Abstract
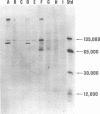
Mink cells nonproductively transformed by the T-8 strain of mink cell focus-inducing virus express two type C viral amino terminal gag gene-coded structural proteins, p15 and p12, in the form of a 90,000 to 110,000 molecular weight polyprotein that lacks detectable immunological reactivity with other known type C virus-coded translational products. The observation concurs with the previous demonstration of similar high-molecular-weight precursor polyproteins in cell lines nonproductively transformed by either of two other mammalian sarcoma viruses also limited in virus-coded structural protein expression to p15 and p12.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbacid M., Stephenson J. R., Aaronson S. A. gag Gene of mammalian type-C RNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):554–559. doi: 10.1038/262554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein A., Mak T. W., Stephenson J. R. The Friend virus genome: evidence for the stable association of MuLV sequences and sequences involved in erythroleukemic transformation. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90206-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilello J. A., Strand M., August J. T. Expression of viral envelope glycoprotein and transformation genes in cells transformed by a defective Kirsten murine sarcoma virus. Virology. 1977 Mar;77(1):233–244. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90421-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Gautsch J. W., Jensen F. C., Lerner R. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Biochemical evidence that MCF murine leukemia viruses are envelope (env) gene recombinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4676–4680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. E., Fischinger P. J. Rate of divergence of cellular sequences homologous to segments of Moloney sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):153–160. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.153-160.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. B., Rongey R. W., Arnstein P., Estes J. D., Sarma P., Huebner R. J., Rickard C. G. Experimental transmission of feline fibrosarcoma to cats and dogs. Nature. 1970 May 30;226(5248):807–809. doi: 10.1038/226807a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARVEY J. J. AN UNIDENTIFIED VIRUS WHICH CAUSES THE RAPID PRODUCTION OF TUMOURS IN MICE. Nature. 1964 Dec 12;204:1104–1105. doi: 10.1038/2041104b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Wolford N. K., Old L. J., Rowe W. P. A new class of murine leukemia virus associated with development of spontaneous lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):789–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. S., Stephenson J. R. Feline leukemia virus: biochemical and immunological characterization of gag gene-coded structural proteins. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):599–607. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.599-607.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moloney J. B. A virus-induced rhabdomyosarcoma of mice. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Sep;22:139–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks W. P., Howk R. S., Anisowicz A., Scolnick E. M. Deletion mapping of moloney type C virus: polypeptide and nucleic acid expression in different transforming virus isolates. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):491–503. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.491-503.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles P. T. An in vitro focus-induction assay for xenotropic murine leukemia virus, feline leukemia virus C, and the feline--primate viruses RD-114/CCC/M-7. Virology. 1975 Sep;67(1):288–291. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90427-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds R. K., Stephenson J. R. Intracistronic mapping of the murine type C viral gag gene by use of conditional lethal replication mutants. Virology. 1977 Sep;81(2):328–340. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90149-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Rands E., Williams D., Parks W. P. Studies on the nucleic acid sequences of Kirsten sarcoma virus: a model for formation of a mammalian RNA-containing sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):458–463. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.458-463.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. Z., Strand M., August J. T. High molecular weight precursor polypeptides to structural proteins of Rauscher murine leukemia virus. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov 15;107(4):459–477. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Sen A., Todaro G. J., Sliski A., Essex M. Pseudotypes of feline sarcoma virus contain an 85,000-dalton protein with feline oncornavirus-associated cell membrane antigen (FOCMA) activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1505–1509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. P., Theilen G. H. Transmissible feline fibrosarcoma. Nature. 1969 Mar 15;221(5185):1074–1075. doi: 10.1038/2211074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staal S. P., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Isolation of transforming murine leukemia viruses from mice with a high incidence of spontaneous lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3065–3067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Khan A. S., Sliski A. H., Essex M. Feline oncornavirus-associated cell membrane antigen: evidence for an immunologically crossreactive feline sarcoma virus-coded protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5608–5612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theilen G. H., Gould D., Fowler M., Dungworth D. L. C-type virus in tumor tissue of a woolly monkey (Lagothrix spp.) with fibrosarcoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Oct;47(4):881–889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., De Larco J. E., Cohen S. Transformation by murine and feline sarcoma viruses specifically blocks binding of epidermal growth factor to cells. Nature. 1976 Nov 4;264(5581):26–31. doi: 10.1038/264026a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida N., Gilden R. V., Hatanaka M. Size of virus-specific RNA in B-34, a hamster tumor cell producing nucleic acids of type C viruses from three species. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):832–837. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.832-837.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaanie D., Gielkens A. L., Dekker-michielsen M. J., Bloemers H. P. Virus-specific precursor polypeptides in cells infected with Rauscher leukemia virus. Virology. 1975 Oct;67(2):544–552. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90454-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]