Abstract
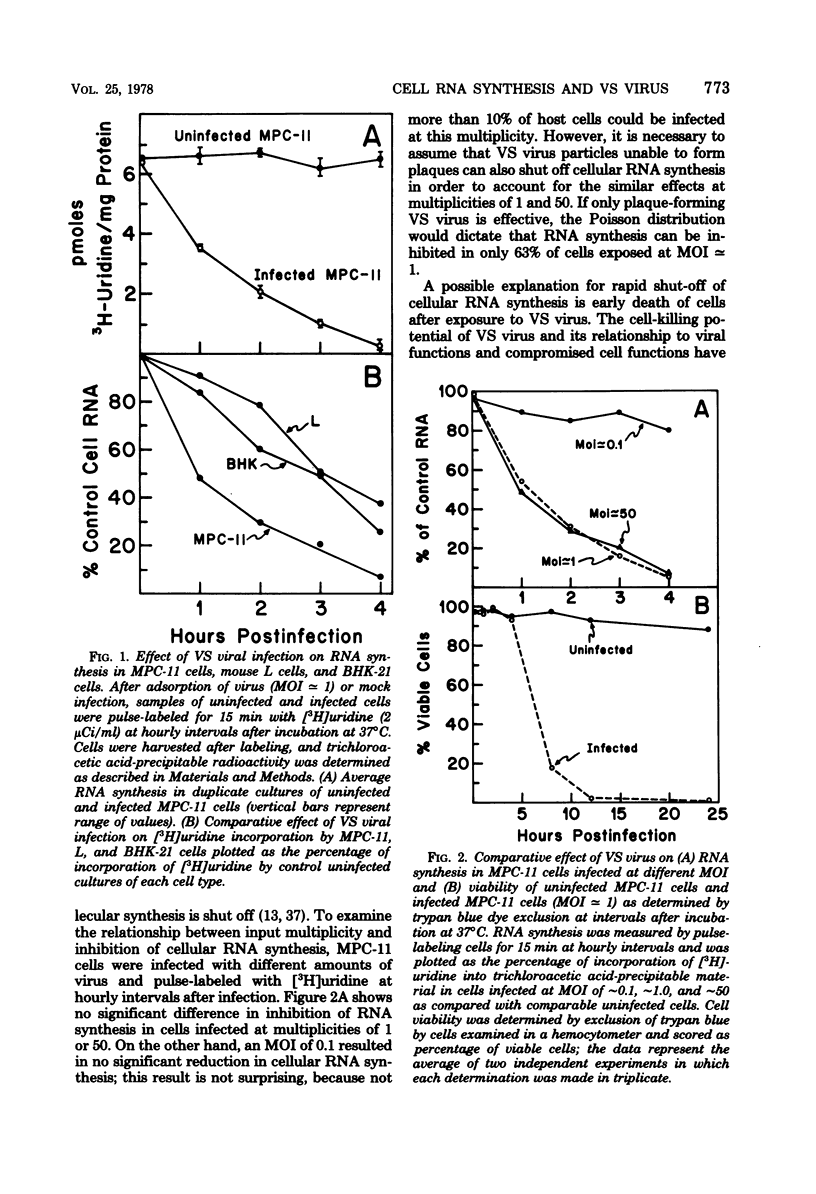
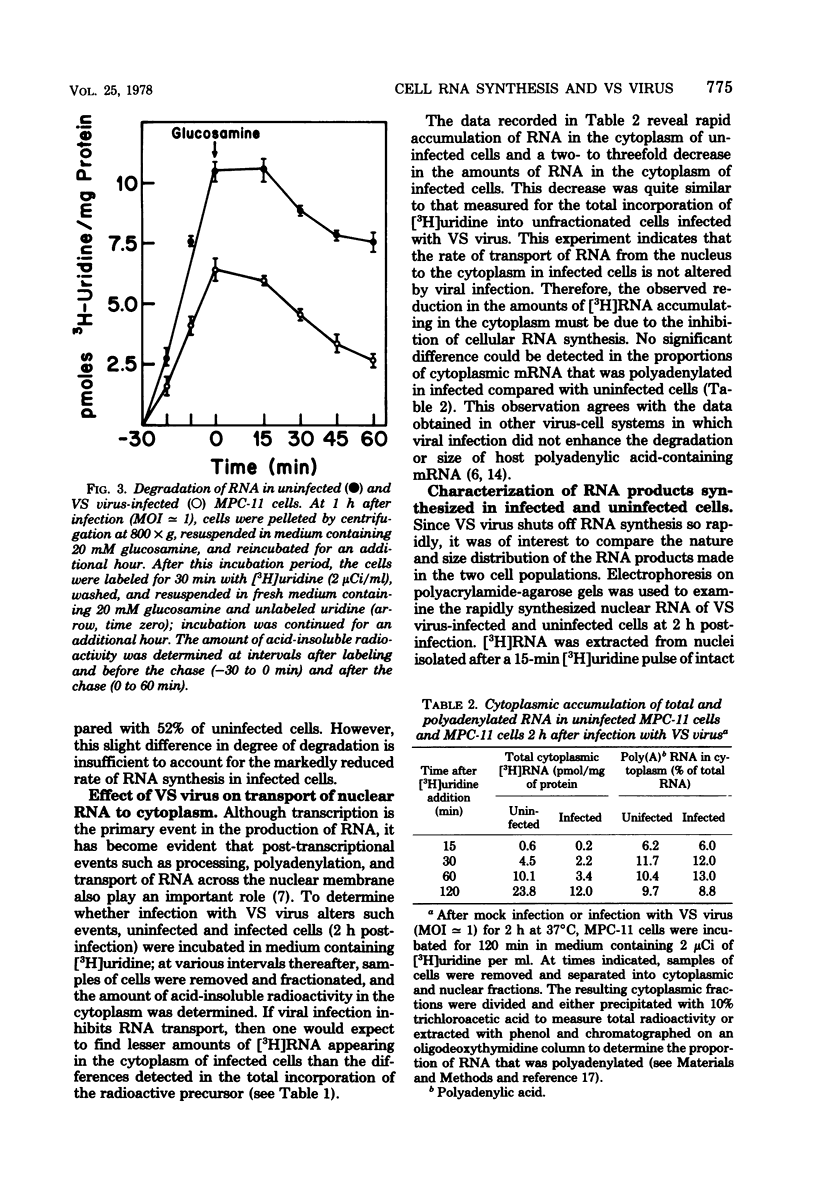
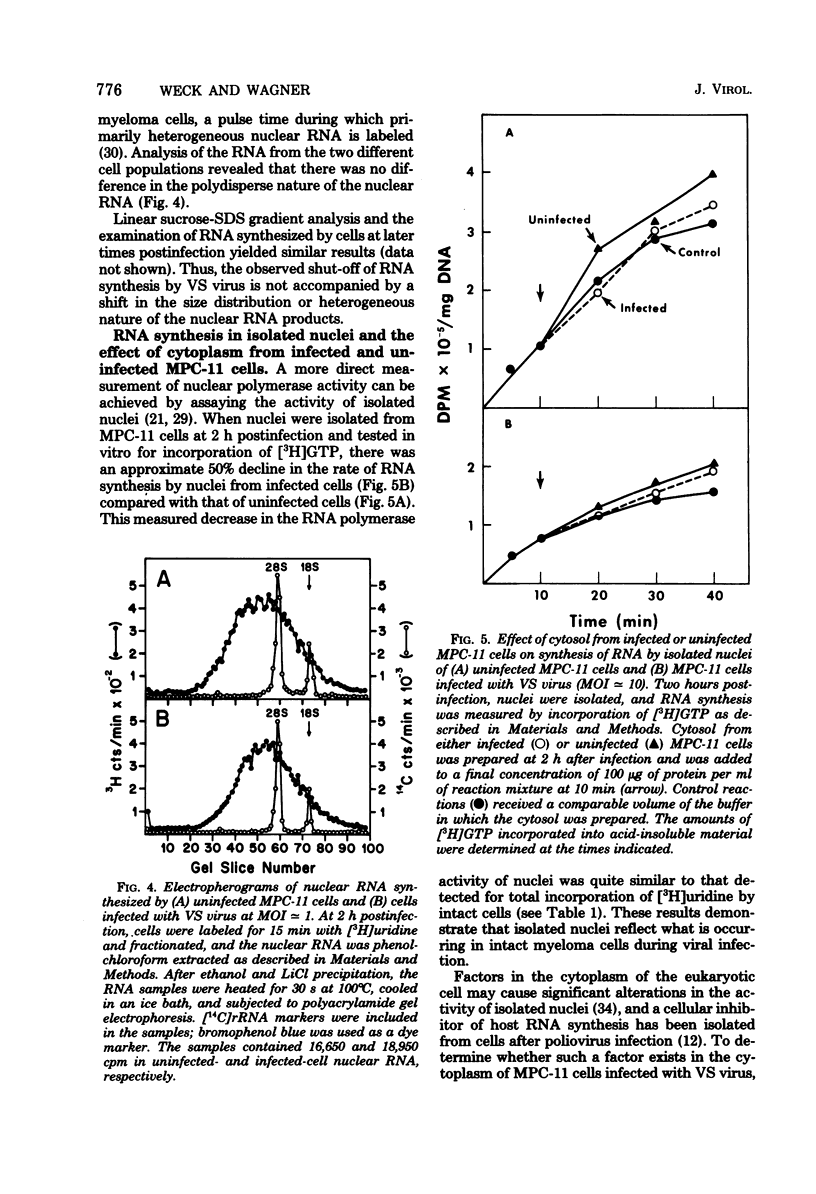
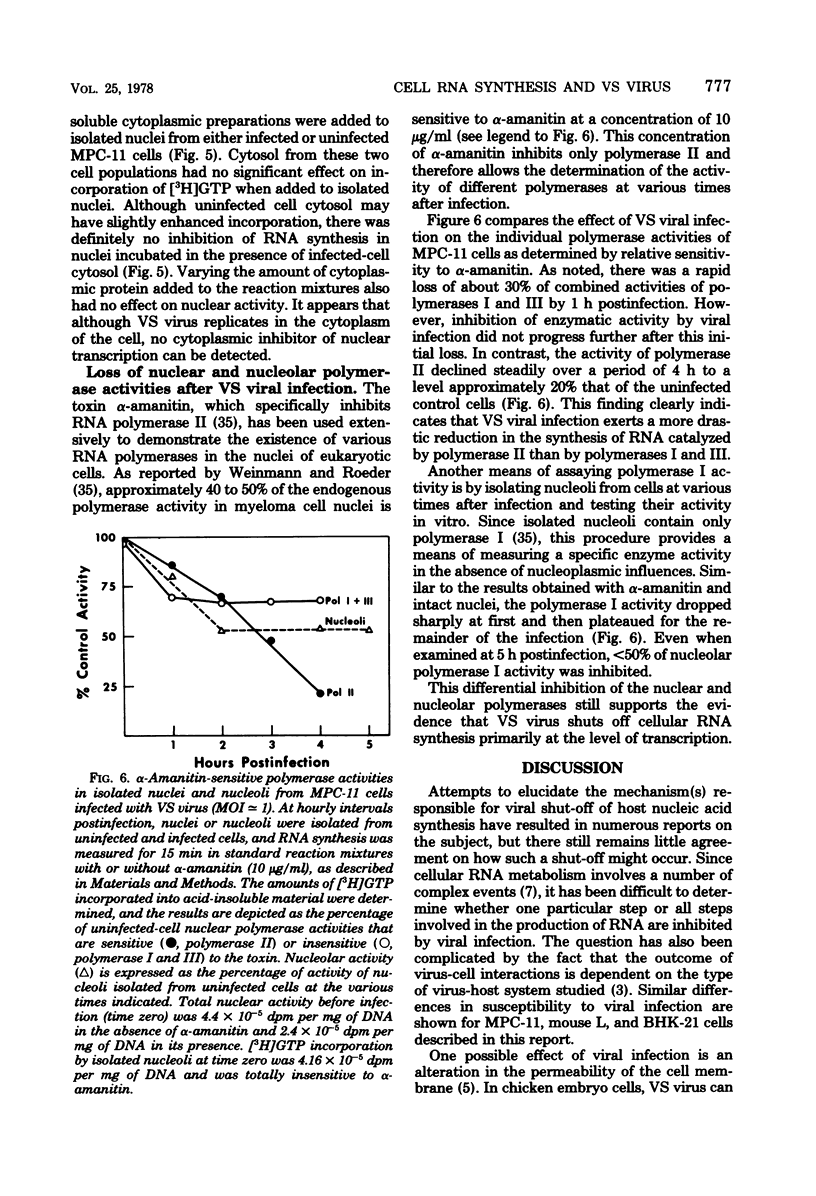
Infection of mouse myeloma cells (MPC-11) with vesicular stomatitis (VS) virus resulted in rapid and marked reduction in cellular RNA synthesis considerably before cell viability was compromised. Mouse myeloma cells responded maximally to viral infection at a multiplicity of 1 and were considerably more se;sitive to shut-off of RNA synthesis than were mouse L cells or BHK-21 cells. This inhibition of cellular RNA synthesis was shown not to be caused by differential membrane permeability of infected and uninfected MPC-11 cells to [3H]uridine, nor was it due to greater degradation of previously synthesized RNA. VS viral infection appeared not to impede transport of newly synthesized nuclear RNA to the cytoplasm; moreover, infected cells accumulated polyadenylated mRNA at the same rate as did uninfected cells. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of newly synthesized nuclear RNA demonstrated that the polydisperse nature and size distribution were not affected by VS viral infection. Isolated nuclei of infected MPC-11 cells also inhibited greatly impaired capacity to synthesize RNA despite the absence of cytoplasmic factors. Infected-cell cytosol did not inhibit transcription by uninfected-cell nuclei, nor did uninfected-cell cytosol reverse viral inhibition of nuclear transcription. Studies with alpha-amanitin revealed that VS viral infection inhibited the activity of polymerases I, II, and III, but only polymerase II was affected progressively throughout infection and to a much greater extent. These data suggest that, even at low multiplicities of infection, VS virus rapidly shuts off cellular RNA synthesis at the level of nuclear transcription.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apriletti J. W., Penhoet E. E. Recovery of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase activities from L cells after mengovirus infection. Virology. 1974 Oct;61(2):597–601. