Abstract
Background
The aim of the present study was to analyse the effect of climate change on phytochemicals, total phenolic content (TPC) and antioxidant potential of methanolic extracts of Aloe vera collected from different climatic zones of the India.
Methods
Crude methanolic extracts of A. vera from the different states of India were screened for presence of various phytochemicals, total phenolic content and in vitro antioxidant activity. Total phenolic content was tested by Folin–Ciocalteau reagent based assay whilst DPPH free radical scavenging assay, metal chelating assay, hydrogen peroxide scavenging assay, reducing power assay and β carotene-linoleic assay were used to assess the antioxidant potential of A. vera methanolic leaf extracts.
Results
Alkaloids, phenols, flavonoids, saponins, and terpenes were the main phytochemicals presents in all accessions. A significant positive correlation was found between TPC and antioxidant activity of different accessions. Extracts of highland and semi-arid zones possessed maximum antioxidant potential. Accessions from tropical zones showed the least antioxidant activity in all assays.
Conclusions
It could be concluded that different agro-climatic conditions have effects on the phytochemicals, total phenolic content (TPC) and antioxidant potential of the A. vera plant. The results reveal that A. vera can be a potential source of novel natural antioxidant compounds.
Keywords: Antioxidant, Aloe vera, Agro-climatic zones, Phytochemicals, Methanol, Total phenolic content (TPC)
Background
Climate change is causing noticeable effects on the life cycle, distribution and phyto-chemical composition of the world’s vegetation, including medicinal and aromatic plants. The changing temperatures and wind patterns associated with climate change are affecting precipitation and thereby plant architecture, flowering, fruiting, phyto-chemical composition and in situ competition with other species. India’s climate is largely controlled by an annual monsoon, appears to be experiencing increasingly severe and erratic precipitation. Therefore, there is a need to understand the effect of higher temperature, various precipitation levels and different soil moisture and fertility, by growing them under such climates and determine how variation in temperature, moisture and edaphic factors might affect the plants’ phenology, nutrient, antioxidant and secondary metabolites levels.
Antioxidative action is one of the prime physiological functions that protect living organisms from oxidative damage caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS). Reactive oxygen species is a term used to describe a number of reactive molecules and free radicals derived from molecular oxygen. During daily activities and with advanced age, oxidative substances and free radicals accumulate in cells affecting various organs and systems in our body. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species are free radicals that are common outcome of normal aerobic cellular metabolic processes [1, 2]. Unbarred generation of these free radicals leads to attack on various biomolecules, cellular machinery, cell membrane, lipids, proteins, enzymes and DNA causing oxidative stress and ultimately cell death [3]. Overproduction of free radicals can lead to many chronic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis, cancer, diabetes, post-ischemic perfusion injury, cardiovascular diseases, myocardial infarction, chronic inflammation, stroke and septic shock, aging and other degenerative diseases in humans [4, 5]. Human body has an intrinsic system of various enzymes and nutrients to protect from these free radicals. Some extrinsic nutrients are required by many people who are subjected to higher production of free radicals due to stress or physical activities. Micronutrients like vitamin E, β carotene, and vitamin C are the major antioxidants which could be provided in the daily diet as our body cannot produce these nutrients [6]. Protection against free radicals can also be enhanced by taking sufficient amounts of exogenous antioxidants [7].
Antioxidants are used to counterbalance the effect of free radicals. An antioxidant is a stable molecule which donates an electron to a charged free radical and terminates the chain reaction before vital molecules are damaged. Free radical scavenging property of antioxidants delays or inhibits cellular damage [8]. Antioxidants are in great demand as they help in reducing ageing signs. Previously many plants have been screened for their antioxidant potential. Thus, there is growing interest in replacing synthetic antioxidants because of the concern over the possible carcinogenic effects of these in foods with natural ingredients [9]. Primary sources of naturally occurring antioxidants for humans are fruits, vegetables and spices. Medicinal plants contain a wide variety of free radical scavenging molecules such as phenolic compounds (phenolic acids, flavonoids, catechins, proanthocyanidins, quinones, coumarins, tannins etc.), nitrogen compounds (alkaloids, amines, betalains etc.), vitamins, terpenoids, carotenoids and other secondary metabolites which are reported to have antioxidant activity [10–13]. Efforts have been made to search for novel natural antioxidants from tea, fruits, vegetables, herbs, and spices. Herbs are on focus of whole world as a source of novel antioxidants compounds due to their safety as compared to synthetic antioxidants.
Aloe vera (syn.: Aloe barbadensis Miller) belongs to the Xanthorrhoeaceae family and is a perennial succulent plant [14]. Out of more than 400 species, only a few species of Aloe have been considered for commercial importance. A. vera being the most potent and, thereby, the most popular plant in the research as well as marketing field [15]. A. vera is a rich source of over 200 naturally occurring nutrients which are water soluble and fat soluble vitamins, minerals, enzymes, polysaccharides, phenolic compounds and organic acids [16]. Its secondary metabolites have multiple properties such as anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antioxidant, immune boosting, anticancer, anti-ageing, sunburn relief and antidiabetic potentials [17–19]. Several traditional uses also have been reported such as for burn injury, eczema, cosmetics, inflammation, fever etc. [20]. This present study focuses on comparative phytochemical analysis, total phenolic content and antioxidant potential of methanolic extracts of A. vera from 6 different agro-climatic zones of India. India is a home to an extraordinary variety of climatic regions, ranging from tropical in the south to temperate and alpine in the Himalayan north, where elevated regions receive sustained winter snowfall. These vast climatic variations may cause a difference in the phytoconstituents of the plant species. This study is the first attempt to evaluate antioxidant potential of different A. vera accessions from different agro-climatic zones of India.
