Abstract
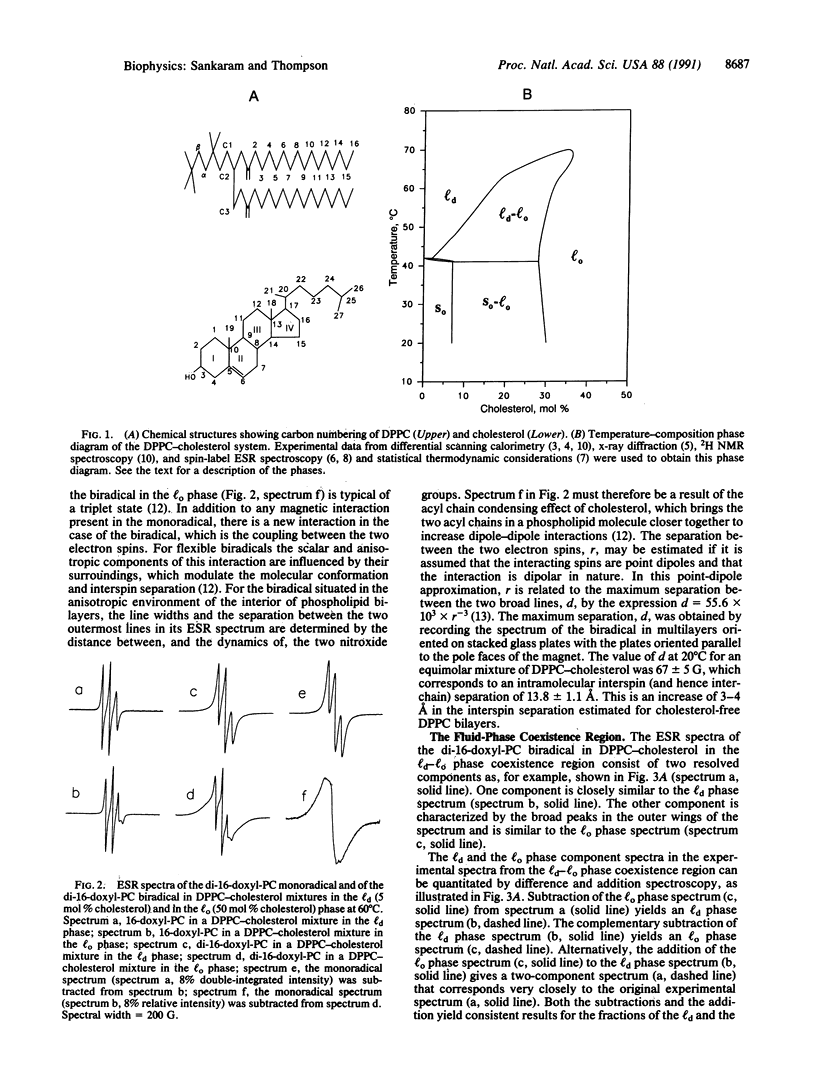
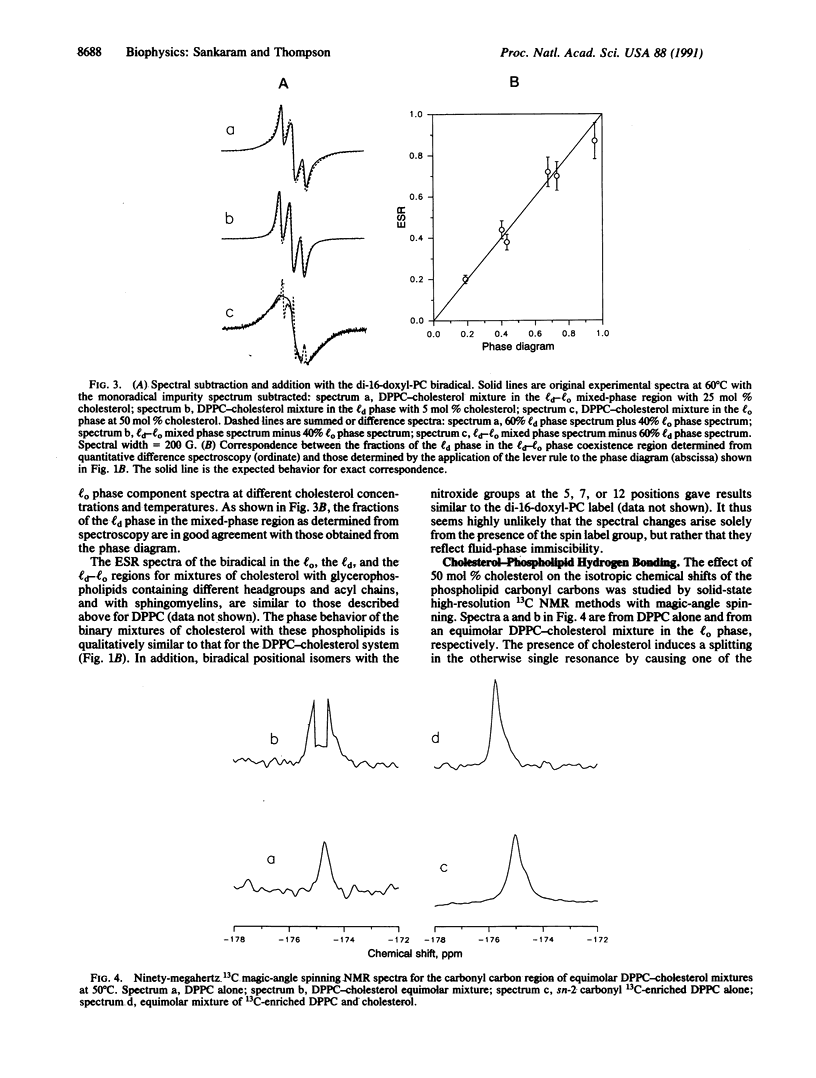
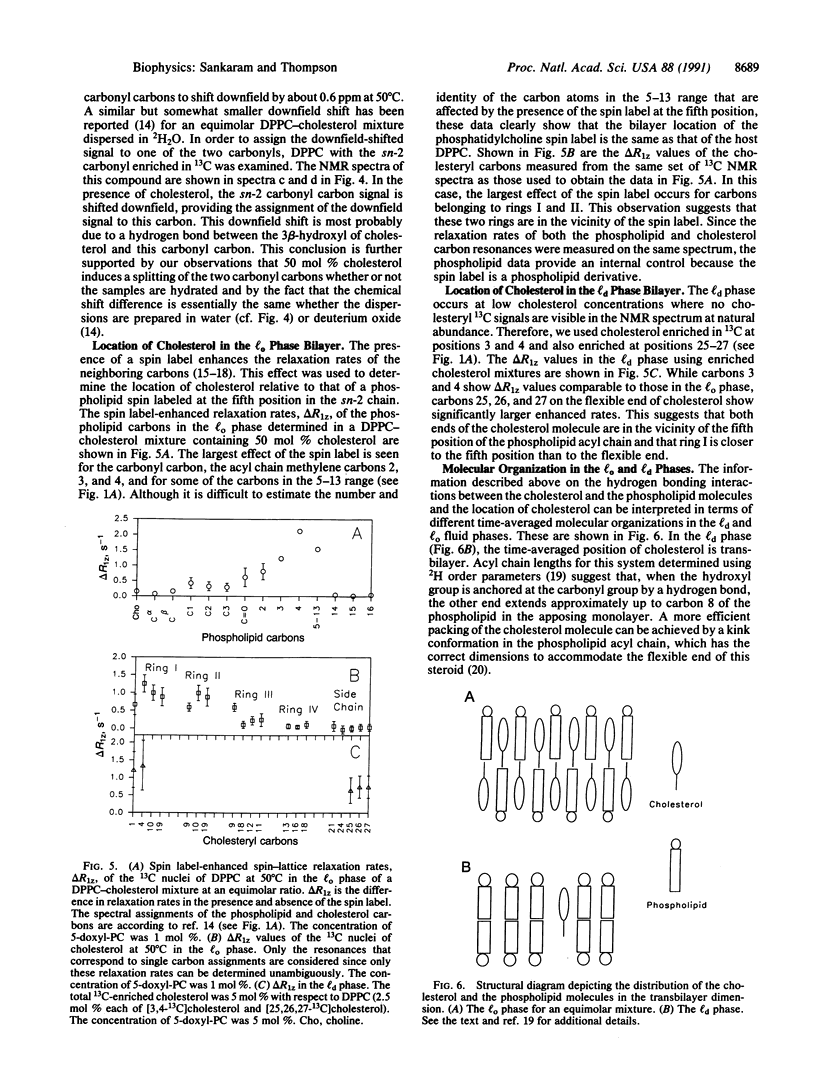
The fluid-phase behavior of binary mixtures of cholesterol with phosphatidylcholines is investigated using magnetic resonance methods. Phospholipid biradicals provide the electron spin resonance spectroscopic resolution of two immiscible fluid phases in the dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine-cholesterol system. Isotropic chemical shifts of the phospholipid carbonyl carbons in binary mixtures with cholesterol measured using solid-state high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance methods furnish evidence for a putative hydrogen bond between the 3 beta-hydroxyl of cholesterol and the sn-2 carbonyl of the phospholipid. The location in the bilayer of cholesterol in the two fluid phases is determined by measuring spin label-enhanced spin-lattice relaxation rates of the 13C nuclei of both the phospholipid and cholesterol molecules. These results suggest, in a time-averaged sense, that in the cholesterol-poor fluid phase the cholesterol molecule essentially spans the bilayer, whereas in the cholesterol-rich fluid phase the molecule is present in both monolayers of the bilayer.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brûlet P., McConnell H. M. Magnetic resonance spectra of membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1451–1455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellena J. F., Archer S. J., Dominey R. N., Hill B. D., Cafiso D. S. Localizing the nitroxide group of fatty acid and voltage-sensitive spin-labels in phospholipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 May 9;940(1):63–70. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Rothman J. E. The planar organization of lecithin-cholesterol bilayers. