Abstract
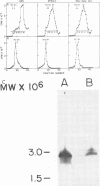
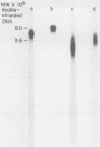
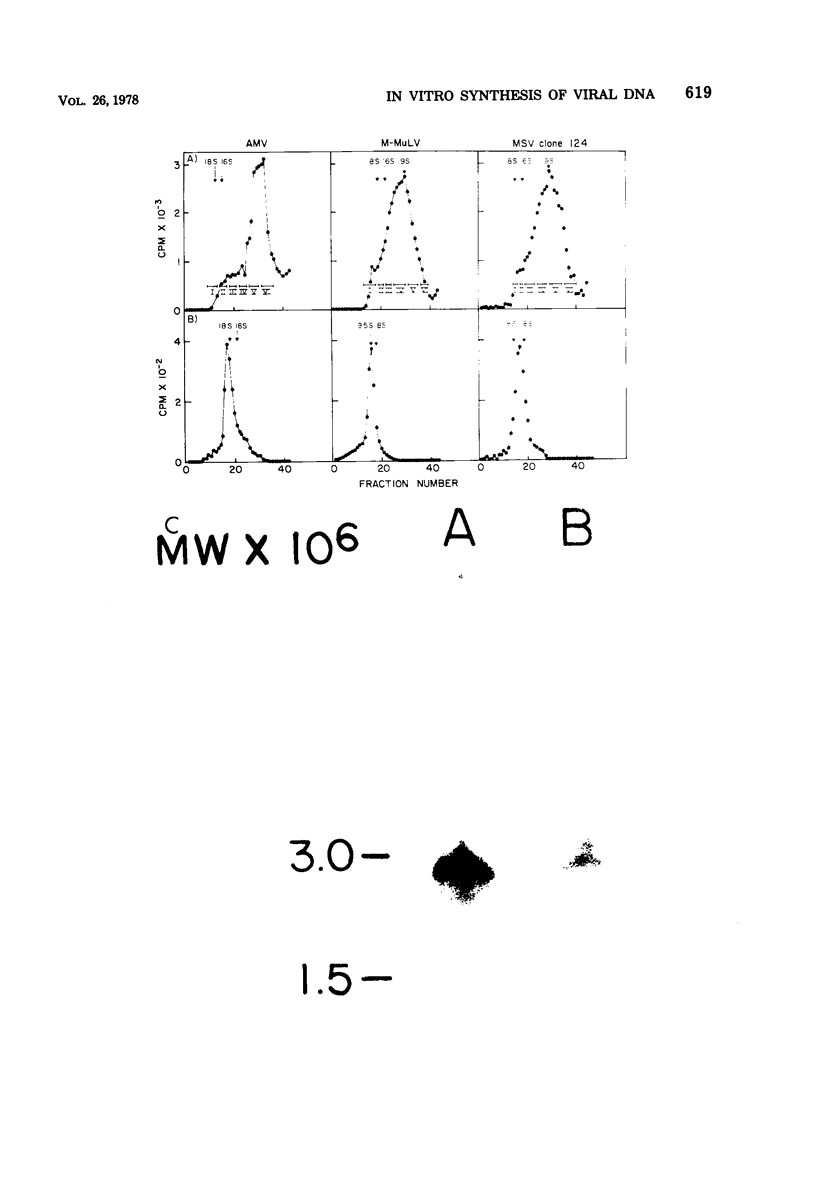
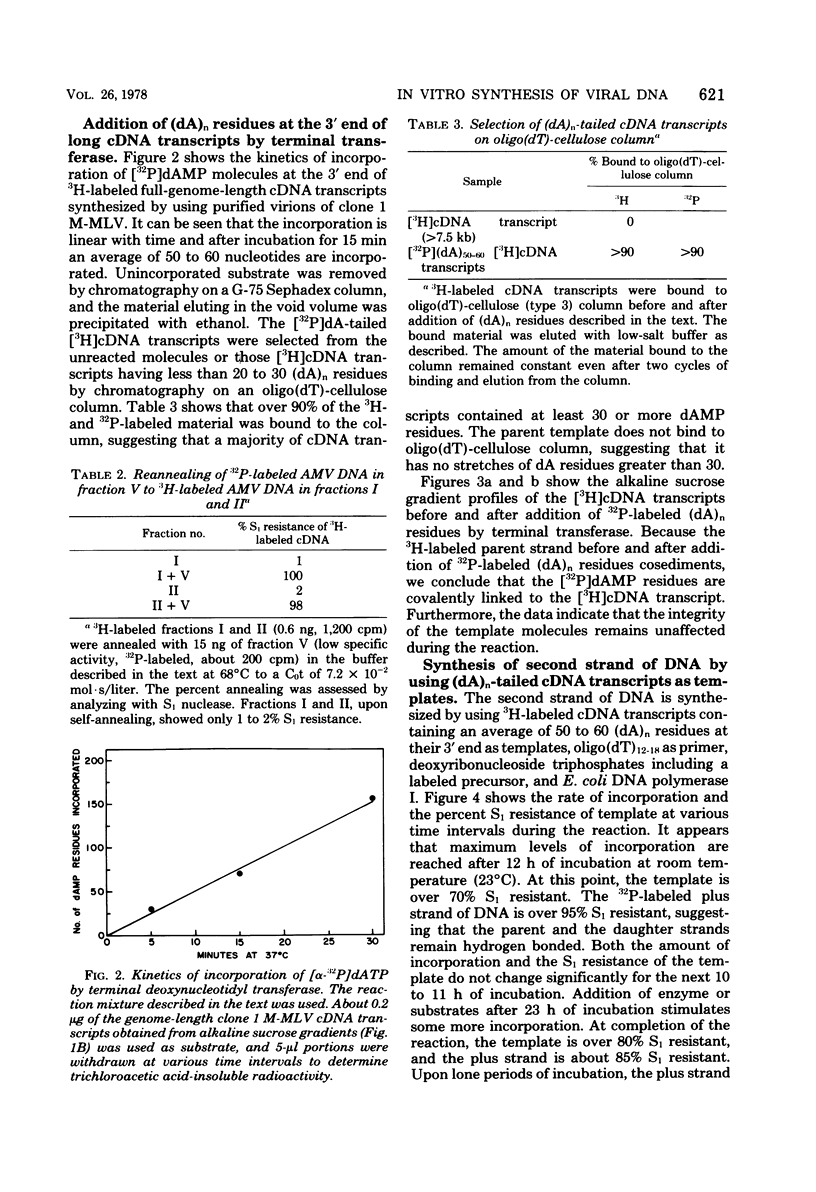
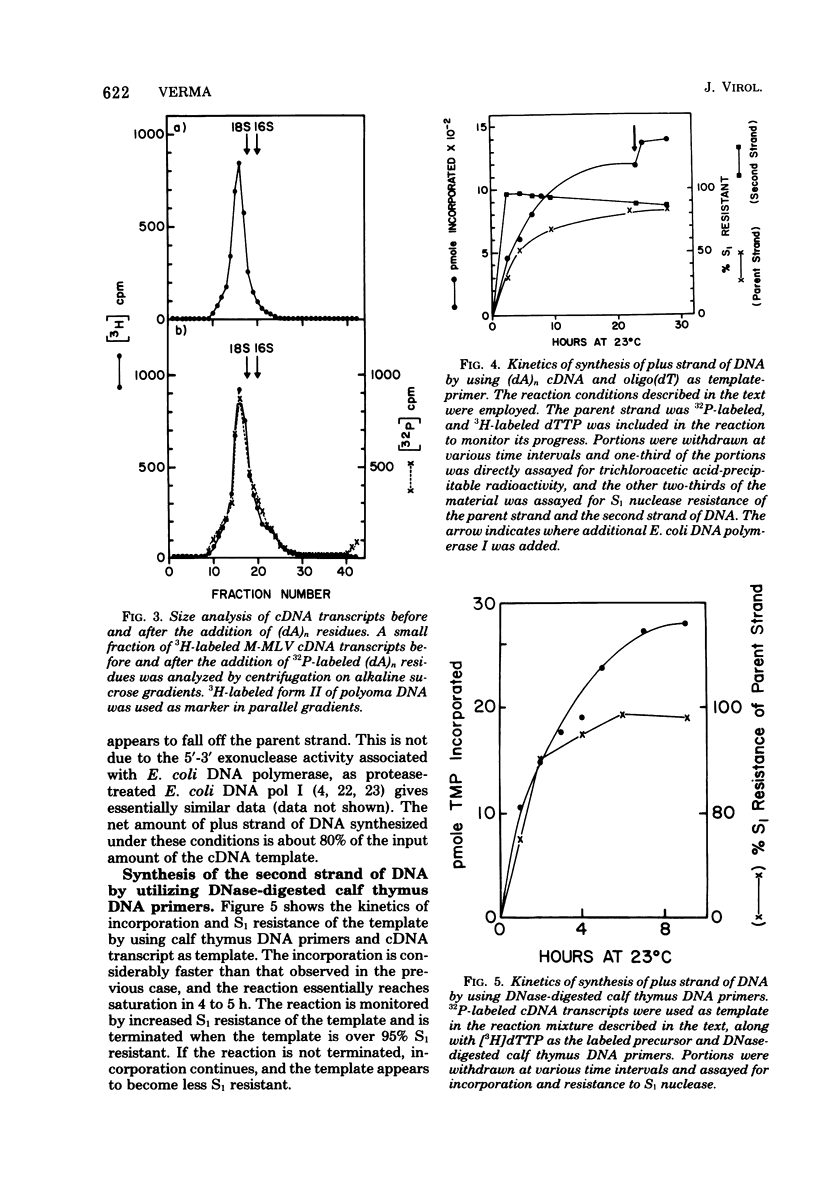
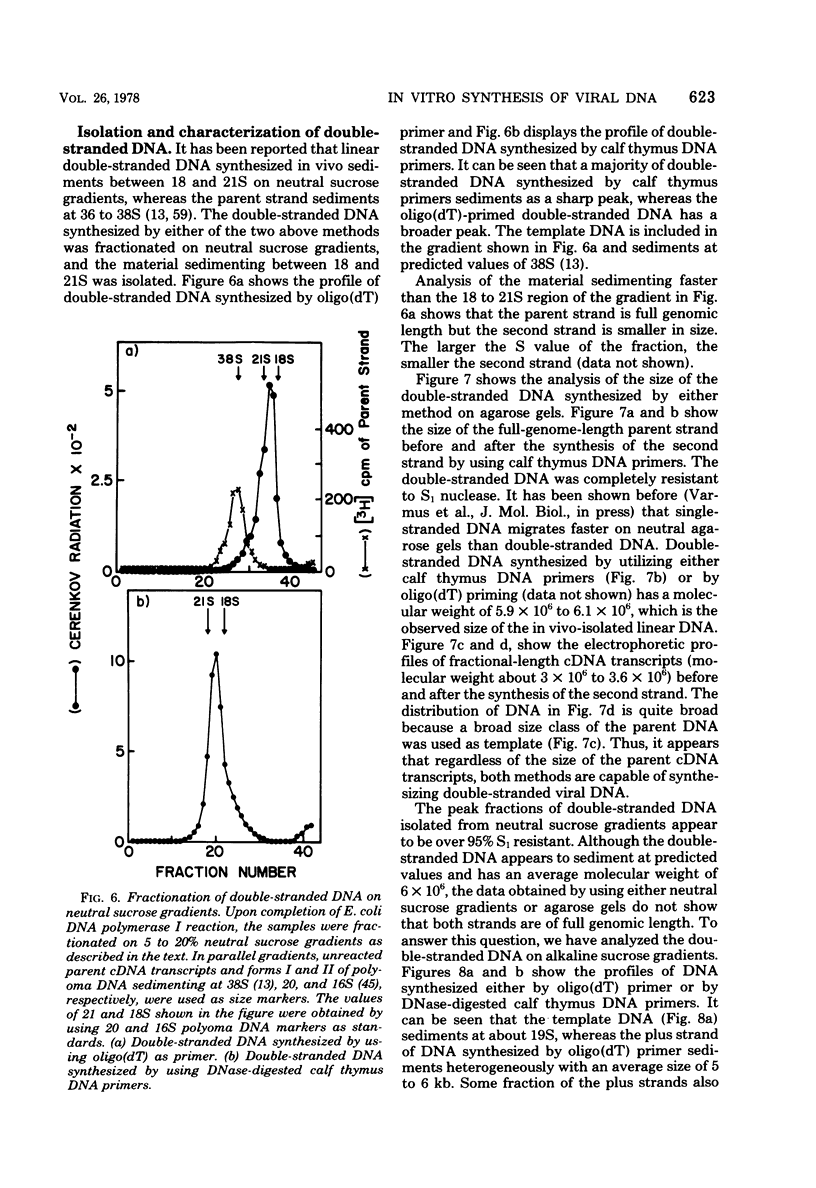
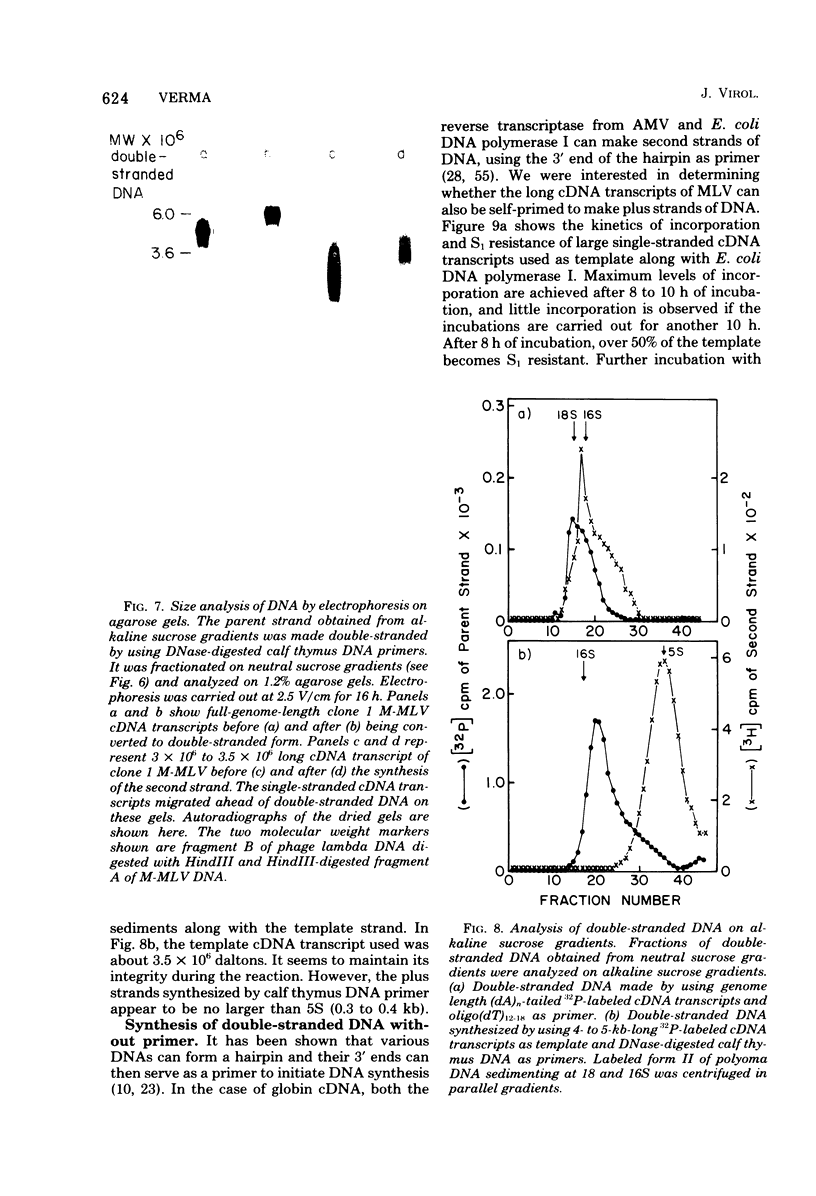
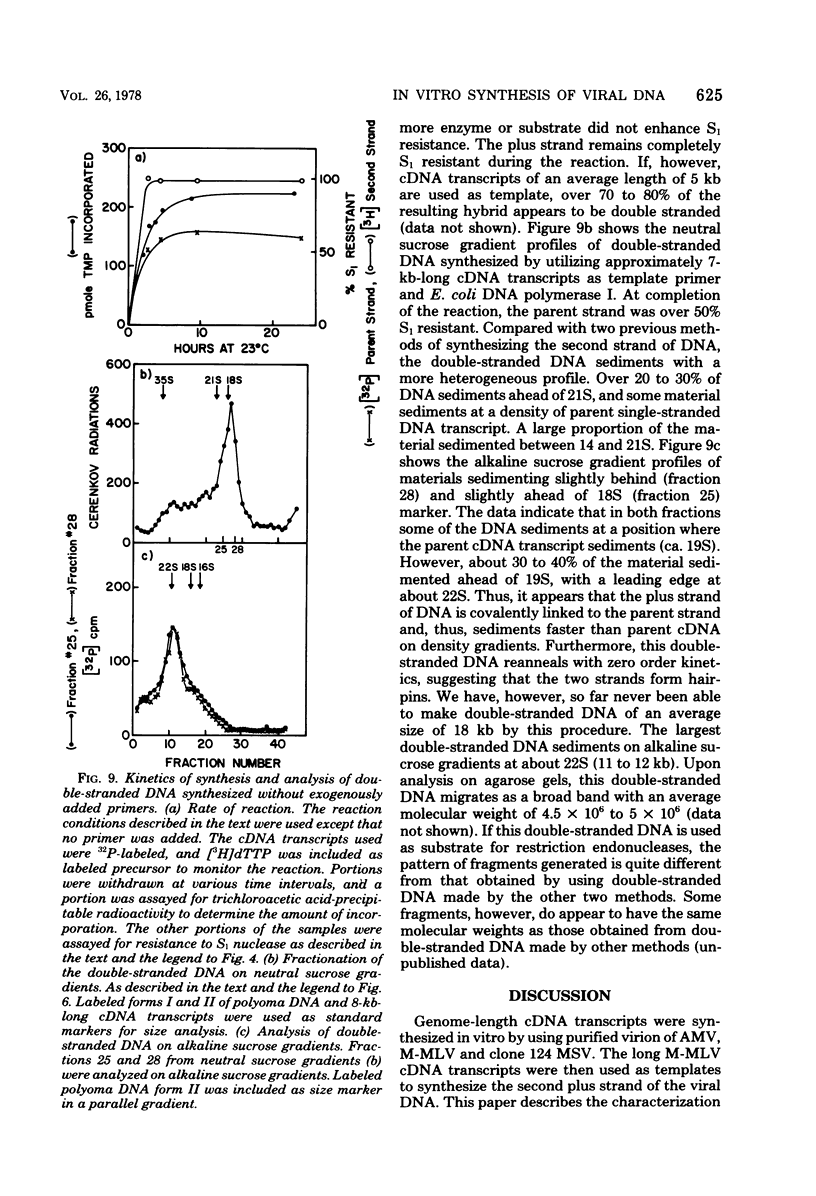
Genome-length complementary DNA (cDNA) transcripts were synthesized in vitro by using purified virions of avian myeloblastosis virus. Moloney murine leukemia virus, and clone 124 mouse sarcoma virus. The size of the genomelenth cDNA transcripts was measured on either alkaline sucrose gradients or alkaline agarose gels. The longest cDNA transcripts synthesized by using avian myeloblastosis virus, Moloney murine leukemia virus, and clone 124 mouse sarcoma virus were 7, 9 and 6 kilobases (kb), respectively. The in vitro system used was capable of synthesizing double-stranded DNA, but the plus strands (same polarity as the viral RNA) were only 0.5 to 1.5 kb long. Lone Moloney murine leukemia virus cDNA transcripts were used as templates to synthesize the second plus strand. Essentially two strategies were employed as follows. (i) The 3' ends of the cDNA transcripts were extended by addition of 50 to 100 dAMP residues by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. The (dA)n-tailed cDNA transcripts were used as templates along with an oligomer of dT as primer and Escherichia coli DNA polymerase to synthesize the plus strands. (ii) DNase-digested calf thymus DNA was used to prime the synthesis of plus strands on long cDNA with E. coli DNA