Abstract
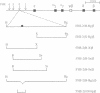
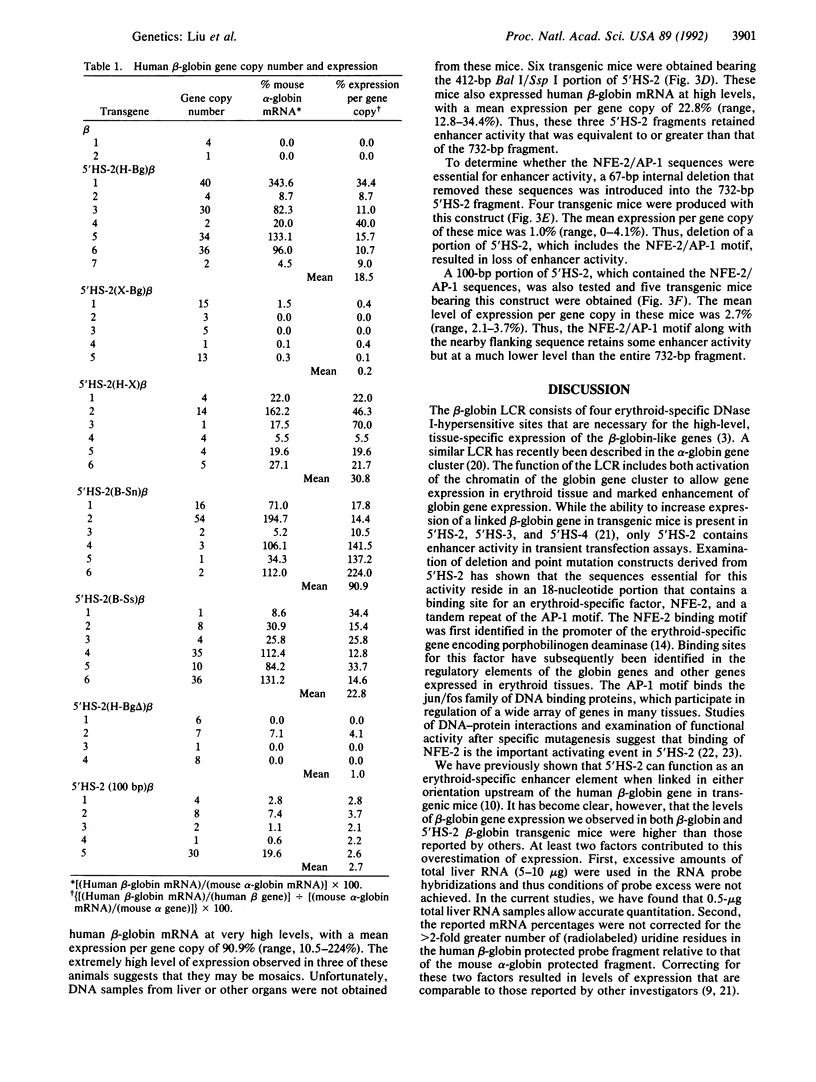
The beta-globin locus control region (LCR) consists of four erythroid-specific DNase I-hypersensitive sites, which are necessary for high-level expression of the beta-like globin genes in erythroid tissues. One of these sites, designated 5'HS-2, functions as an erythroid-specific enhancer element in transfection and transgenic mouse experiments. Recent transfection experiments and studies of DNA-protein interactions have localized the 5'HS-2 enhancer to 18 nucleotides that contain a binding site for both the erythroid-specific factor nuclear factor erythroid 2 (NFE-2) and for activator protein 1 (AP-1). To define the sequences necessary for in vivo enhancer activity, several deletion mutants of 5'HS-2 were linked to the human beta-globin gene and their activity was tested in transgenic mice. Three upstream fragments of 5'HS-2 [341, 374, and 412 base pairs (bp)], each of which contained the NFE-2/AP-1 sequences, resulted in beta-globin expression at levels equivalent to or higher than those observed with the entire 732-bp 5'HS-2 fragment. In contrast, a 358-bp downstream portion of 5'HS-2, which lacked the NFE-2/AP-1 sequences, resulted in beta-globin expression at the low levels seen with the beta-globin gene alone. Removal of the NFE-2/AP-1 sequences by a 67-bp internal deletion resulted in similar low levels of beta-globin expression. A 100-bp 5' fragment that contained the NFE-2/AP-1 sequences resulted in beta-globin expression that was higher than the beta-globin gene alone but lower than the entire 5'HS-2 fragment or the three larger upstream fragments. These studies demonstrate that the NFE-2/AP-1 sequences are essential for enhancer activity of 5'HS-2 but that other sequences are required for full activity in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caterina J. J., Ryan T. M., Pawlik K. M., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Behringer R. R., Townes T. M. Human beta-globin locus control region: analysis of the 5' DNase I hypersensitive site HS 2 in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1626–1630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtin P. T., Liu D. P., Liu W., Chang J. C., Kan Y. W. Human beta-globin gene expression in transgenic mice is enhanced by a distant DNase I hypersensitive site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7082–7086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtin P., Pirastu M., Kan Y. W., Gobert-Jones J. A., Stephens A. D., Lehmann H. A distant gene deletion affects beta-globin gene function in an atypical gamma delta beta-thalassemia. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1554–1558. doi: 10.1172/JCI112136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll M. C., Dobkin C. S., Alter B. P. Gamma delta beta-thalassemia due to a de novo mutation deleting the 5' beta-globin gene activation-region hypersensitive sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7470–7474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser P., Hurst J., Collis P., Grosveld F. DNaseI hypersensitive sites 1, 2 and 3 of the human beta-globin dominant control region direct position-independent expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3503–3508. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs D. R., Wood W. G., Jarman A. P., Sharpe J., Lida J., Pretorius I. M., Ayyub H. A major positive regulatory region located far upstream of the human alpha-globin gene locus. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1588–1601. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikuta T., Kan Y. W. In vivo protein-DNA interactions at the beta-globin gene locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10188–10192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Haslinger A., Karin M., Tjian R. Activation of transcription by two factors that bind promoter and enhancer sequences of the human metallothionein gene and SV40. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):368–372. doi: 10.1038/325368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignotte V., Eleouet J. F., Raich N., Romeo P. H. Cis- and trans-acting elements involved in the regulation of the erythroid promoter of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6548–6552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moi P., Kan Y. W. Synergistic enhancement of globin gene expression by activator protein-1-like proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):9000–9004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.9000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ney P. A., Sorrentino B. P., McDonagh K. T., Nienhuis A. W. Tandem AP-1-binding sites within the human beta-globin dominant control region function as an inducible enhancer in erythroid cells. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):993–1006. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ney P. A., Sorrentino B. P., McDonagh K. T., Nienhuis A. W. Tandem AP-1-binding sites within the human beta-globin dominant control region function as an inducible enhancer in erythroid cells. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):993–1006. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. Globin gene regulation and switching: circa 1990. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):665–672. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90133-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy P. M., Shen C. K. Protein-DNA interactions in vivo of an erythroid-specific, human beta-globin locus enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8676–8680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. M., Behringer R. R., Martin N. C., Townes T. M., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. A single erythroid-specific DNase I super-hypersensitive site activates high levels of human beta-globin gene expression in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):314–323. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Grosveld F. The 5'HS2 of the globin locus control region enhances transcription through the interaction of a multimeric complex binding at two functionally distinct NF-E2 binding sites. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1391–1398. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Philipsen S., Fraser P., Grosveld F. Detailed analysis of the site 3 region of the human beta-globin dominant control region. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2169–2177. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. F., Martin D. I., Zon L. I., D'Andrea A. D., Wong G. G., Orkin S. H. Cloning of cDNA for the major DNA-binding protein of the erythroid lineage through expression in mammalian cells. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):446–451. doi: 10.1038/339446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D. Y., Solomon W. B., London I. M., Lee D. P. An erythroid-specific, developmental-stage-independent enhancer far upstream of the human "beta-like globin" genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2554–2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D., Solomon W., Li Q., London I. M. The "beta-like-globin" gene domain in human erythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6384–6388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Konings A., Oort M., Roos D., Bernini L., Flavell R. A. gamma-beta-Thalassaemia studies showing that deletion of the gamma- and delta-genes influences beta-globin gene expression in man. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):637–642. doi: 10.1038/283637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]