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90294-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Girard M. An intermediate in the synthesis of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):741–748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxt B., Bablanian R. Mechansims of vesicular stomatitis virus-induced cytopathic effects. II. Inhibition of macromolecular synthesis induced by infectious and defective-interfering particles. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90167-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L. The inhibition of cell functions after viral infection. A proposed general mechanism. FEBS Lett. 1977 Apr 1;76(1):11–15. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80110-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby D. S., Finnerty V., Lucas-Lenard J. Fate of mRNA of L-cells infected with mengovirus. J Virol. 1974 Apr;13(4):858–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.4.858-869.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell F. E. mRNA structure and function. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1976;19:493–511. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60941-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Munoz R., Darnell J. E. Structural difference between the 5' termini of viral and cellular mRNA in poliovirus-infected cells: possible basis for the inhibition of host protein synthesis. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):719–726. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.719-726.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follett E. A., Pringle C. R., Wunner W. H., Skehel J. J. Virus replication in enucleate cells: vesicular stomatitis virus and influenza virus. J Virol. 1974 Feb;13(2):394–399. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.2.394-399.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRARD M., PENMAN S., DARNELL J. E. THE EFFECT OF ACTINOMYCIN ON RIBOSOME FORMATION IN HELA CELLS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Feb;51:205–211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.2.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genty N. Analysis of uridine incorporation in chicken embryo cells infected by vesicular stomatitis virus and its temperature-sensitive mutants: uridine transport. