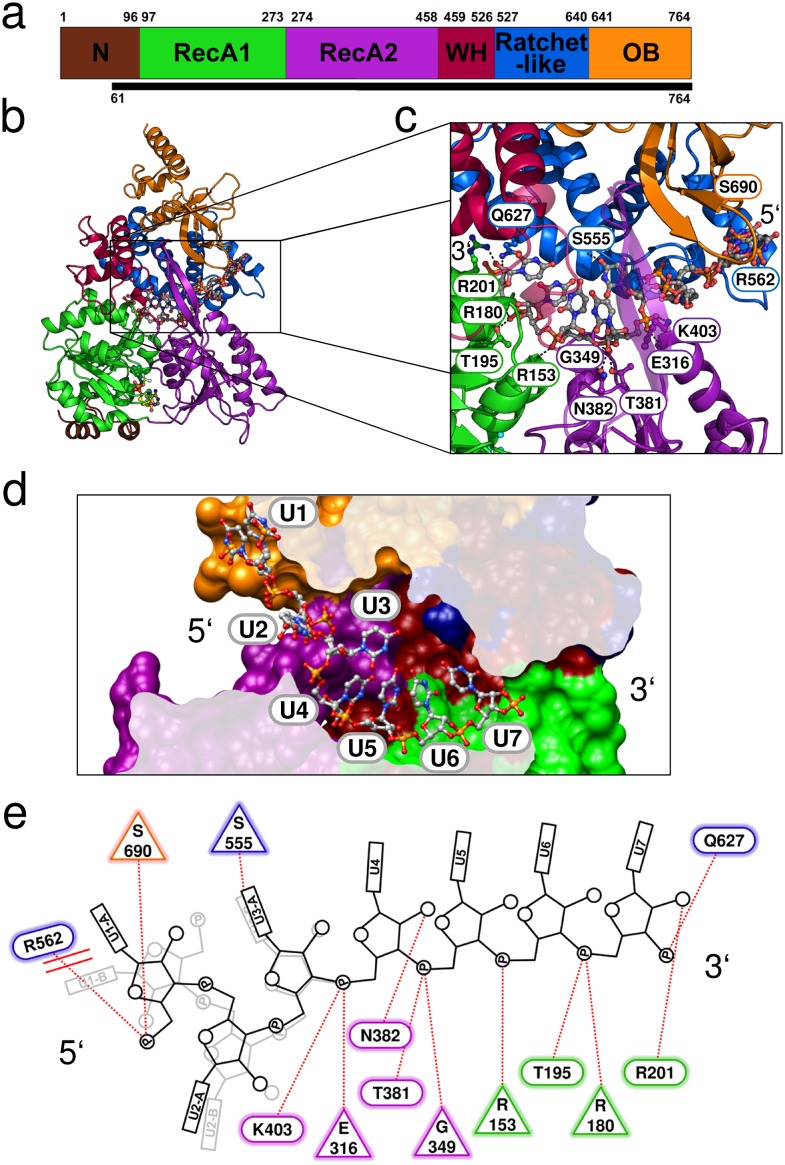
Figure 1. Crystal structure of Prp43 in complex with U7-RNA and the ATP-analog ADP•BeF3-.
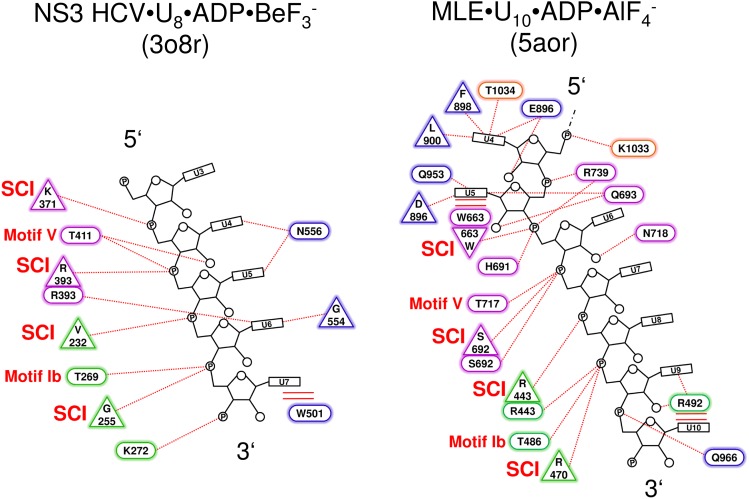
(a) Domain overview of ctPrp43. The bottom bar indicates the N-terminally truncated construct (ΔN, 61–764) used for crystallization. (b) Overall structure of ctPrp43ΔN•U7•ADP•BeF3-. Domains are colored according to a and the bound U7-RNA is shown in gray with two alternative conformations for nucleotides U1-U3. The ADP•BeF3- is bound in the cleft between the RecA domains. (c) Close-up of the bound U7-RNA. Residues involved in interactions are labeled according to the wild-type ctPrp43 sequence. The 5’ and 3’ end of the RNA is indicated. (d) Cross-section of the Prp43 RNA-binding tunnel. Prp43 is shown in surface representation and the RNA in ball-and-sticks mode. (e) Schematic figure of the Prp43-RNA interactions. Residues which interact with the RNA via their main chain are shown as triangles and residues which exhibit side chain interactions are presented as ellipses. The coloring of the residues corresponds to a. The alternative conformation of the first three nucleotides is shown light gray. Stacking interactions are highlighted by double lines and polar interactions by dotted lines.
