Abstract
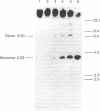
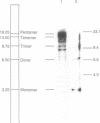
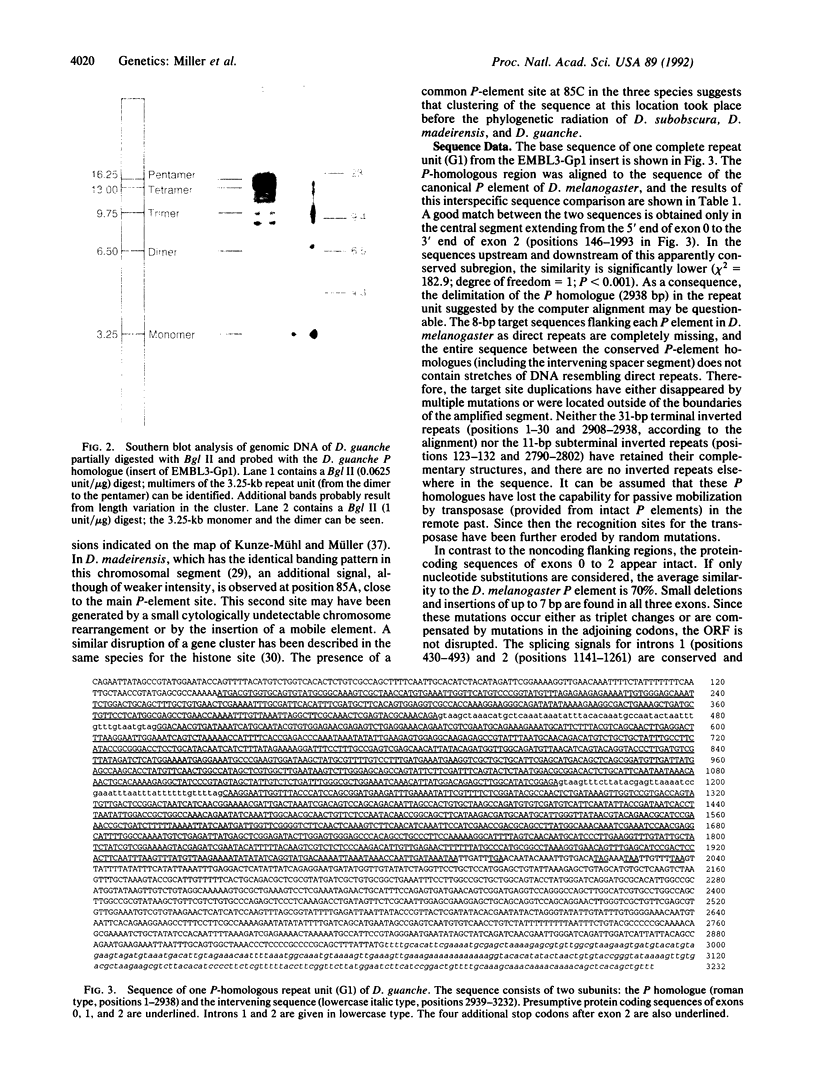
In Drosophila guanche, P-homologous sequences were found to be located in a tandem repetitive array (copy number: 20-50) at a single genomic site. The cytological position on the polytene chromosomes was determined by in situ hybridization (chromosome O: 85C). Sequencing of one complete repeat unit (3.25 kilobases) revealed high sequence similarity between the central coding region comprising exons 0 to 2 and the corresponding section of the Drosophila melanogaster P element. The rest of the sequence has diverged considerably. Exon 3 has no coding function and the inverted repeats have disappeared. The P homologues of D. guanche apparently have lost their mobility but have retained the coding capacity for a protein similar to the 66-kDa P-element repressor of D. melanogaster. Divergence between different repeat units indicates early amplification of the sequence at this particular genomic site. The presence of a common P-element site at 85C in Drosophila subobscura, Drosophila madeirensis, and D. guanche suggests that clustering of the sequence at this location took place before the phylogenetic radiation of the three species.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beverley S. M., Wilson A. C. Molecular evolution in Drosophila and the higher Diptera II. A time scale for fly evolution. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF02100622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. M., Jackson M. S., Kidwell M. G., Dover G. A. KP elements repress P-induced hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4125–4135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookfield J. F., Montgomery E., Langley C. H. Apparent absence of transposable elements related to the P elements of D. melanogaster in other species of Drosophila. 1984 Jul 26-Aug 1Nature. 310(5975):330–332. doi: 10.1038/310330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth B., Langley C. H. The population genetics of Drosophila transposable elements. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:251–287. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels S. B., Peterson K. R., Strausbaugh L. D., Kidwell M. G., Chovnick A. Evidence for horizontal transmission of the P transposable element between Drosophila species. Genetics. 1990 Feb;124(2):339–355. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engels W. R. Extrachromosomal control of mutability in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4011–4015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engels W. R., Johnson-Schlitz D. M., Eggleston W. B., Sved J. High-frequency P element loss in Drosophila is homolog dependent. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):515–525. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engels W. R. The P family of transposable elements in Drosophila. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:315–344. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.001531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagemann S., Miller W. J., Pinsker W. P-related sequences in Drosophila bifasciata: a molecular clue to the understanding of P-element evolution in the genus Drosophila. J Mol Evol. 1990 Dec;31(6):478–484. doi: 10.1007/BF02102074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh M., Iwabuchi M., Yoshida K., Hori S. H. Four tandem defective P elements associated with positive regulation of the Drosophila melanogaster glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene. Biochem Genet. 1989 Dec;27(11-12):699–718. doi: 10.1007/BF02396062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. S., Black D. M., Dover G. A. Amplification of KP elements associated with the repression of hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1988 Dec;120(4):1003–1013. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.4.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNZE-MUHL E., MULLER E. Weitere Untersuchungen über die chromosomale Struktur und die natürlichen Strukturtypen von Drosophila subobscura Coll. Chromosoma. 1958;9(6):559–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan N., Darden T., Langley C. H. Evolution and extinction of transposable elements in Mendelian populations. Genetics. 1985 Feb;109(2):459–480. doi: 10.1093/genetics/109.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidwell M. G. Evolution of hybrid dysgenesis determinants in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1655–1659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidwell M. G., Kidwell J. F., Sved J. A. Hybrid Dysgenesis in DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER: A Syndrome of Aberrant Traits Including Mutation, Sterility and Male Recombination. Genetics. 