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):8–15. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.8-15.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho P. P., Washington A. L. Evidence for a cellular ribonucleic acid synthesis inhibitor from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Biochemistry. 1971 Sep 28;10(20):3646–3651. doi: 10.1021/bi00796a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Wagner R. R. Inhibition of cellular RNA synthesis by nonreplicating vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1579–1584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koschel K. Poliovirus infection and poly(A) sequences of cytoplasmic cellular RNA. J Virol. 1974 May;13(5):1061–1066. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.5.1061-1066.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake R. S., Ludwig E. H. Cellular changes attending mengovirus-induced cytolysis of mouse L-cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 19;244(2):466–477. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90251-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Sekellick M. J. Cell killing by viruses. I. Comparison of cell-killing, plaque-forming, and defective-interfering particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):321–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90172-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Sekellick M. J. Cell killing by viruses. II. Cell killing by vesicular stomatitis virus: a requirement for virion-derived transcription. Virology. 1975 Jan;63(1):176–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90383-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F., Jr, Murphy E. C., Jr, Huang R. C. Transcription of ribonucleic acid in isolated mouse myeloma nuclei. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3440–3446. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F., Jr, Murphy E. C., Jr, Huang R. C. Transcription of the genes for 5S ribosomal RNA and transfer RNA in isolated mouse myeloma cell nuclei. