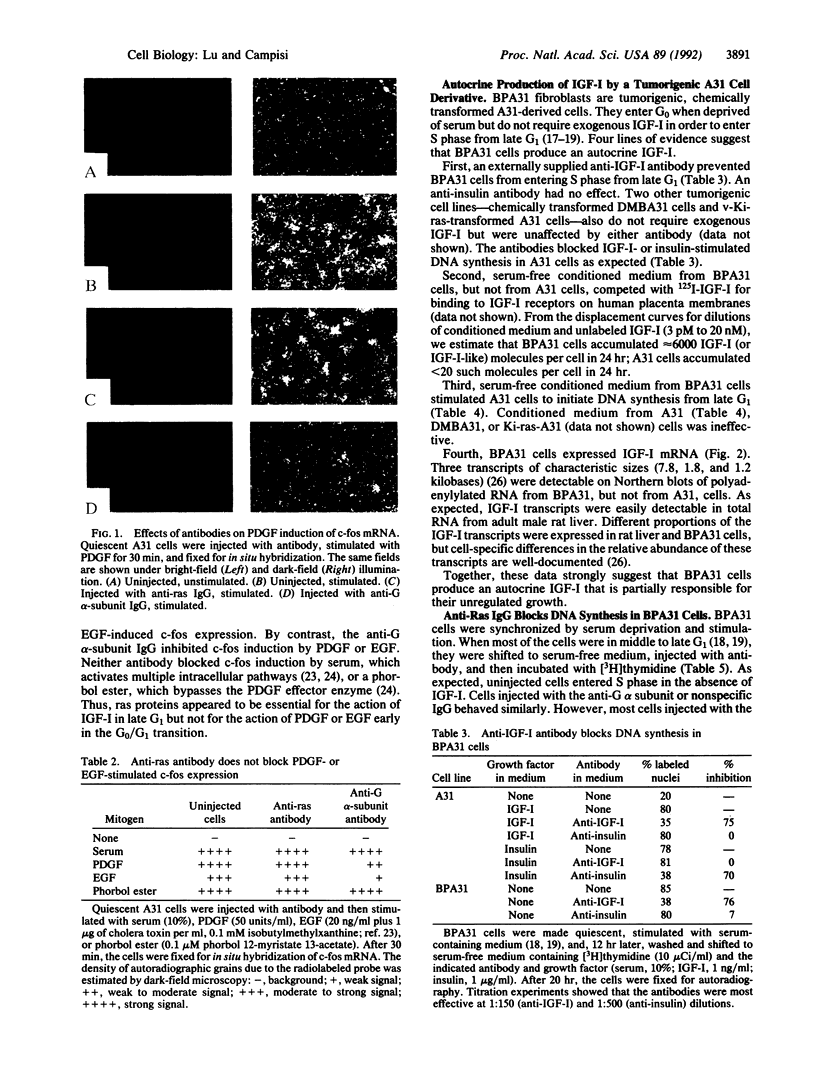
BALB/c 3T3 cells (A31 cells) require the sequential action of growth factors in order to proliferate from a quiescent growth state. Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) is needed late in the G1 phase of the cell cycle, a time at which expression of the c-Ha-ras protooncogene is near maximal. An anti-ras antibody, introduced by microinjection, specifically blocked the ability of IGF-I to stimulate initiation of DNA synthesis. The antibody was specific for IGF-I; it failed to block serum, platelet-derived growth factor, or epidermal growth factor from inducing c-fos mRNA. By contrast, an anti-G alpha-subunit antibody had no effect on IGF-I-stimulated DNA synthesis but inhibited the induction of c-fos mRNA by platelet-derived growth factor or epidermal growth factor. BPA31 cells are tumorigenic A31-derived cells that progress through G1 in the absence of IGF-I. BPA31 cells produced an autocrine IGF-I that was responsible for the loss of late G1 control; the anti-ras antibody arrested the growth of these cells in late G1. The results suggest that ras proteins are essential for an IGF-I-sensitive, G1 control point.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar-Sagi D., Feramisco J. R. Microinjection of the ras oncogene protein into PC12 cells induces morphological differentiation. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benito M., Porras A., Nebreda A. R., Santos E. Differentiation of 3T3-L1 fibroblasts to adipocytes induced by transfection of ras oncogenes. Science. 1991 Aug 2;253(5019):565–568. doi: 10.1126/science.1857988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Broek D., Wigler M. ras proteins can induce meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):615–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90233-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgering B. M., Medema R. H., Maassen J. A., van de Wetering M. L., van der Eb A. J., McCormick F., Bos J. L. Insulin stimulation of gene expression mediated by p21ras activation. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1103–1109. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Gray H. E., Pardee A. B., Dean M., Sonenshein G. E. Cell-cycle control of c-myc but not c-ras expression is lost following chemical transformation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Medrano E. E., Morreo G., Pardee A. B. Restriction point control of cell growth by a labile protein: evidence for increased stability in transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):436–440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Pardee A. B. Post-transcriptional control of the onset of DNA synthesis by an insulin-like growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1807–1814. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Graves J. D., Warne P. H., Rayter S., Cantrell D. A. Stimulation of p21ras upon T-cell activation. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):719–723. doi: 10.1038/346719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feramisco J. R., Gross M., Kamata T., Rosenberg M., Sweet R. W. Microinjection of the oncogene form of the human H-ras (T-24) protein results in rapid proliferation of quiescent cells. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90531-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagag N., Halegoua S., Viola M. Inhibition of growth factor-induced differentiation of PC12 cells by microinjection of antibody to ras p21. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):680–682. doi: 10.1038/319680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt J. T., Gopal T. V., Moulton A. D., Nienhuis A. W. Inducible production of c-fos antisense RNA inhibits 3T3 cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4794–4798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J., Siebel C. W., McCormick F., Roth R. A. Ras p21 as a potential mediator of insulin action in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):840–843. doi: 10.1126/science.3554510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Van Wyk J. J., O'Keefe E. J., Pledger W. J. