Abstract
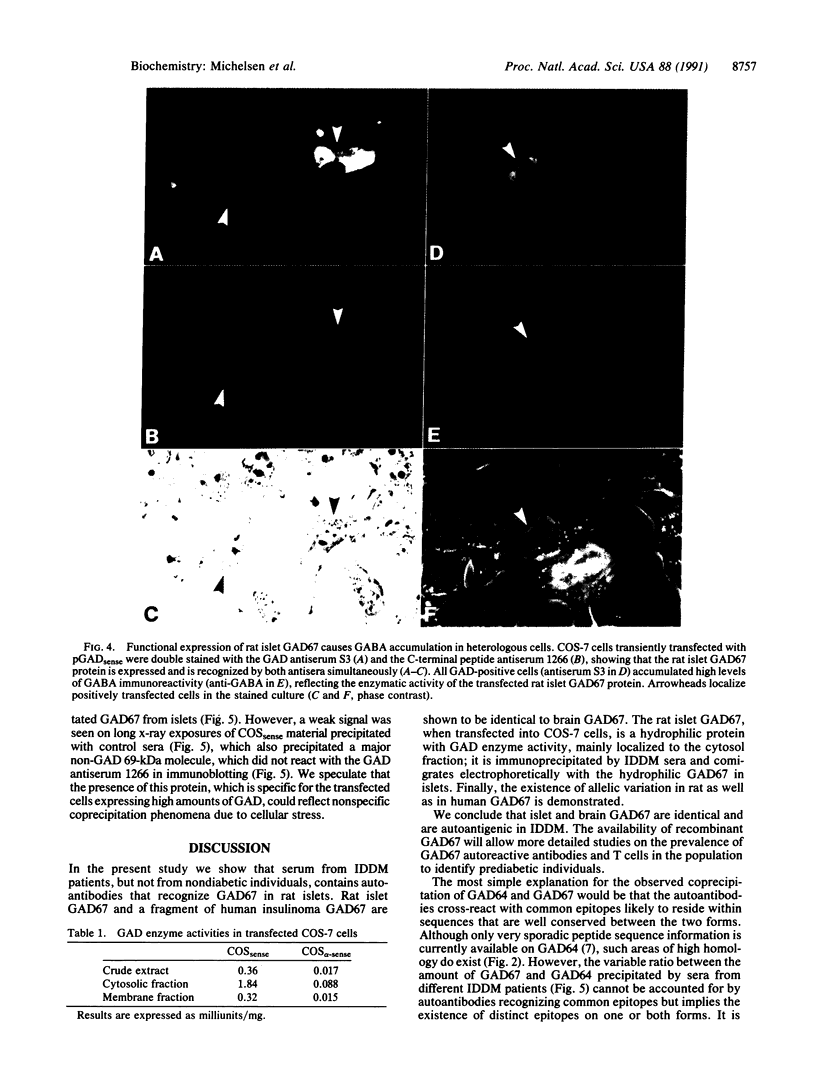
A 64-kDa islet protein is a major autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM). Autoantibodies against the 64-kDa protein were recently shown to immunoprecipitate glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD; L-glutamate 1-carboxy-lyase, EC 4.1.1.15) from brain and from islets. We present evidence that the autoantisera also recognize a hydrophilic islet protein of approximately 67 kDa in addition to the amphiphilic 64-kDa form. We have isolated a full-length rat islet GAD cDNA encoding a hydrophilic 67-kDa protein, which appears to be identical to rat brain 67-kDa GAD. A partial sequence of human insulinoma 67-kDa GAD was identical to human brain 67-kDa GAD. Allelic variations were observed in rat as well as in human 67-kDa GAD sequences. The expressed rat islet 67-kDa GAD protein is functional and is immunoprecipitated by IDDM sera; it comigrates electrophoretically with the 67-kDa islet autoantigen. The hydrophilic 67-kDa form of GAD in islets is an additional autoantigen in IDDM and is recognized by a different subset of autoantibodies than the 64-kDa autoantigen. Thus, mammalian cell lines expressing functionally active, recombinant GAD may become important tools to study the nature and the role of GAD autoreactivity in IDDM.
