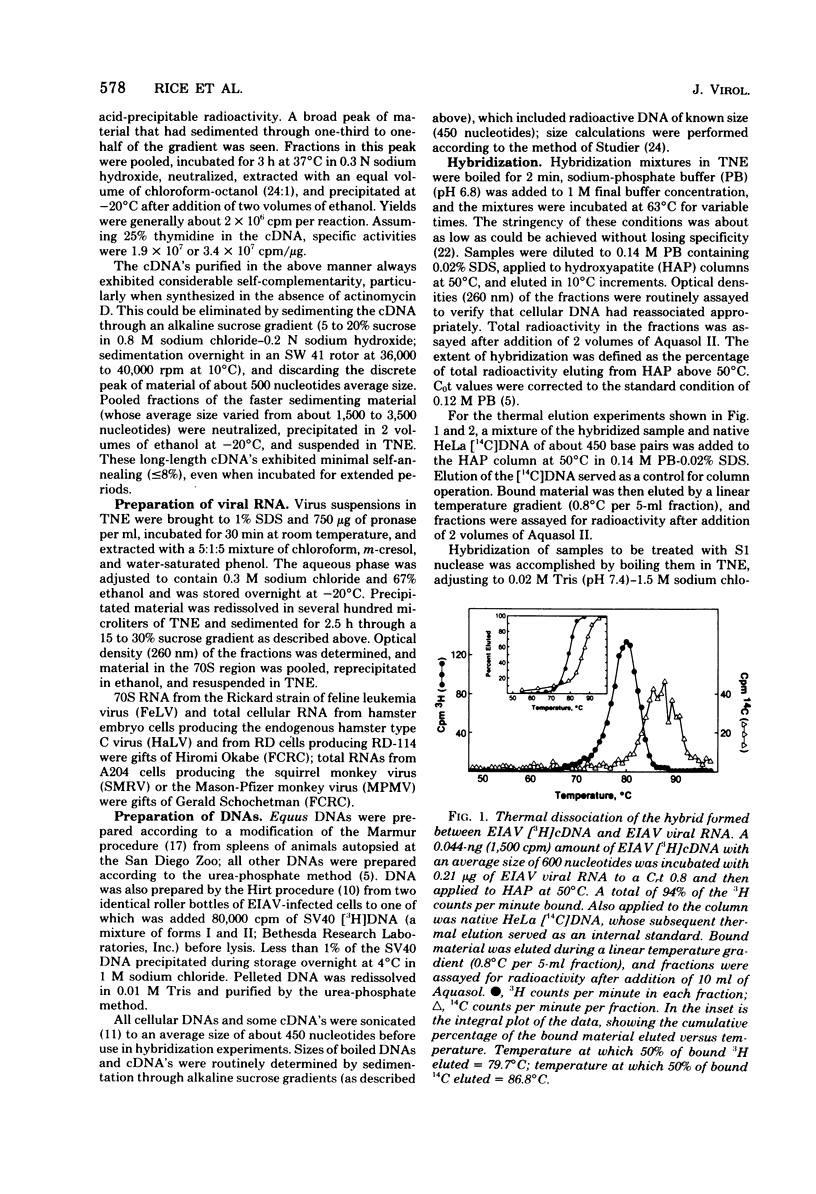
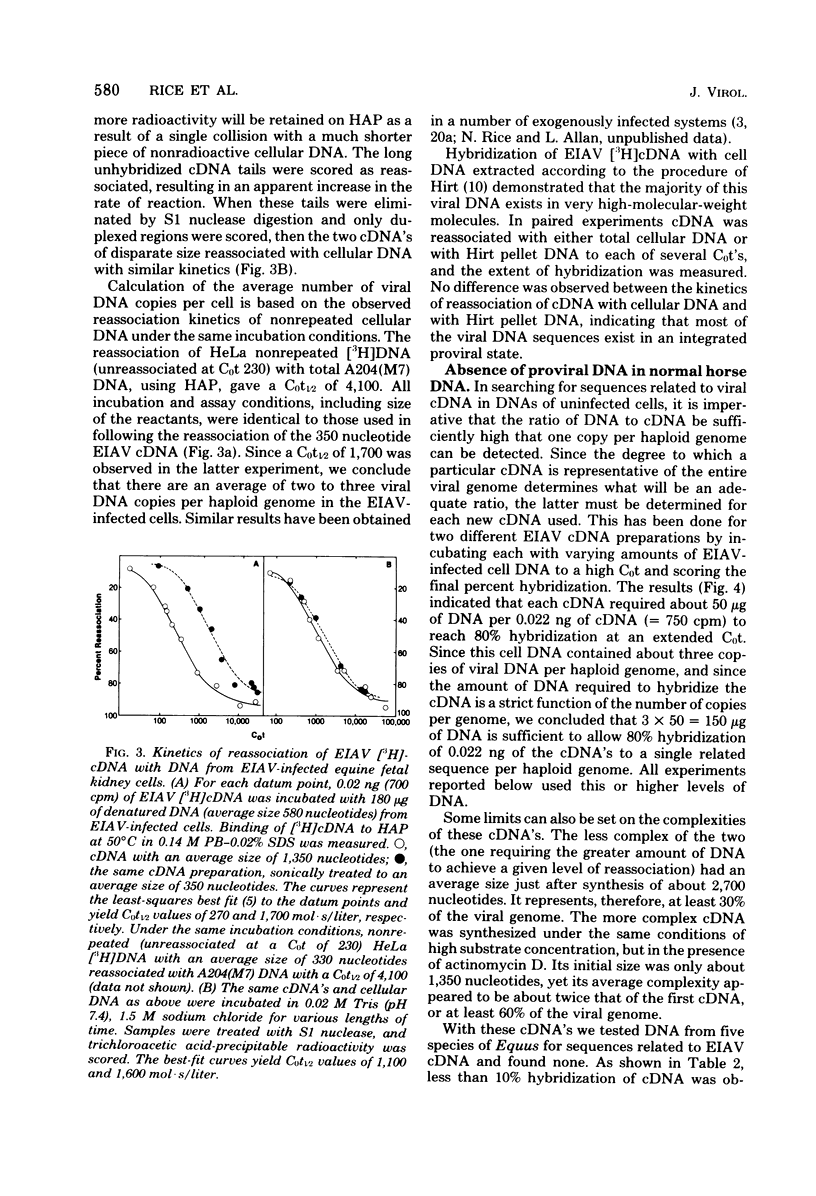
Abstract
Equine infectious anemia virus (EIAV) recently has been shown to possess a high-molecular-weight RNA genome and a virion reverse transcriptase. We completed the demonstration that EIAV is a retrovirus by showing the presence of proviral DNA in equine cells infected in vitro, but not in normal horse DNA. These studies were performed by using a highly representative cDNA probe synthesized by the virion polymerase. It was found that this cDNA reassociated extensively, and with high thermal stability, with either viral RNA or DNA extracted from infected cells, but showed no detectable reassociation with DNA from uninfected horse cells. Similarly, sequences related to EIAV were neither found in the DNA of four other Equus species, nor in a variety of other mammals including sheep, cows, pigs- dogs, cats, and humans; nor did EIAV cDNA hybridize with a variety of other retrovirus RNAs. These experiments were performed under conditions of very low stringency to enable detection of distantly related sequences, with a sufficient ratio of DAN to cDNA to allow detection of less than one viral copy per haploid genome. We conclude that EIAV is not an endogenous virus of the horse or of the other species tested.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer B. G., Crawford T. B., McGuire T. C., Frazier M. E. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase associated with equine infectious anemia virus. J Virol. 1977 Apr;22(1):16–22. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.1.16-22.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENDIXEN H. J. PREVENTIVE MEASURES IN CATTLE LEUKEMIA: LEUKOSIS ENZOOTICA BOVIS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Nov 4;108:1241–1267. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb13448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R. E., Todaro G. J. Multiple divergent copies of endogenous C-type virogenes in mammalian cells. Nature. 1974 Nov 8;252(5479):170–173. doi: 10.1038/252170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Graham D. E., Neufeld B. R. Analysis of repeating DNA sequences by reassociation. Methods Enzymol. 1974;29:363–418. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)29033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheevers W. P., Archer B. G., Crawford T. B. Characterization of RNA from equine infectious anemia virus. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):489–497. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.489-497.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drohan W., Colcher D., Schochetman G., Schlom J. Distribution of Mason-Pfizer virus-specific sequences in the DNA of primates. J Virol. 1977 Jul;23(1):36–43. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.1.36-43.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. W., Perry A., Robinson O. R., Jr, Shibley G. P. Method for reproducible large-volume production and purification of Rauscher murine leukemia virus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Feb;31(2):182–188. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.2.182-188.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemen M. J., Jr, Coggins L. Equine infectious anemia: transmission from infected mares to foals. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Sep 1;161(5):496–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber M. M., Sherr C. J., Todaro G. J., Benveniste R. E., Callahan R., Coon H. G. Isolation from the asian mouse Mus caroli of an endogenous type C virus related to infectious primate type C viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2315–2319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheka H. D., Coggins L., Shively J. N., Norcross N. L. Purification and characterization of equine infectious anemia virus. Arch Virol. 1976;51(1-2):107–114. doi: 10.1007/BF01317839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. M., Miller L. D., Olson C., Gillette K. G. Virus-like particles in phytohemagglutinin-stimulated lymphocyte cultures with reference to bovine lymphosarcoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 Dec;43(6):1297–1305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks W. P., Gilden R. V., Bykovsky A. F., Miller G. G., Zhdanov V. M., Soloviev V. D., Scolnick E. M. Mason-Pfizer virus characterization: a similar virus in a human amniotic cell line. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1540–1547. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1540-1547.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUDIER F. W. SEDIMENTATION STUDIES OF THE SIZE AND SHAPE OF DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:373–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umphenour N. W., Kemen M. J., Coggins L. Equine infectious anemia: a retrospective study of an epizootic. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1974 Jan 1;164(1):66–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