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 27;13(18):3689–3696. doi: 10.1021/bi00715a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister P. E., Wagner R. R. Differential inhibition of host protein synthesis in L cells infected with RNA - temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):550–558. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.550-558.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. I., Penhoet E. E. Differential inhibition of nuclear RNA polymerases in L cells infected with mengovirus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Jun;140(2):435–438. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuss D. L., Koch G. Translation of individual host mRNA's in MPC-11 cells is differentially suppressed after infection by vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):572–578. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.572-578.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S. RNA metabolism in the HeLa cell nucleus. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Roeder R. G. Ribosomal RNA synthesis in isolated nuclei. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):433–441. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90461-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Lawrence C., Thach R. E., Roeder R. G. Encephalomyocarditis virus infection of mouse plasmacytoma cells. II. Effect on host RNA synthesis and RNA polymerases. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):611–619. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.611-619.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Sklar V. E., Jaehning J. A., Weinmann R., Roeder R. G. Isolation and partial characterization of the multiple forms of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase in the mouse myeloma, MOPC 315. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5889–5897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeiro R., Vaughan M. H., Warner J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr The turnover of nuclear DNA-like RNA in HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1968 Oct;39(1):112–118. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.1.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER R. R., LEVEY A. H., SNYDER R. M., RATCLIFF G. A., Jr, HYATT D. F. BIOLOGIC PROPERTIES OF TWO PLAQUE VARIANTS OF VESICULAR STOMATITIS VIRUS (INDIANA SEROTYPE). J Immunol. 1963 Jul;91:112–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Huang A. S. Inhibition of RNA and interferon synthesis in Krebs-2 cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1966 Jan;28(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90300-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weck P. K., Johnson T. C. Nuclear-cytosol interactions that modulate RNA synthesis and transcript size of mouse brain nuclei. J Neurochem. 1976 Dec;27(6):1367–1374. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb02617.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann R., Roeder R. G. Role of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase 3 in the transcription of the tRNA and 5S RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1790–1794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W. Method of examining viral RNA metabolism in cells in culture: metabolism of vesicular stomatitis virus RNA. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1340–1344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1340-1344.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W., Youngner J. S. Interferon production and inhibition of host synthesis in cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1970 Oct;6(4):476–484. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.4.476-484.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki S., Wagner R. R. Action of interferon: kinetics and differential effects on viral functions. J Virol. 1970 Oct;6(4):421–429. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.4.421-429.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaoi Y., Mitsui H., Amano M. Effect of U.v.-irradiated vesicular stomatitis virus on nucleic acid synthesis in chick embryo cells. J Gen Virol. 1970 Sep;8(3):165–172. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-8-3-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