Full text
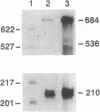
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aruffo A., Seed B. Molecular cloning of a CD28 cDNA by a high-efficiency COS cell expression system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8573–8577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekkeskov S., Aanstoot H. J., Christgau S., Reetz A., Solimena M., Cascalho M., Folli F., Richter-Olesen H., De Camilli P., Camilli P. D. Identification of the 64K autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):151–156. doi: 10.1038/347151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond R. W., Jansen K. R., Gottlieb D. I. Pattern of expression of glutamic acid decarboxylase mRNA in the developing rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3231–3234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond R. W., Wyborski R. J., Gottlieb D. I. Developmentally regulated expression of an exon containing a stop codon in the gene for glutamic acid decarboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8771–8775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. C., Gottlieb D. I. Characterization of the proteins purified with monoclonal antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase. J Neurosci. 1988 Jun;8(6):2123–2130. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-06-02123.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie M., Landin-Olsson M., Sundkvist G., Dahlquist G., Lernmark A., Baekkeskov S. Antibodies to a Mr-64,000 islet cell protein in Swedish children with newly diagnosed type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes. Diabetologia. 1988 Aug;31(8):597–602. doi: 10.1007/BF00264766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cram D. S., Barnett L. D., Joseph J. L., Harrison L. C. Cloning and partial nucleotide sequence of human glutamic acid decarboxylase cDNA from brain and pancreatic islets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 15;176(3):1239–1244. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90418-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielson P. E., Forss-Petter S., Brow M. A., Calavetta L., Douglass J., Milner R. J., Sutcliffe J. G. p1B15: a cDNA clone of the rat mRNA encoding cyclophilin. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):261–267. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denner L. A., Wu J. Y. Two forms of rat brain glutamic acid decarboxylase differ in their dependence on free pyridoxal phosphate. J Neurochem. 1985 Mar;44(3):957–965. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb12910.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower W. J., Miller J. F., Ragsdale C. W. High efficiency transformation of E. coli by high voltage electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6127–6145. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U. Second-strand cDNA synthesis: mRNA fragments as primers. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:330–335. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Fiddes J. C., Hanahan D. Directional cDNA cloning in plasmid vectors by sequential addition of oligonucleotide linkers. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:349–359. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson F. R., Newby L. M., Kulkarni S. J. Drosophila GABAergic systems: sequence and expression of glutamic acid decarboxylase. J Neurochem. 1990 Mar;54(3):1068–1078. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb02359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson F. R. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic pyridoxal-dependent decarboxylases are homologous. J Mol Evol. 1990 Oct;31(4):325–329. doi: 10.1007/BF02101126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson A. Purification and fractionation of poly(A)+ RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:254–261. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julien J. F., Samama P., Mallet J. Rat brain glutamic acid decarboxylase sequence deduced from a cloned cDNA. J Neurochem. 1990 Feb;54(2):703–705. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katarova Z., Szabo G., Mugnaini E., Greenspan R. J. Molecular Identification of the 62 kd Form of Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase from the Mouse. Eur J Neurosci. 1990;2(3):190–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1990.tb00412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. L., Houser C. R., Tobin A. J. Two forms of the gamma-aminobutyric acid synthetic enzyme glutamate decarboxylase have distinct intraneuronal distributions and cofactor interactions. J Neurochem. 1991 Feb;56(2):720–723. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Kaufman D. L., Tobin A. J. Glutamic acid decarboxylase cDNA: nucleotide sequence encoding an enzymatically active fusion protein. J Neurosci. 1987 Sep;7(9):2768–2772. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-09-02768.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krug M. S., Berger S. L. First-strand cDNA synthesis primed with oligo(dT). Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:316–325. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legay F., Henry S., Tappaz M. Evidence for two distinct forms of native glutamic acid decarboxylase in rat brain soluble extract: an immunoblotting study. J Neurochem. 1987 Apr;48(4):1022–1026. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb05620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen O. D., Andersen L. C., Michelsen B., Owerbach D., Larsson L. I., Lernmark A., Steiner D. F. Tissue-specific expression of transfected human insulin genes in pluripotent clonal rat insulinoma lines induced during passage in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6652–6656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Taniguchi H., Schimada C. High concentration of GABA and high glutamate decarboxylase activity in rat pancreatic islets and human insulinoma. Science. 1976 Nov 5;194(4265):620–622. doi: 10.1126/science.185693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Pelto-Huikko M., Metsis M., Söder O., Brene S., Skog S., Hökfelt T., Ritzén E. M. Expression of the neurotransmitter-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase in male germ cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4701–4711. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spink D. C., Porter T. G., Wu S. J., Martin D. L. Kinetically different, multiple forms of glutamate decarboxylase in rat brain. Brain Res. 1987 Sep 22;421(1-2):235–244. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91293-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogeli G., Kaytes P. S. Amplification, storage, and replication of libraries. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:407–415. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Berger S. L. Screening colonies or plaques with radioactive nucleic acid probes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:415–423. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R., Wu T., Ray A. Adaptors, linkers, and methylation. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:343–349. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyborski R. J., Bond R. W., Gottlieb D. I. Characterization of a cDNA coding for rat glutamic acid decarboxylase. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1990 Aug;8(3):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(90)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]