Abstract
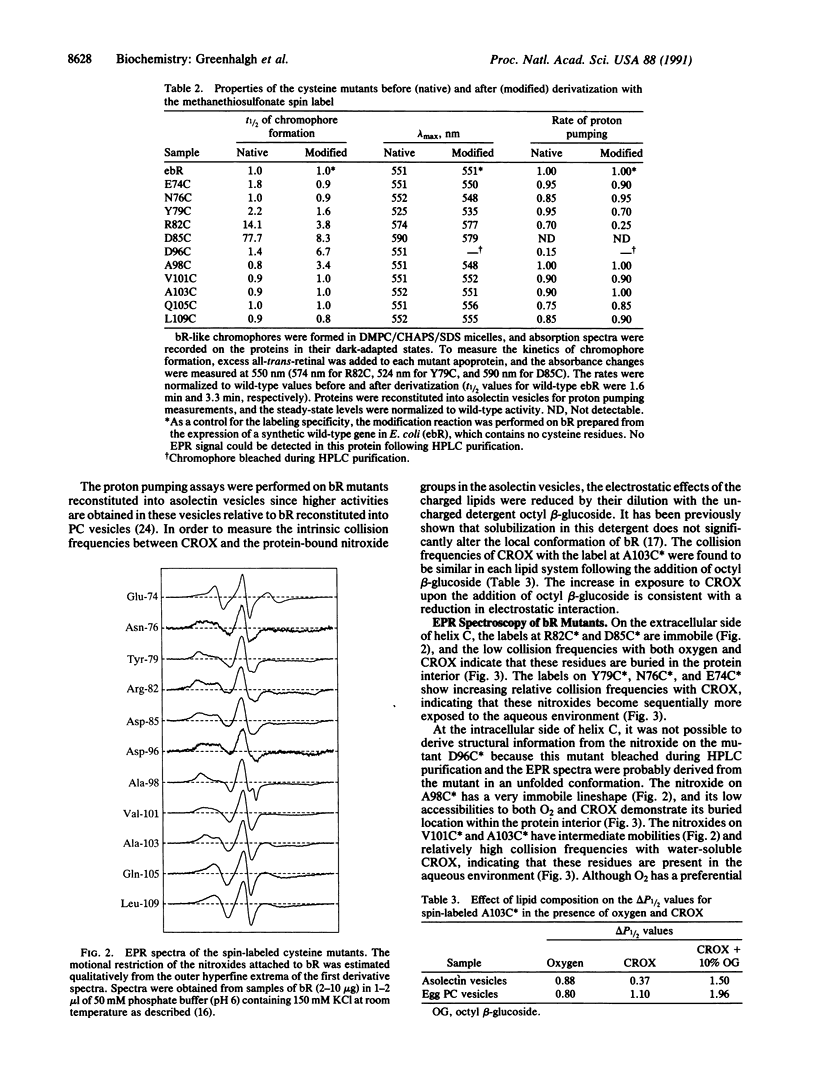
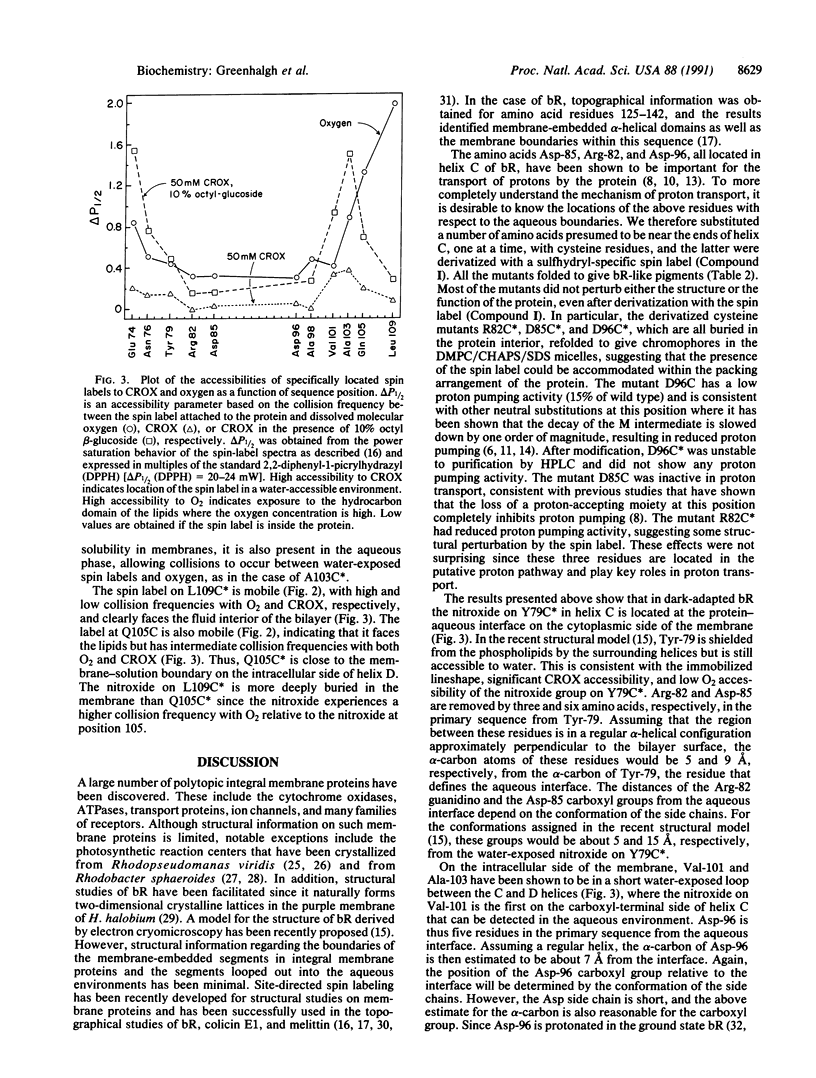
The amino acids Asp-96, Asp-85, and Arg-82, which are important for proton transport by bacteriorhodopsin, are located in helix C. Site-directed spin labeling has been used to map their positions relative to the aqueous boundaries of the membrane. Selected amino acids in helix C, in the B-C loop on the extracellular side, and in the C-D loop on the intracellular side of the membrane were replaced by cysteine residues and derivatized with a sulfhydryl-specific spin label. The topographical locations of the nitroxide groups were determined by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy in terms of both motional restriction and collision frequencies with dissolved molecular oxygen and membrane-impermeable chromium oxalate. The results show that in dark-adapted bacteriorhodopsin, Tyr-79 is at the aqueous-protein interface on the extracellular side of helix C whereas Val-101 is close to the aqueous boundary on the intracellular side of the protein. Further, Asp-96 is estimated to be within 7 A of the aqueous medium on the intracellular side of the membrane, whereas Arg-82 and Asp-85 are within 5 A and 9 A, respectively, of the aqueous boundary on the extracellular side of the membrane.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. P., Feher G., Yeates T. O., Komiya H., Rees D. C. Structure of the reaction center from Rhodobacter sphaeroides R-26: protein-cofactor (quinones and Fe2+) interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8487–8491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altenbach C., Flitsch S. L., Khorana H. G., Hubbell W. L. Structural studies on transmembrane proteins. 2. Spin labeling of bacteriorhodopsin mutants at unique cysteines. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7806–7812. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altenbach C., Froncisz W., Hyde J. S., Hubbell W. L. Conformation of spin-labeled melittin at membrane surfaces investigated by pulse saturation recovery and continuous wave power saturation electron paramagnetic resonance. Biophys J. 1989 Dec;56(6):1183–1191. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82765-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altenbach C., Marti T., Khorana H. G., Hubbell W. L. Transmembrane protein structure: spin labeling of bacteriorhodopsin mutants. Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1088–1092. doi: 10.1126/science.2160734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames J. B., Mathies R. A. The role of back-reactions and proton uptake during the N----O transition in bacteriorhodopsin's photocycle: a kinetic resonance Raman study. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 7;29(31):7181–7190. doi: 10.1021/bi00483a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berliner L. J., Grunwald J., Hankovszky H. O., Hideg K. A novel reversible thiol-specific spin label: papain active site labeling and inhibition. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 15;119(2):450–455. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90612-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M. S., Mogi T., Marti T., Stern L. J., Khorana H. G., Rothschild K. J. Vibrational spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin mutants: light-driven proton transport involves protonation changes of aspartic acid residues 85, 96, and 212. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8516–8520. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M. S., Stern L. J., Chao B. H., Khorana H. G. Structure-function studies on bacteriorhodopsin. IV. Purification and renaturation of bacterio-opsin polypeptide expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9271–9276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt H. J., Fendler K., Bamberg E., Tittor J., Oesterhelt D. Aspartic acids 96 and 85 play a central role in the function of bacteriorhodopsin as a proton pump. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1657–1663. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03556.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisenhofer J., Michel H. Nobel lecture. The photosynthetic reaction centre from the purple bacterium Rhodopseudomonas viridis. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2149–2170. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08338.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dencher N. A., Dresselhaus D., Zaccai G., Büldt G. Structural changes in bacteriorhodopsin during proton translocation revealed by neutron diffraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7876–7879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flitsch S. L., Khorana H. G. Structural studies on transmembrane proteins. 1. Model study using bacteriorhodopsin mutants containing single cysteine residues. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7800–7805. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerwert K., Hess B., Soppa J., Oesterhelt D. Role of aspartate-96 in proton translocation by bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4943–4947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Baldwin J. M., Ceska T. A., Zemlin F., Beckmann E., Downing K. H. Model for the structure of bacteriorhodopsin based on high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):899–929. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz M., Drachev L. A., Mogi T., Otto H., Kaulen A. D., Heyn M. P., Skulachev V. P., Khorana H. G. Replacement of aspartic acid-96 by asparagine in bacteriorhodopsin slows both the decay of the M intermediate and the associated proton movement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2167–2171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., Bayley H., Khorana H. G. Delipidation of bacteriorhodopsin and reconstitution with exogenous phospholipid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):323–327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnik S. S., Nassal M., Doi T., Jay E., Sgaramella V., Khorana H. G. Structure-function studies on bacteriorhodopsin. II. Improved expression of the bacterio-opsin gene in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9255–9263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch M. H., Dencher N. A., Oesterhelt D., Plöhn H. J., Rapp G., Büldt G. Time-resolved X-ray diffraction study of structural changes associated with the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):521–526. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07978.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouyama T., Nasuda-Kouyama A., Ikegami A., Mathew M. K., Stoeckenius W. Bacteriorhodopsin photoreaction: identification of a long-lived intermediate N (P,R350) at high pH and its M-like photoproduct. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 9;27(16):5855–5863. doi: 10.1021/bi00416a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B. A., Engelman D. M. Bacteriorhodopsin remains dispersed in fluid phospholipid bilayers over a wide range of bilayer thicknesses. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 15;166(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A., Stoeckenius W. Bacteriorhodopsin: a light-driven proton pump in Halobacterium Halobium. Biophys J. 1975 Sep;15(9):955–962. