Abstract
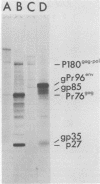
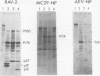
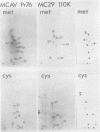
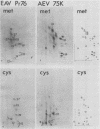
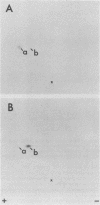
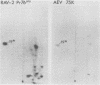
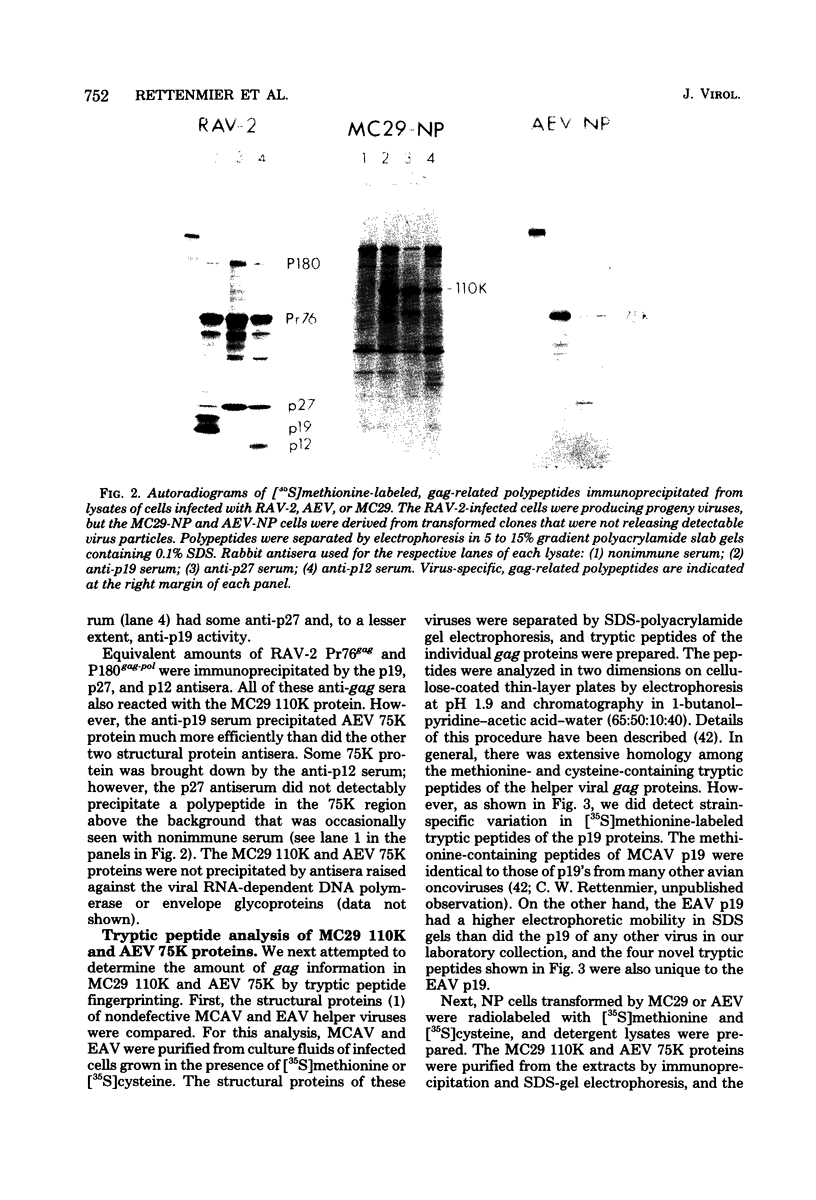
The content of viral structural (gag) protein sequences in polypeptides encoded by replication-defective avian erythroblastosis virus (AEV) and myelocytomatosis virus MC29 was assessed by immunological and peptide analyses. Direct comparison with gag proteins of the associated helper viruses revealed that MC29 110K polypeptide contained p19, p12, and p27, whereas the AEV 75K polypeptide had sequences related only to p19 and p12. Both of these polypeptides contained some information that was unrelated to gag, pol, or env gene products. In addition, no homology was detected between these unique peptides of MC29 110K and AEV 75K. The AEV 75K polypeptide shared strain-specific tryptic peptides with the p19 encoded by its naturally occurring helper virus; this observation suggests that gag-related sequences in 75K were originally derived from the helper viral gag gene. Digestion of oxidized MC29 110K and AEV 75K proteins with the Staphylococcus aureus V8 protease generated a fragment which comigrated with N-acetylmethionylsulfoneglutamic acid, a blocked dipeptide which is the putative amino-terminal sequence of structural protein p19 and gag precursor Pr76gag. This last finding is evidence that the gag sequences are located at the N-terminal end of the MC29 110K and AEV 75K polypeptides.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- August J. T., Bolognesi D. P., Fleissner E., Gilden R. V., Nowinski R. C. A proposed nomenclature for the virion proteins of oncogenic RNA viruses. Virology. 1974 Aug;60(2):595–600. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90356-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Tumor viruses: 1974. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):1187–1200. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:35–88. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.000343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Hayman M. J., Vogt P. K. Defectiveness of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29: isolation of long-term nonproducer cultures and analysis of virus-specific polypeptide synthesis. Virology. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):431–448. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Vogt P. K. Genetic analysis of the defectiveness in strain MC29 avian leukosis virus. Virology. 1978 Jul 15;88(2):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90278-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Stedman J. D. Efficient fluorography of 3H and 14C on thin layers. Anal Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):247–256. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90747-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchhagen D. L., Hanafusa H. Intracellular precursors to the major glycoprotein of avian oncoviruses in chicken embryo fibroblasts. J Virol. 1978 Mar;25(3):845–851. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.3.845-851.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson R. L. Protein kinase activity associated with the avian sarcoma virus src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2021–2024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Vogt P. K. Avian acute leukemia viruses MC29 and MH2 share specific RNA sequences: evidence for a second class of transforming genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1633–1637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman R. N., Vogt V. M. The biosynthesis of oncovirus proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 6;473(3-4):187–239. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman R., Shaikh R., Mason W. S. Identification of an avian oncovirus polyprotein in uninfected chick cells. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):89–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90304-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Gautsch J. W., Jensen F. C., Lerner R. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Biochemical evidence that MCF murine leukemia viruses are envelope (env) gene recombinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4676–4680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England J. M., Dietzschold B., Halpern M. S. Antibody-independent detection of virus-specific glycoprotein synthesis is oncornavirus-infected cells. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):820–824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.820-824.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. E., Fischinger P. J. Nucleotide sequences in mouse DNA and RNA specific for Moloney sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3705–3709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., Ade N., Beug H. Temperature-sensitive mutant of avian erythroblastosis virus suggests a block of differentiation as mechanism of leukaemogenesis. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):496–501. doi: 10.1038/275496a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., Beug H. Avian leukemia viruses: interaction with their target cells in vivo and in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 17;516(3):269–299. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa H., Halpern C. C., Buchhagen D. L., Kawai S. Recovery of avian sarcoma virus from tumors induced by transformation-defective mutants. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1735–1747. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa H., Hanafusa T., Kawai S. Genetic control of expression of endogenous virus genes in chicken cells. Virology. 1974 Apr;58(2):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90078-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa H. Rapid transformation of cells by Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):318–325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi R. Carboxypeptidase Y in sequence determination of peptides. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:84–93. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. J., Royer-Pokora B., Graf T. Defectiveness of avian erythroblastosis virus: synthesis of a 75K gag-related protein. Virology. 1979 Jan 15;92(1):31–45. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90212-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. J. Viral polyproteins in chick embryo fibroblasts infected with avian sarcoma leukosis viruses. Virology. 1978 Mar;85(1):241–252. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90428-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houmard J., Drapeau G. R. Staphylococcal protease: a proteolytic enzyme specific for glutamoyl bonds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3506–3509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. S., Lai M. M., Vogt P. K. Genome of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29: analysis by heteroduplex mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1265–1268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. S., Vogt P. K. Avian oncovirus MH2 is defective in Gag, Pol, and Env. Virology. 1979 Jan 30;92(2):278–284. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90132-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. S., Deobagkar D. N., Stephenson J. R. Isolation and characterization of a feline sarcoma virus-coded precursor polyprotein. Competition immunoassay for nonstructural components. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8894–8901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemenz R., Diggelmann H. Extracellular cleavage of the glycoprotein precursor of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):285–292. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.285-292.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Pawson A., Bister K., Martin G. S., Duesberg P. H. Specific RNA sequences and gene products of MC29 avian acute leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5874–5878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moelling K., Hayami M. Analysis of precursors to the envelope glycoproteins of avian RNA tumor viruses in chicken and quail cells. J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):598–607. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.598-607.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oskarsson M. K., Elder J. H., Gautsch J. W., Lerner R. A., Vande Woude G. F. Chemical determination of the m1 Moloney sarcoma virus pP60gag gene order: evidence for unique peptides in the carboxy terminus of the polyprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4694–4698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Gagnon J., Vogt V. M., Ripley S., Eisenman R. N. The NH2-terminal sequence of the avian oncovirus gag precursor polyprotein (Pr76gag). Virology. 1978 Dec;91(2):423–433. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90388-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porzig K. J., Barbacid M., Aaronson S. A. Biological properties and translational products of three independent isolates of feline sarcoma virus. Virology. 1979 Jan 15;92(1):91–107. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchio A. F., Erikson E., Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Identification of a polypeptide encoded by the avian sarcoma virus src gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1567–1571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R., Todaro C. Generation of new mouse sarcoma viruses in cell culture. Science. 1978 Sep 1;201(4358):821–824. doi: 10.1126/science.210501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed S., Gardner M. B., Huebner R. J. In vitro isolation of stable rat sarcoma viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2972–2976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettenmier C. W., Hanafusa H. Structural protein markers in the avian oncoviruses. J Virol. 1977 Dec;24(3):850–864. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.3.850-864.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettenmier C. W., Karess R. E., Anderson S. M., Hanafusa H. Tryptic peptide analysis of avian oncovirus gag and pol gene products. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):102–113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.102-113.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds F. H., Jr, Sacks T. L., Deobagkar D. N., Stephenson J. R. Cells nonproductively transformed by Abelson murine leukemia virus express a high molecular weight polyprotein containing structural and nonstructural components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3974–3978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer-Pokora B., Beug H., Claviez M., Winkhardt H. J., Friis R. R., Graf T. Transformation parameters in chicken fibroblasts transformed by AEV and MC29 avian leukemia viruses. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):751–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks T. L., Reynolds F. H., Jr, Deobagkar D. N., Stephenson J. R. Murine leukemia virus (T-8)-transformed cells: identification of a precursor polyprotein containing gag gene-coded proteins (p15 and p12) and a nonstructural component. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):809–814. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.809-814.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Rands E., Williams D., Parks W. P. Studies on the nucleic acid sequences of Kirsten sarcoma virus: a model for formation of a mammalian RNA-containing sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):458–463. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.458-463.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh R., Linial M., Brown S., Sen A., Eisenman R. Recombinant avian oncoviruses. II. Alterations in the gag proteins and evidence for intragenic recombination. Virology. 1979 Jan 30;92(2):463–481. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiness D., Fanshier L., Bishop J. M. Identification of nucleotide sequences which may encode the oncogenic capacity of avian retrovirus MC29. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):600–610. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.600-610.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Williams D. R., Weeks M. O., Maryak J. M., Vass W. C., Scolnick E. M. Comparison of the genomic organization of Kirsten and Harvey sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):45–55. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.45-55.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stéhelin D., Graf T. Avian myelocytomatosis and erythroblastosis viruses lack the transforming gene src of avian sarcoma viruses. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):745–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronick S. R., Cabradilla C. D., Aaronson S. A., Haseltine W. A. 5'-terminal nucleotide sequences of mammalian type C helper viruses are conserved in the genomes of replication-defective mammalian transforming viruses. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):570–576. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.570-576.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler D. H., Boyars J. K., Parks W. P., Scolnick E. M. Friend strain of spleen focus-forming virus: a recombinant between mouse type C ecotropic viral sequences and sequences related to xenotropic virus. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):361–372. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.361-372.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler D. H., Yuan E., Linemeyer D., Ruscetti S., Scolnick E. M. Helper-independent mink cell focus-inducing strains of Friend murine type-C virus: potential relationship to the origin of replication-defective spleen focus-forming virus. J Exp Med. 1978 Sep 1;148(3):639–653. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.3.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Coffin J. M. Recombination between the defective component of an acute leukemia virus and Rous associated virus O, an endogenous virus of chickens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):3001–3005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.3001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P. K., Hu S. S. The genetic structure of RNA tumor viruses. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:203–238. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.001223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M., Eisenman R., Diggelmann H. Generation of avian myeloblastosis virus structural proteins by proteolytic cleavage of a precursor polypeptide. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 15;96(3):471–493. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Halpern C. C., Nadel M., Hanafusa H. Recombination between viral and cellular sequences generates transforming sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5812–5816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte O. N., Rosenberg N., Paskind M., Shields A., Baltimore D. Identification of an Abelson murine leukemia virus-encoded protein present in transformed fibroblast and lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2488–2492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]