Abstract
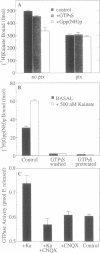
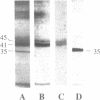
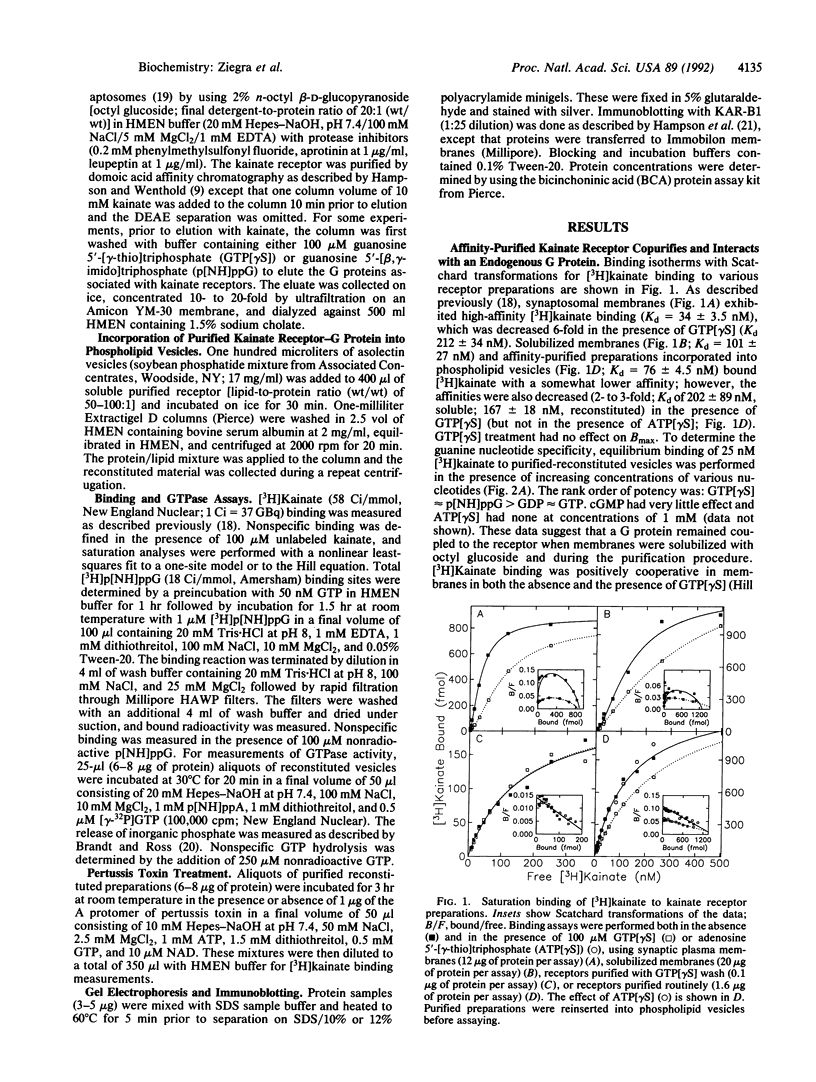
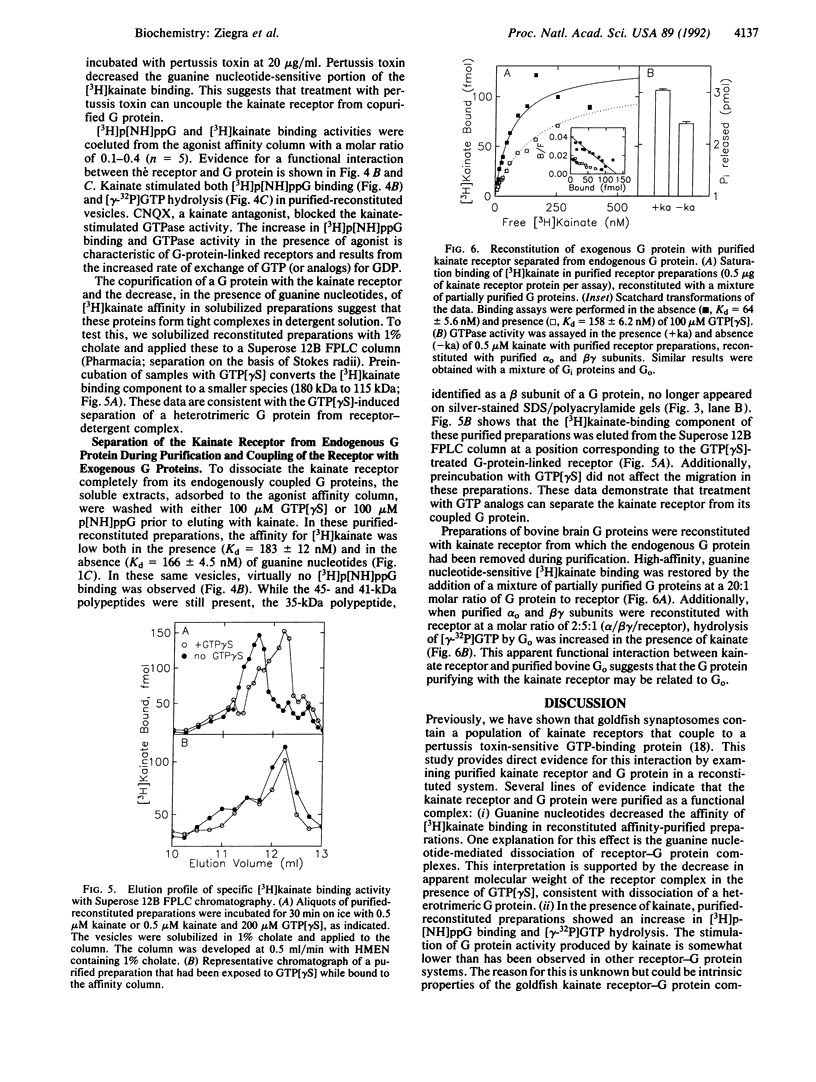
Goldfish brain has a high density of [3H]kainate-binding sites, a subpopulation of which appears to be coupled to a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein. We show here that a purified kainate receptor preparation reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles exhibits guanine nucleotide-sensitive high-affinity [3H]kainate binding. Pertussis toxin treatment abolishes the guanine nucleotide-sensitive portion of the [3H]kainate binding, and kainate promotes [3H]guanosine 5'-[beta,gamma-imido]triphosphate binding and [gamma-32P]GTP hydrolysis. Guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTP[gamma S]) decreases the apparent Stokes radius of the soluble purified receptor preparation, consistent with dissociation of the kainate receptor-G protein complexes. The affinity-purified preparations contain proteins of 45, 41, and 35 kDa. The 45- and 41-kDa proteins crossreact with antibodies against the kainate receptor cloned from frog brain. The 35-kDa protein is recognized by an antiserum (SW) directed against the beta subunit of G proteins. When kainate receptors are purified in the presence of GTP[gamma S], the 35-kDa protein is no longer present. Also, [3H]kainate affinity is decreased and is no longer guanine nucleotide sensitive. Upon reconstitution with purified G proteins, high-affinity guanine nucleotide-sensitive binding and kainate-stimulated GTPase activity can be restored. These observations indicate that a kainate receptor from goldfish brain functionally interacts with a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baudry M., Evans J., Lynch G. Excitatory amino acids inhibit stimulation of phosphatidylinositol metabolism by aminergic agonists in hippocampus. Nature. 1986 Jan 23;319(6051):329–331. doi: 10.1038/319329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., Hollmann M., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Hartley M., Deneris E., Maron C., Heinemann S. Molecular cloning and functional expression of glutamate receptor subunit genes. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1033–1037. doi: 10.1126/science.2168579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt D. R., Ross E. M. GTPase activity of the stimulatory GTP-binding regulatory protein of adenylate cyclase, Gs. Accumulation and turnover of enzyme-nucleotide intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):266–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell-Bell A. H., Finkbeiner S. M., Cooper M. S., Smith S. J. Glutamate induces calcium waves in cultured astrocytes: long-range glial signaling. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):470–473. doi: 10.1126/science.1967852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Bettler B., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., Heinemann S. Cloning of a cDNA for a glutamate receptor subunit activated by kainate but not AMPA. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):745–748. doi: 10.1038/351745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J., Southam E., Anderton M. A kainate receptor linked to nitric oxide synthesis from arginine. J Neurochem. 1989 Dec;53(6):1952–1954. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb09266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gho M., King A. E., Ben-Ari Y., Cherubini E. Kainate reduces two voltage-dependent potassium conductances in rat hippocampal neurons in vitro. Brain Res. 1986 Oct 22;385(2):411–414. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor P., Eshhar N., Ortega A., Teichberg V. I. Isolation, immunochemical characterization and localization of the kainate sub-class of glutamate receptor from chick cerebellum. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2673–2679. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03120.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor P., Mano I., Maoz I., McKeown M., Teichberg V. I. Molecular structure of the chick cerebellar kainate-binding subunit of a putative glutamate receptor. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):689–692. doi: 10.1038/342689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampson D. R., Wenthold R. J. A kainic acid receptor from frog brain purified using domoic acid affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2500–2505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampson D. R., Wheaton K. D., Dechesne C. J., Wenthold R. J. Identification and characterization of the ligand binding subunit of a kainic acid receptor using monoclonal antibodies and peptide mapping. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13329–13335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henley J. M., Oswald R. E. Solubilization and characterization of kainate receptors from goldfish brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 13;937(1):103–111. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90232-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Rogers S. W., Heinemann S. Cloning by functional expression of a member of the glutamate receptor family. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):643–648. doi: 10.1038/342643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houamed K. M., Kuijper J. L., Gilbert T. L., Haldeman B. A., O'Hara P. J., Mulvihill E. R., Almers W., Hagen F. S. Cloning, expression, and gene structure of a G protein-coupled glutamate receptor from rat brain. Science. 