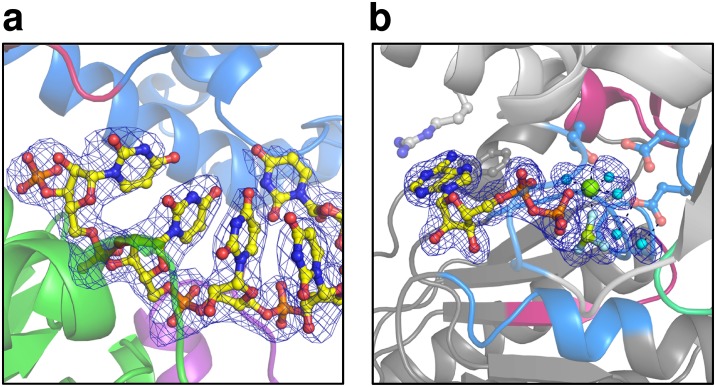
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Omit maps of a fraction of the U7-RNA from the ctPrp43ΔN•U7•ADP•BeF3- complex structure and of the active site of ctPrp43ΔN•ADP•BeF3-(HR) (Figure 2a).
Figure 1—figure supplement 2. The two alternative conformations of the U7-RNA in the ctPrp43ΔN•U7•ADP•BeF3- complex structure.
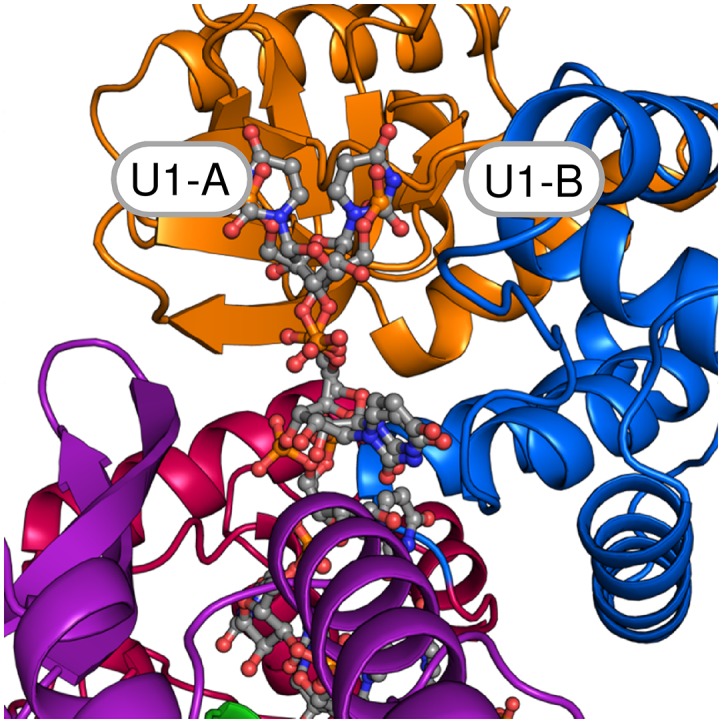
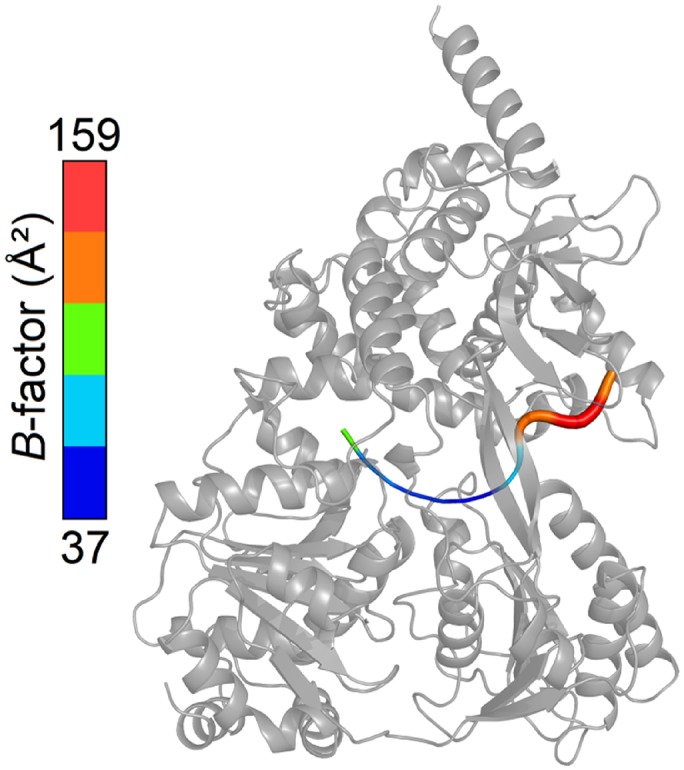
Figure 1—figure supplement 3. Overview of the B-factors of the U7-RNA in the ctPrp43ΔN•U7•ADP•BeF3- complex structure.