Abstract
The RAD6 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (E2) that is required for DNA repair, damage-induced mutagenesis, and sporulation. We have cloned the two human RAD6 homologs, designated HHR6A and HHR6B. The two 152-amino acid human proteins share 95% sequence identity with each other and approximately 70% and approximately 85% overall identity with the homologs from yeasts (S. cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe) and Drosophila melanogaster, respectively. Neither of the human RAD6 homologs possess the acidic C-terminal sequence present in the S. cerevisiae RAD6 protein. Genetic complementation experiments reveal that HHR6A as well as HHR6B can carry out the DNA repair and mutagenesis functions of RAD6 in S. cerevisiae rad6 delta mutants.
Full text
PDF



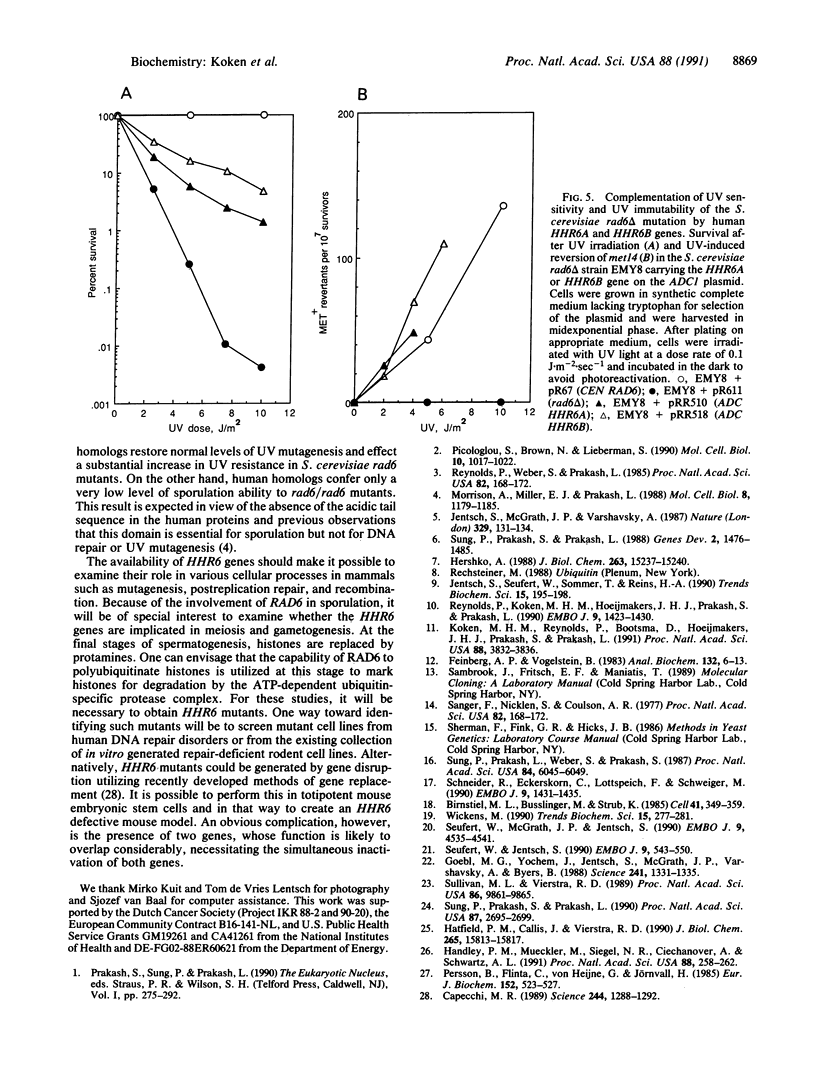
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R. Altering the genome by homologous recombination. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1288–1292. doi: 10.1126/science.2660260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebl M. G., Yochem J., Jentsch S., McGrath J. P., Varshavsky A., Byers B. The yeast cell cycle gene CDC34 encodes a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1331–1335. doi: 10.1126/science.2842867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley P. M., Mueckler M., Siegel N. R., Ciechanover A., Schwartz A. L. Molecular cloning, sequence, and tissue distribution of the human ubiquitin-activating enzyme E1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):258–262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield P. M., Callis J., Vierstra R. D. Cloning of ubiquitin activating enzyme from wheat and expression of a functional protein in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15813–15817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A. Ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15237–15240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch S., McGrath J. P., Varshavsky A. The yeast DNA repair gene RAD6 encodes a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Nature. 1987 Sep 10;329(6135):131–134. doi: 10.1038/329131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch S., Seufert W., Sommer T., Reins H. A. Ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes: novel regulators of eukaryotic cells. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 May;15(5):195–198. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90161-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koken M., Reynolds P., Bootsma D., Hoeijmakers J., Prakash S., Prakash L. Dhr6, a Drosophila homolog of the yeast DNA-repair gene RAD6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3832–3836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A., Miller E. J., Prakash L. Domain structure and functional analysis of the carboxyl-terminal polyacidic sequence of the RAD6 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1179–1185. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson B., Flinta C., von Heijne G., Jörnvall H. Structures of N-terminally acetylated proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Nov 4;152(3):523–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09227.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picologlou S., Brown N., Liebman S. W. Mutations in RAD6, a yeast gene encoding a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, stimulate retrotransposition. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1017–1022. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P., Koken M. H., Hoeijmakers J. H., Prakash S., Prakash L. The rhp6+ gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe: a structural and functional homolog of the RAD6 gene from the distantly related yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1423–1430. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08258.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P., Weber S., Prakash L. RAD6 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a protein containing a tract of 13 consecutive aspartates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):168–172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R., Eckerskorn C., Lottspeich F., Schweiger M. The human ubiquitin carrier protein E2(Mr = 17,000) is homologous to the yeast DNA repair gene RAD6. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1431–1435. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08259.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seufert W., Jentsch S. Ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes UBC4 and UBC5 mediate selective degradation of short-lived and abnormal proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):543–550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08141.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seufert W., McGrath J. P., Jentsch S. UBC1 encodes a novel member of an essential subfamily of yeast ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes involved in protein degradation. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4535–4541. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07905.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan M. L., Vierstra R. D. A ubiquitin carrier protein from wheat germ is structurally and functionally similar to the yeast DNA repair enzyme encoded by RAD6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9861–9865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung P., Prakash L., Weber S., Prakash S. The RAD3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a DNA-dependent ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6045–6049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung P., Prakash S., Prakash L. Mutation of cysteine-88 in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD6 protein abolishes its ubiquitin-conjugating activity and its various biological functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2695–2699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung P., Prakash S., Prakash L. The RAD6 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae polyubiquitinates histones, and its acidic domain mediates this activity. Genes Dev. 1988 Nov;2(11):1476–1485. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.11.1476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M. How the messenger got its tail: addition of poly(A) in the nucleus. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jul;15(7):277–281. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90054-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]