1991 May 31;252(5010):1318–1321. doi: 10.1126/science.1656524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida A. T., Neyton J. Quisqualate and L-glutamate inhibit retinal horizontal-cell responses to kainate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1837–1841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keinänen K., Wisden W., Sommer B., Werner P., Herb A., Verdoorn T. A., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. A family of AMPA-selective glutamate receptors. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):556–560. doi: 10.1126/science.2166337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masu M., Tanabe Y., Tsuchida K., Shigemoto R., Nakanishi S. Sequence and expression of a metabotropic glutamate receptor. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):760–765. doi: 10.1038/349760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. The physiology of excitatory amino acids in the vertebrate central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1987;28(3):197–276. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(87)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. W., Johnston M. V. Physiological and pathophysiological roles of excitatory amino acids during central nervous system development. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1990 Jan-Apr;15(1):41–70. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(90)90011-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S. N., Miller R. J. A glutamate receptor regulates Ca2+ mobilization in hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8737–8741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovira C., Gho M., Ben-Ari Y. Block of GABAb-activated K+ conductance by kainate and quisqualate in rat CA3 hippocampal pyramidal neurones. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Jan;415(4):471–478. doi: 10.1007/BF00373625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladeczek F., Récasens M., Bockaert J. A new mechanism for glutamate receptor action: phosphoinositide hydrolysis. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Dec;11(12):545–549. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90183-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada K., Dechesne C. J., Shimasaki S., King R. G., Kusano K., Buonanno A., Hampson D. R., Banner C., Wenthold R. J., Nakatani Y. Sequence and expression of a frog brain complementary DNA encoding a kainate-binding protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):684–689. doi: 10.1038/342684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner P., Voigt M., Keinänen K., Wisden W., Seeburg P. H. Cloning of a putative high-affinity kainate receptor expressed predominantly in hippocampal CA3 cells. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):742–744. doi: 10.1038/351742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard J. M., Ziegra C. J., Oswald R. E. The interaction of a kainate receptor from goldfish brain with a pertussis toxin-sensitive GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10196–10200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]