polymerase I. In both cases, the synthesis of the plus strands was monitored by increased resistance of the cDNA templates to single-strand-specific S1 nuclease. The double-stranded DNA was fractionated on neutral sucrose gradients. Analysis of the double-stranded DNA synthesized by using oligo(dT) primer showed the plus strands to be about 5 to 6 kb long, whereas the plus strands synthesized by using DNase-digested calf thymus DNA primers were only 0.3 to 0.5 kb long. Double-stranded DNA synthesized by either method has an average size of 6 x 10(6) daltons. Double-stranded DNA was also synthesized by using cDNA transcripts as templates without the addition of any primers. In this case, the plus strands were covalently linked to the template strand and were not representative of the whole parent strand.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D., Smoler D. Primer requirement and template specificity of the DNA polymerase of RNA tumor viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1507–1511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D., Atkinson M. R., Setlow P., Kornberg A. An active fragment of DNA polymerase produced by proteolytic cleavage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Dec 4;37(6):982–989. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Faras A. J. In vitro transcription of DNA from the 70S RNA of Rous sarcoma virus: identification and characterization of various size classes of DNA transcripts. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1220–1228. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1220-1228.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Canaani E. Complementarity between Rous sarcoma virus (RSV) RNA and the in vitro-synthesized DNA of the virus-associated DNA polymerase. Virology. 1970 Nov;42(3):783–788. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Vogt P. K. Gel electrophoresis of avian leukosis and sarcoma viral RNA in formamide: comparison with other viral and cellular RNA species. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):594–599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.594-599.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan H., Paskind M. Measurement of the sequence complexity of cloned Moloney murine leukemia virus 60 to 70S RNA: evidence for a haploid genome. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):421–429. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.421-429.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianni A. M., Smotkin D., Weinberg R. A. Murine leukemia virus: detection of unintegrated double-stranded DNA forms of the provirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):447–451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guntaka R. V., Mahy B. W., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Ethidium bromide inhibits appearance of closed circular viral DNA and integration of virus-specific DNA in duck cells infected by avian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1975 Feb 13;253(5492):507–511. doi: 10.1038/253507a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guntaka R. V., Richards O. C., Shank P. R., Kung H. J., Davidson N. Covalently closed circular DNA of avian sarcoma virus: purification from nuclei of infected quail tumor cells and measurement by electron microscopy and gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 15;106(2):337–357. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90090-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi K., Zinder N. D. Site-specific cleavage of single-stranded DNA by a Hemophilus restriction endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2555–2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenow H., Henningsen I. Selective elimination of the exonuclease activity of the deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from Escherichia coli B by limited proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jan;65(1):168–175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold G. M., Yamamoto K. R., Shank P. R., Varmus H. E. Mouse mammary tumor virus DNA in infected rat cells: characterization of unintegrated forms. Cell. 1977 Jan;10(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90135-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Yoshimura F. K., Weinberg R. A. Infectious, linear, unintegrated DNA of Moloney murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1976 Dec;20(3):621–626. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.3.621-626.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton W. D. A crude nuclease preparation suitable for use in DNA reassociation experiments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 29;240(4):522–531. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90709-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Illmensee R., Summers J. Efficeint transcription of RNA into DNA by avian sarcoma virus polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 6;442(3):324–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M., Baltimore D. RNA-directed DNA synthesis and RNA tumor viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1972;17:129–186. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60749-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronick S. R., Stephenson J. R., Verma I. M., Aaronson S. A. Thermolabile reverse transcriptase of a mammalian leukemia virus mutant temperature sensitive in its replication and sarcoma virus helper functions. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1476–1482. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1476-1482.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E., Guntaka R. V., Deng C. T., Bishop J. M. Synthesis, structure and function of avian sarcoma virus-specific DNA in permissive and nonpermissive cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):987–996. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E., Shank P. R. Unintegrated viral DNA is synthesized in the cytoplasm of avian sarcoma virus-transformed duck cells by viral DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):567–573. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.567-573.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., Baltimore D. Purification of the RNA-directed DNA polymerase from avian myeloblastosis virus and its assay with polynucleotide templates. Methods Enzymol. 1974;29:125–130. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)29015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., Mason W. S., Drost S. D., Baltimore D. DNA polymerase activity from two temperature-sensitive mutants of Rous sarcoma virus is thermolabile. Nature. 1974 Sep 6;251(5470):27–31. doi: 10.1038/251027a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., McKennett M. A. Genome organization of RNA tumor viruses II. Physical maps of in vitro-synthesized Moloney murine leukemia virus double-stranded DNA by restriction endonucleases. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):630–645. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.630-645.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M. Studies on reverse transcriptase of RNA tumor viruses. I. Localization of thermolabile DNA polymerase and RNase H activities on one polypeptide. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):121–126. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.121-126.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M. The reverse transcriptase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 21;473(1):1–38. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(77)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., Varmus H. E., Hunter E. Characterization of "early" temperature-sensitive mutants of avian sarcoma viruses: biological properties, thermolability of reverse transcriptase in vitro, and synthesis of viral DNA in infected cells. Virology. 1976 Oct 1;74(1):16–29. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]