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 10;247(11):3694–3697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estep T. N., Mountcastle D. B., Biltonen R. L., Thompson T. E. Studies on the anomalous thermotropic behavior of aqueous dispersions of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine-cholesterol mixtures. Biochemistry. 1978 May 16;17(10):1984–1989. doi: 10.1021/bi00603a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godici P. E., Landsberger F. R. The dynamic structure of lipid membranes. A 13C nuclear magnetic resonance study using spin labels. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):362–368. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong-wei S., McConnell H. Phase separations in phospholipd membranes. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 25;14(4):847–854. doi: 10.1021/bi00675a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. H. A structural model for the cholesterol-phosphatidylcholine complexes in bilayer membranes. Lipids. 1977 Apr;12(4):348–356. doi: 10.1007/BF02533637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. Mixed-chain phospholipids and interdigitated bilayer systems. Klin Wochenschr. 1990 Feb 1;68(3):149–165. doi: 10.1007/BF01649079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipsen J. H., Karlström G., Mouritsen O. G., Wennerström H., Zuckermann M. J. Phase equilibria in the phosphatidylcholine-cholesterol system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 27;905(1):162–172. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine Y. K., Birdsall N. J., Lee A. G., Metcalfe J. C. 13 C nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation measurements of synthetic lecithins and the effect of spin-labeled lipids. Biochemistry. 1972 Apr 11;11(8):1416–1421. doi: 10.1021/bi00758a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabrey S., Mateo P. L., Sturtevant J. M. High-sensitivity scanning calorimetric study of mixtures of cholesterol with dimyristoyl- and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholines. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2464–2468. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. T., Broccoli A. V., Huang C. A method for the synthesis of isomerically pure saturated mixed-chain phosphatidylcholines. Anal Biochem. 1981 May 1;113(1):96–101. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recktenwald D. J., McConnell H. M. Phase equilibria in binary mixtures of phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 21;20(15):4505–4510. doi: 10.1021/bi00518a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankaram M. B., Thompson T. E. Interaction of cholesterol with various glycerophospholipids and sphingomyelin. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 27;29(47):10670–10675. doi: 10.1021/bi00499a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankaram M. B., Thompson T. E. Modulation of phospholipid acyl chain order by cholesterol. A solid-state 2H nuclear magnetic resonance study. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 27;29(47):10676–10684. doi: 10.1021/bi00499a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater J. L., Huang C. H. Interdigitated bilayer membranes. Prog Lipid Res. 1988;27(4):325–359. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(88)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaz W. L., Melo E. C., Thompson T. E. Translational diffusion and fluid domain connectivity in a two-component, two-phase phospholipid bilayer. Biophys J. 1989 Nov;56(5):869–876. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82733-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vist M. R., Davis J. H. Phase equilibria of cholesterol/dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine mixtures: 2H nuclear magnetic resonance and differential scanning calorimetry. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 16;29(2):451–464. doi: 10.1021/bi00454a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