1977 Aug;86(4):813–833. doi: 10.1093/genetics/86.4.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lansman R. A., Shade R. O., Grigliatti T. A., Brock H. W. Evolution of P transposable elements: sequences of Drosophila nebulosa P elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6491–6495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laski F. A., Rio D. C., Rubin G. M. Tissue specificity of Drosophila P element transposition is regulated at the level of mRNA splicing. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):7–19. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90480-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra S., Rio D. C. Cytotype control of Drosophila P element transposition: the 66 kd protein is a repressor of transposase activity. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):269–284. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90365-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moltó M. D., De Frutos R., Martinez-Sebastián M. J. The banding pattern of polytene chromosomes of Drosophila guanche compared with that of D. subobscura. Genetica. 1987 Nov 16;75(1):55–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00056033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitasaka E., Mukai T., Yamazaki T. Repressor of P elements in Drosophila melanogaster: Cytotype determination by a defective P element carrying only open reading frames 0 through 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7605–7608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare K., Rubin G. M. Structures of P transposable elements and their sites of insertion and excision in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orgel L. E., Crick F. H. Selfish DNA: the ultimate parasite. Nature. 1980 Apr 17;284(5757):604–607. doi: 10.1038/284604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. R., Engels W. R. Spread of P transposable elements in inbred lines of Drosophila melanogaster. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1989;36:71–85. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60162-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond J. D., Ojala T. A., White J., Simmons M. J. Inheritance of P-element regulation in Drosophila melanogaster. Genet Res. 1991 Jun;57(3):227–234. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300029372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D. C., Laski F. A., Rubin G. M. Identification and immunochemical analysis of biologically active Drosophila P element transposase. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90481-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D. C. Molecular mechanisms regulating Drosophila P element transposition. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:543–578. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.002551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. M., Engels W. R. Modified P elements that mimic the P cytotype in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1989 Dec;123(4):815–824. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.4.815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronsseray S., Lehmann M., Anxolabéhère D. The maternally inherited regulation of P elements in Drosophila melanogaster can be elicited by two P copies at cytological site 1A on the X chromosome. Genetics. 1991 Oct;129(2):501–512. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.2.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons M. J., Bucholz L. M. Transposase titration in Drosophila melanogaster: a model of cytotype in the P-M system of hybrid dysgenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8119–8123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons M. J., Raymond J. D., Rasmusson K. E., Miller L. M., McLarnon C. F., Zunt J. R. Repression of P element-mediated hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1990 Mar;124(3):663–676. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.3.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonelig M., Anxolabéhère D. A P element of Scaptomyza pallida is active in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6102–6106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey S. N., Lansman R. A., Brock H. W., Grigliatti T. A. Distribution and conservation of mobile elements in the genus Drosophila. Mol Biol Evol. 1986 Nov;3(6):522–534. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsubota S. I., Huong D. V. Capture of flanking DNA by a P element in Drosophila melanogaster: creation of a transposable element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):693–697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]