Abstract
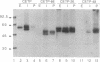
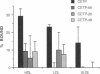
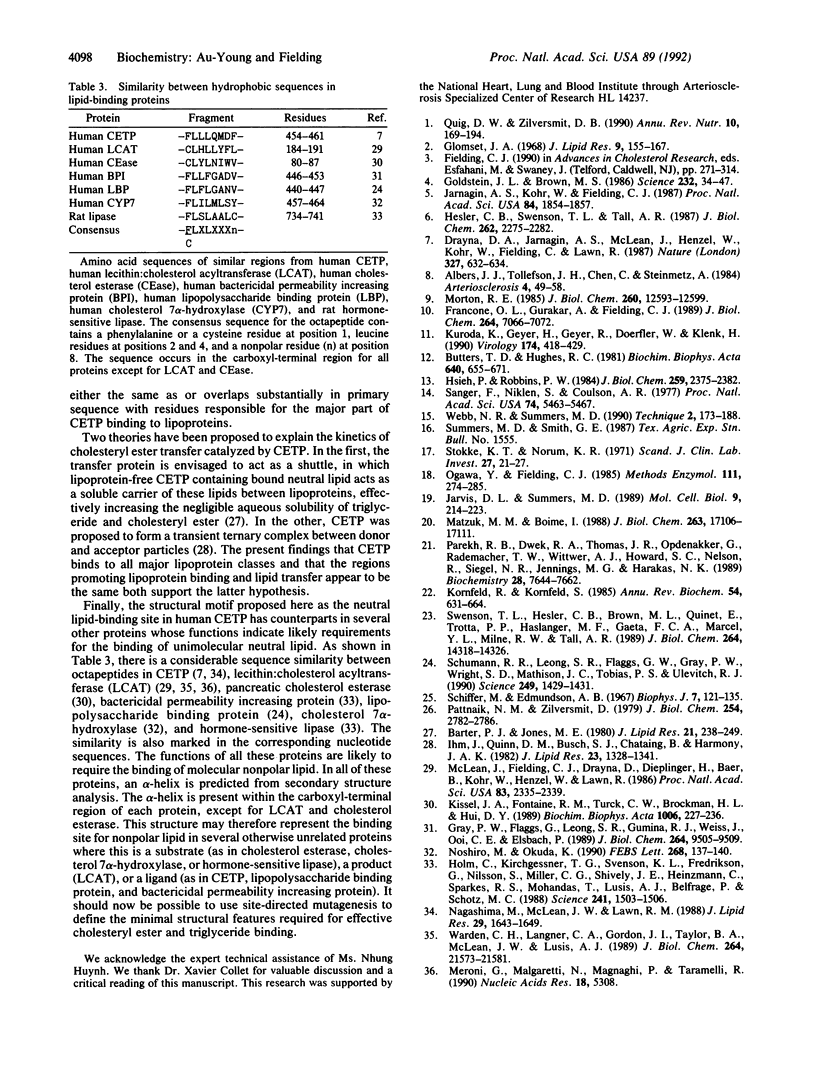
Functional plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP; 476 amino acids) has been expressed in baculovirus-transfected Sf9 insect cells by using a full-length cDNA derived from a human placental library. The product bound to each major plasma lipoprotein class, and it catalyzed the transfer of both cholesteryl esters and triglyceride. CETP species with overlapping deletions were generated in the carboxyl-terminal region. These mutants were defective in cholesteryl ester and triglyceride transfer. Structural and functional analysis suggests that normal lipoprotein binding and effective catalysis may require the carboxyl-terminal sequence -Phe-Leu-Leu-Leu- (residues 454-457), possibly with the involvement of other sequences in the carboxyl-terminal region. A similar sequence is contained in several other proteins whose functions involve binding nonpolar lipids, including lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase, lipopolysaccharide-binding protein, bactericidal permeability-increasing protein, cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase, cholesterol esterase, and hormone-sensitive lipase. These data suggest that a conserved neutral lipid-binding sequence may be one important factor in the activity of CETP and possibly in several other proteins of plasma and cellular lipid metabolism.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers J. J., Tollefson J. H., Chen C. H., Steinmetz A. Isolation and characterization of human plasma lipid transfer proteins. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 Jan-Feb;4(1):49–58. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barter P. J., Jones M. E. Kinetic studies of the transfer of esterified cholesterol between human plasma low and high density lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1980 Feb;21(2):238–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):34–47. doi: 10.1126/science.3513311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butters T. D., Hughes R. C. Isolation and characterization of mosquito cell membrane glycoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 6;640(3):655–671. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., Jarnagin A. S., McLean J., Henzel W., Kohr W., Fielding C., Lawn R. Cloning and sequencing of human cholesteryl ester transfer protein cDNA. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):632–634. doi: 10.1038/327632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francone O. L., Gurakar A., Fielding C. Distribution and functions of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase and cholesteryl ester transfer protein in plasma lipoproteins. Evidence for a functional unit containing these activities together with apolipoproteins A-I and D that catalyzes the esterification and transfer of cell-derived cholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):7066–7072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A. The plasma lecithins:cholesterol acyltransferase reaction. J Lipid Res. 1968 Mar;9(2):155–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Flaggs G., Leong S. R., Gumina R. J., Weiss J., Ooi C. E., Elsbach P. Cloning of the cDNA of a human neutrophil bactericidal protein. Structural and functional correlations. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9505–9509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesler C. B., Swenson T. L., Tall A. R. Purification and characterization of a human plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2275–2282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C., Kirchgessner T. G., Svenson K. L., Fredrikson G., Nilsson S., Miller C. G., Shively J. E., Heinzmann C., Sparkes R. S., Mohandas T. Hormone-sensitive lipase: sequence, expression, and chromosomal localization to 19 cent-q13.3. Science. 1988 Sep 16;241(4872):1503–1506. doi: 10.1126/science.3420405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh P., Robbins P. W. Regulation of asparagine-linked oligosaccharide processing. Oligosaccharide processing in Aedes albopictus mosquito cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2375–2382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihm J., Quinn D. M., Busch S. J., Chataing B., Harmony J. A. Kinetics of plasma protein-catalyzed exchange of phosphatidylcholine and cholesteryl ester between plasma lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1982 Dec;23(9):1328–1341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarnagin A. S., Kohr W., Fielding C. Isolation and specificity of a Mr 74,000 cholesteryl ester transfer protein from human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1854–1857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis D. L., Summers M. D. Glycosylation and secretion of human tissue plasminogen activator in recombinant baculovirus-infected insect cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):214–223. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissel J. A., Fontaine R. N., Turck C. W., Brockman H. L., Hui D. Y. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNA for rat pancreatic cholesterol esterase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Nov 28;1006(2):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90201-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda K., Geyer H., Geyer R., Doerfler W., Klenk H. D. The oligosaccharides of influenza virus hemagglutinin expressed in insect cells by a baculovirus vector. Virology. 1990 Feb;174(2):418–429. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90095-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzuk M. M., Boime I. Site-specific mutagenesis defines the intracellular role of the asparagine-linked oligosaccharides of chorionic gonadotropin beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):17106–17111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean J., Fielding C., Drayna D., Dieplinger H., Baer B., Kohr W., Henzel W., Lawn R. Cloning and expression of human lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2335–2339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meroni G., Malgaretti N., Magnaghi P., Taramelli R. Nucleotide sequence of the cDNA for lecithin-cholesterol acyl transferase (LCAT) from the rat. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5308–5308. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton R. E. Binding of plasma-derived lipid transfer protein to lipoprotein substrates. The role of binding in the lipid transfer process. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12593–12599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagashima M., McLean J. W., Lawn R. M. Cloning and mRNA tissue distribution of rabbit cholesteryl ester transfer protein. J Lipid Res. 1988 Dec;29(12):1643–1649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noshiro M., Okuda K. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA encoding human cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jul 30;268(1):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80992-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa Y., Fielding C. J. Assay of cholesteryl ester transfer activity and purification of a cholesteryl ester transfer protein. Methods Enzymol. 1985;111:274–285. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(85)11015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parekh R. B., Dwek R. A., Thomas J. R., Opdenakker G., Rademacher T. W., Wittwer A. J., Howard S. C., Nelson R., Siegel N. R., Jennings M. G. Cell-type-specific and site-specific N-glycosylation of type I and type II human tissue plasminogen activator. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7644–7662. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattnaik N. M., Zilversmit D. B. Interaction of cholesteryl ester exchange protein with human plasma lipoproteins and phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2782–2786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quig D. W., Zilversmit D. B. Plasma lipid transfer activities. Annu Rev Nutr. 1990;10:169–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.10.070190.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer M., Edmundson A. B. Use of helical wheels to represent the structures of proteins and to identify segments with helical potential. Biophys J. 1967 Mar;7(2):121–135. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86579-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumann R. R., Leong S. R., Flaggs G. W., Gray P. W., Wright S. D., Mathison J. C., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J. Structure and function of lipopolysaccharide binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1429–1431. doi: 10.1126/science.2402637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokke K. T., Norum K. R. Determination of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransfer in human blood plasma. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1971 Feb;27(1):21–27. doi: 10.3109/00365517109080184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson T. L., Hesler C. B., Brown M. L., Quinet E., Trotta P. P., Haslanger M. F., Gaeta F. C., Marcel Y. L., Milne R. W., Tall A. R. Mechanism of cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibition by a neutralizing monoclonal antibody and mapping of the monoclonal antibody epitope. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14318–14326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warden C. H., Langner C. A., Gordon J. I., Taylor B. A., McLean J. W., Lusis A. J. Tissue-specific expression, developmental regulation, and chromosomal mapping of the lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase gene. Evidence for expression in brain and testes as well as liver. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21573–21581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]