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85875-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinetti T., Subramaniam S., Mogi T., Marti T., Khorana H. G. Replacement of aspartic residues 85, 96, 115, or 212 affects the quantum yield and kinetics of proton release and uptake by bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):529–533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogi T., Stern L. J., Hackett N. R., Khorana H. G. Bacteriorhodopsin mutants containing single tyrosine to phenylalanine substitutions are all active in proton translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5595–5599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogi T., Stern L. J., Marti T., Chao B. H., Khorana H. G. Aspartic acid substitutions affect proton translocation by bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4148–4152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassal M., Mogi T., Karnik S. S., Khorana H. G. Structure-function studies on bacteriorhodopsin. III. Total synthesis of a gene for bacterio-opsin and its expression in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9264–9270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Rhodopsin-like protein from the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 29;233(39):149–152. doi: 10.1038/newbio233149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormos P. Infrared spectroscopic demonstration of a conformational change in bacteriorhodopsin involved in proton pumping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):473–477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto H., Marti T., Holz M., Mogi T., Lindau M., Khorana H. G., Heyn M. P. Aspartic acid-96 is the internal proton donor in the reprotonation of the Schiff base of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9228–9232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto H., Marti T., Holz M., Mogi T., Stern L. J., Engel F., Khorana H. G., Heyn M. P. Substitution of amino acids Asp-85, Asp-212, and Arg-82 in bacteriorhodopsin affects the proton release phase of the pump and the pK of the Schiff base. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1018–1022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern L. J., Khorana H. G. Structure-function studies on bacteriorhodopsin. X. Individual substitutions of arginine residues by glutamine affect chromophore formation, photocycle, and proton translocation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14202–14208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and related pigments of halobacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:587–616. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and the purple membrane of halobacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 14;505(3-4):215–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniam S., Marti T., Rösselet S. J., Rothschild K. J., Khorana H. G. The reaction of hydroxylamine with bacteriorhodopsin studied with mutants that have altered photocycles: selective reactivity of different photointermediates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2583–2587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tittor J., Soell C., Oesterhelt D., Butt H. J., Bamberg E. A defective proton pump, point-mutated bacteriorhodopsin Asp96----Asn is fully reactivated by azide. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3477–3482. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08512.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd A. P., Cong J., Levinthal F., Levinthal C., Hubbell W. L. Site-directed mutagenesis of colicin E1 provides specific attachment sites for spin labels whose spectra are sensitive to local conformation. Proteins. 1989;6(3):294–305. doi: 10.1002/prot.340060312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeates T. O., Komiya H., Chirino A., Rees D. C., Allen J. P., Feher G. Structure of the reaction center from Rhodobacter sphaeroides R-26 and 2.4.1: protein-cofactor (bacteriochlorophyll, bacteriopheophytin, and carotenoid) interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7993–7997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


