Description
A 64-year-old male patient presented with fleshy lesion over the right temporal conjunctiva for the past 3 months with a gradual increase in size. History of trauma and pain was absent, and past history did not reveal any significant ocular/systemic morbidities. Right eye examination showed single 6*8 mm lesion fleshy mass on the temporal aspect of right conjunctiva extending from the limbus, and the surface showed ‘corkscrew’ vessels, with prominent ‘feeder’ vessel; impression cytology revealed dysplastic cells consistent with ocular surface squamous neoplasia (OSSN) (figure 1A).
Figure 1.
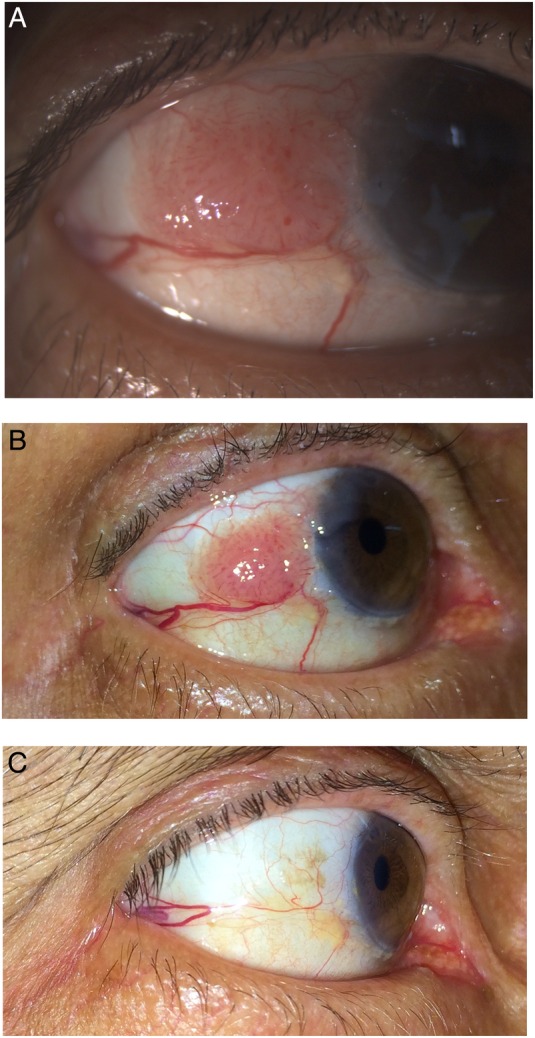
(A) Clinical picture of the tumour before starting topical interferon α 2b. (B) At the end of 2 weeks, approximately a quarter reduction in the size of the tumour mass. (C) At the end of 5 weeks, there is a complete regression of the tumour mass along with feeder vessel.
The patient requested for medical line of management, and he was started on eye drop interferon α-2b (1 million IU/mL) four times/day; at the end of 2 weeks, there was small reduction (∼25%) in the size of the lesion (figure 1B) and at the end of 5 weeks, there was complete resolution of the lesion (figure 1C). There has been no recurrence during 1 year of follow-up.
OSSN includes tumours that vary from mild dysplasia to carcinoma in situ and invasive carcinoma breaching the basement membrane; they mainly involve the cornea and conjunctiva. The preferred treatment modality is surgical excision with ‘no-touch technique’ along with the application of cryotherapy to the conjunctival margins, but surgery can cause infection, limbal stem cell deficiency, symblepharon and other complications.
Nowadays there is a growing experience about the use of interferon-α 2b as the initial treatment modality. As compared to surgical modality and earlier use of mitomycin-C, the side effect profile of this medication is minimal. Other agents used as topical chemotherapy include 5-fluorouracil and mitomycin-C. In this scenario interferon, α-2b eye drops showed an excellent response with complete regression of the mass along with the feeder vessel.1 2
Learning points.
Interferon α 2b is a very effective topical chemotherapeutic drug for the treatment of ocular surface squamous neoplasia (OSSN) with minimal adverse effects.
This clinical example highlights the important role of this drug in early, small, limbal, corneal and giant OSSN tumours.
Footnotes
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient consent: Obtained.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
- 1.Nanji AA, Moon CS, Galor A et al. . Surgical versus medical treatment of ocular surface squamous neoplasia: a comparison of recurrences and complications. Ophthalmology 2014;121:994–1000. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2013.11.017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kusumesh R, Ambastha A, Sinha B et al. . Topical interferon α-2b as a single therapy for primary ocular surface squamous neoplasia. Asia-Pac J Ophthalmol 2015;4:279–82. doi:10.1097/APO.0000000000000104 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