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is required only during the traverse of early G1 in PDGF stimulated density-arrested BALB/c-3T3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Aug;147(1):202–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu K. H., Levine R. A., Campisi J. c-ras-Ha gene expression is regulated by insulin or insulinlike growth factor and by epidermal growth factor in murine fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3411–3417. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey P., Ran W., Campisi J., Rosner M. R. Two independent growth factor-generated signals regulate c-fos and c-myc mRNA levels in Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1442–1445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F. ras GTPase activating protein: signal transmitter and signal terminator. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90976-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulcahy L. S., Smith M. R., Stacey D. W. Requirement for ras proto-oncogene function during serum-stimulated growth of NIH 3T3 cells. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):241–243. doi: 10.1038/313241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy L. J., Bell G. I., Friesen H. G. Growth hormone stimulates sequential induction of c-myc and insulin-like growth factor I expression in vivo. Endocrinology. 1987 May;120(5):1806–1812. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-5-1806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Ko M., Ogura A., Liu D. G., Amano T., Takano T., Ikawa Y. Sarcoma viruses carrying ras oncogenes induce differentiation-associated properties in a neuronal cell line. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):73–75. doi: 10.1038/318073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park H. Y., Campisi J. Posttranslational control of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase by phorbol ester in normal but not in chemically transformed 3T3 cells. Cancer Res. 1990 Nov 15;50(22):7145–7152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pledger W. J., Stiles C. D., Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D. An ordered sequence of events is required before BALB/c-3T3 cells become committed to DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2839–2843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ran W., Dean M., Levine R. A., Henkle C., Campisi J. Induction of c-fos and c-myc mRNA by epidermal growth factor or calcium ionophore is cAMP dependent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8216–8220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E. Early signals in the mitogenic response. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):161–166. doi: 10.1126/science.3018928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassoon D. A., Garner I., Buckingham M. Transcripts of alpha-cardiac and alpha-skeletal actins are early markers for myogenesis in the mouse embryo. Development. 1988 Sep;104(1):155–164. doi: 10.1242/dev.104.1.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Endo M., Nakafuku M., Nakamura S., Kaziro Y. Platelet-derived growth factor stimulates formation of active p21ras.GTP complex in Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5993–5997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Nakafuku M., Miyajima A., Kaziro Y. Involvement of ras p21 protein in signal-transduction pathways from interleukin 2, interleukin 3, and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor, but not from interleukin 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3314–3318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Feig L. A., Gibbs J. B. Dominant inhibitory Ras mutants selectively inhibit the activity of either cellular or oncogenic Ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4053–4064. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Kung H. F. Transformation of NIH 3T3 cells by microinjection of Ha-ras p21 protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):508–511. doi: 10.1038/310508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Watson T., Kung H. F., Curran T. Microinjection of transforming ras protein induces c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):523–527. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]