Abstract
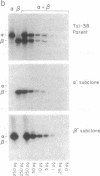
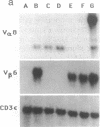
Antigen-specific suppressor T-cell hybridomas release soluble suppressor factors (TsF) in the supernatant that modulate both in vivo delayed-type hypersensitivity and in vitro plaque-forming cell responses in an antigen-specific manner. To study the relationship between the T-cell receptor (TcR) and TsF, we developed a series of TcR alpha- or TcR beta- expression variants from suppressor T-cell hybridomas that expressed the CD3-TcR alpha/beta complex. We demonstrate that loss of TcR alpha but not TcR beta mRNA was accompanied by the concomitant loss of suppressor bioactivity. Homologous transfection of TcR alpha cDNA into a TcR alpha- beta+ clone reconstituted both CD3-TcR expression and suppressor function. Furthermore, suppressor activity from TcR beta- variants was specifically absorbed by antigen and anti-TcR alpha antibodies, but not by anti-CD3 or anti-TcR beta affinity columns. These data directly establish a role for the TcR alpha chain in suppressor T-cell function and suggest that the TcR alpha chain is part of the antigen-specific TsF molecule.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonifacino J. S., Suzuki C. K., Klausner R. D. A peptide sequence confers retention and rapid degradation in the endoplasmic reticulum. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):79–82. doi: 10.1126/science.2294595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien Y., Becker D. M., Lindsten T., Okamura M., Cohen D. I., Davis M. M. A third type of murine T-cell receptor gene. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):31–35. doi: 10.1038/312031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. R. Regulation of autoimmune disease physiological and therapeutic. Immunol Rev. 1986 Dec;94:5–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M., Kuchroo V. K., Whitters M. J., O'Hara R. M., Jr, Kelleher K., Kubo R. T., Dorf M. E. Expression of functional alpha beta T cell receptor gene rearrangements in suppressor T cell hybridomas correlates with antigen binding, but not with suppressor cell function. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):2809–2819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Santis R., Givol D., Hsu P. L., Adorini L., Doria G., Appella E. Rearrangement and expression of the alpha- and beta-chain genes of the T-cell antigen receptor in functional murine suppressor T-cell clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8638–8642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorf M. E., Benacerraf B. Suppressor cells and immunoregulation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:127–157. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairchild R. L., Kubo R. T., Moorhead J. W. DNP-specific/class I MHC-restricted suppressor molecules bear determinants of the T cell receptor alpha- and beta-chains. The V beta 8+ chain dictates restriction to either K or D. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 1;145(7):2001–2009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairchild R. L., Kubo R. T., Moorhead J. W. Soluble factors in tolerance and contact sensitivity to 2,4-dinitro-fluorobenzene in mice. IX. A monoclonal T cell suppressor molecule is structurally and serologically related to the alpha/beta T cell receptor. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3342–3348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausman P. B., Sherr D. H., Dorf M. E. An in vitro system for the generation of suppressor cells and the requirement for B cells in their induction. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1388–1396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick S. M., Germain R. N., Bevan M. J., Dorf M., Engel I., Fink P., Gascoigne N., Heber-Katz E., Kapp J., Kaufmann Y. Rearrangement and transcription of a T-cell receptor beta-chain gene in different T-cell subsets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):531–535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai K., Kanno M., Kimoto H., Shigemoto K., Yamamoto S., Taniguchi M. Sequence and expression of transcripts of the T-cell antigen receptor alpha-chain gene in a functional, antigen-specific suppressor-T-cell hybridoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8708–8712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata M., Katamura K., Kubo R. T., Grey H. M., Ishizaka K. Relationship between T cell receptors and antigen-binding factors. II. Common antigenic determinants and epitope recognition shared by T cell receptors and antigen-binding factors. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):3917–3924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata M., Katamura K., Kubo R. T., Ishizaka K. Relationship between T cell receptors and antigen-binding factors. I. Specificity of functional T cell receptors on mouse T cell hybridomas that produce antigen-binding T cell factors. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):3909–3916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman S., Bellone C. J. Hapten-specific responses to the phenyltrimethylamino hapten. V. A single chain antigen-binding I-J+ first-order T suppressor factor requires antigen to induce anti-idiotypic second-order suppressor T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):1010–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishi H., Borgulya P., Scott B., Karjalainen K., Traunecker A., Kaufman J., von Boehmer H. Surface expression of the beta T cell receptor (TCR) chain in the absence of other TCR or CD3 proteins on immature T cells. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):93–100. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07924.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronenberg M., Goverman J., Haars R., Malissen M., Kraig E., Phillips L., Delovitch T., Suciu-Foca N., Hood L. Rearrangement and transcription of the beta-chain genes of the T-cell antigen receptor in different types of murine lymphocytes. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):647–653. doi: 10.1038/313647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchroo V. K., Steele J. K., Billings P. R., Selvaraj P., Dorf M. E. Expression of CD3-associated antigen-binding receptors on suppressor T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9209–9213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchroo V. K., Steele J. K., O'Hara R. M., Jr, Jayaraman S., Selvaraj P., Greenfield E., Kubo R. T., Dorf M. E. Relationships between antigen-specific helper and inducer suppressor T cell hybridomas. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 15;145(2):438–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salgame P., Convit J., Bloom B. R. Immunological suppression by human CD8+ T cells is receptor dependent and HLA-DQ restricted. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2598–2602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. An LFA-3 cDNA encodes a phospholipid-linked membrane protein homologous to its receptor CD2. 1987 Oct 29-Nov 4Nature. 329(6142):840–842. doi: 10.1038/329840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen C. M., Pierce C. W. Monoclonal antibodies specific for single chain or two chain GAT-specific suppressor factors: production and analysis of in vitro modulating properties. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):362–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takata M., Maiti P. K., Kubo R. T., Chen Y. H., Holford-Strevens V., Rector E. S., Sehon A. H. Cloned suppressor T cells derived from mice tolerized with conjugates of antigen and monomethoxypolyethylene glycol. Relationship between monoclonal T suppressor factor and the T cell receptor. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):2846–2853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan K. N., Datlof B. M., Gilmore J. A., Kronman A. C., Lee J. H., Maxam A. M., Rao A. The T cell receptor V alpha 3 gene segment is associated with reactivity to p-azobenzenearsonate. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):247–261. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90557-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner D. B., Liu J., Hanna N., Bluestone J. A., Coligan J. E., Williams W. V., Greene M. I. CD3-associated heterodimeric polypeptides on suppressor hybridomas define biologically active inhibitory cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6077–6081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wileman T., Carson G. R., Shih F. F., Concino M. F., Terhorst C. The transmembrane anchor of the T-cell antigen receptor beta chain contains a structural determinant of pre-Golgi proteolysis. Cell Regul. 1990 Nov;1(12):907–919. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.12.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. D., Burd P. R., Billings P. R., Martin C. A., Dorf M. E. The expression and regulation of a potential lymphokine gene (TCA3) in CD4 and CD8 T cell clones. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1563–1570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng H., Sahai B. M., Kilgannon P., Fotedar A., Green D. R. Specific inhibition of cell-surface T-cell receptor expression by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides and its effect on the production of an antigen-specific regulatory T-cell factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3758–3762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]