Methods
Collection of plant material
Samples were collected from 12 different sites covering 6 agro-climatic zones of India. Each zone had 2 sites (Fig. 1). Collection sites geographical locations along with their average temperature and rainfall are depicted in Table 1. Samples were collected in the months of Jan–Feb 2013. Healthy leaves of A. vera were collected from individual plants at each location. The plant material was identified and authenticated by comparing the herbarium specimen (MDU-6803) available in Department of Genetics, M. D. University, Rohtak (India). Samples were placed in sterile plastic bags and were brought to the laboratory in an ice box for analyses.
Fig. 1.
Showing different collection sites from 6 agro-climatic zones of India
Table 1.
Showing plant collection sites along with their average temperature and rainfall
| Agro-climatic zones | Accessions | Place of collection | Latitude | Longitude | Average temp. (°C). | Average rainfall (mm). |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Highland | Jammu and Kashmir (J&K) | Jammu | 32°72′N | 74°85′E | 7–20 | 1011 |
| Himachal Pradesh (H.P.) | Palampur | 32°11′N | 76°53′E | 10–17 | 1251 | |
| Semi-arid | Punjab | Sangrur | 30°24′N | 75°84′E | 15–35 | 649 |
| Haryana | Rohtak | 28°89′N | 76°60′E | 20–34 | 617 | |
| Arid | Rajasthan | Jaisalmer | 25°55′N | 70°57′E | 22–35 | 209.5 |
| Gujarat | Gandhinagar | 23°21′N | 72°63′E | 22–33 | 1107 | |
| Humid Subtropical | Uttar Pradesh (U.P.) | Pratapgarh | 25°89′N | 81°94′E | 19–32 | 904 |
| Madhya Pradesh (MP) | Bhopal | 23°25′N | 77°41′E | 19–32 | 1146 | |
| Tropical wet and dry | West Bengal (W.B.) | Kolkata | 22°34′N | 88°24′E | 22–32 | 1582 |
| Telangana | Hyderabad | 17°20′N | 78°30′E | 23–30 | 812.5 | |
| Tropical wet | Kerala | Kochi | 09°93′N | 76°26′E | 24–32 | 3005 |
| Goa | Vasco | 15°24′N | 73°50′E | 23–32 | 3055 |
Chemicals
Chemicals and reagents used are Gallic acid, Folin- Ciocalteu reagent, 2,2 diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), Trichloroacetic acid (TCA), Hydrogen peroxide, Methanol, FeCl3, FeCl2, Phosphate buffer, Ferrozine, Potassium ferricyanide, β carotene, linoleic acid, Tween 80, Chloroform of Sigma-Aldrich (USA) and Himedia Laboratories Pvt. Ltd. India. All solvents used were of analytical grade.
Preparation of extracts
The leaves of the selected plants were collected and washed under running tap water to remove dust and dirt. The washed leaves were cut into small pieces and air dried for few days. Dried leaves were crushed into coarse powder with wiley mill and stored in polythene bags for further use. The methanolic extracts were prepared by cold percolation method. The solution and residue were separated by a centrifuge at a rolling speed of 4000 rpm. A reddish brown colloid containing Aloe extract was obtained. Chloroform and sulphuric acid were used to remove the chloroform extractive [21]. After the chloroform evaporation, a yellowish-brown colloid was obtained as crude extract. Stock solution was prepared by dissolving in methanol.
Phytochemical screening of A. vera extracts
Phytochemical constituents of A. vera can be classified into nine categories: anthraquinones, inorganic compounds, essential and non essential amino acids, fatty acids, alkaloids, carbohydrates, enzymes, vitamins, and other miscellaneous compounds [22]. A. vera methanolic extracts were subjected to phytochemical screening for the presence or absence of various phytochemicals. Phytochemicals were tested in methanolic extracts according to standard protocols [23, 24].
Determination of total phenolic content
The total phenolic content of the obtained extracts was spectrometrically analyzed by Folin–Ciocalteu method [25]. Gallic acid was used as standard for TPC estimation [26]. Final volume of 5 ml was made by adding 500 µl of Folin–Ciocalteau reagent, 1.5 ml of 20% Na2CO3 and 2 ml of distilled water to 1 ml (1 mg/ml) of each extract. The mixture was incubated at room temperature for 30–40 min and the absorbance of the developed colour was recorded at 765 nm using UV–Vis spectrophotometer. Calibration curve was constituted using various concentrations of gallic acid ranging from 20 to 100 µg/ml. Total phenolic value was obtained from the regression equation: y = 0.056x + 1.454 with R2 = 0.9967 and expressed as mg/g gallic acid equivalent using the formula, C = cV/M; where C = total content of phenolic compounds in mg/g GAE, c = the concentration of gallic acid established from the calibration curve, V = volume of extract and M = the weight of the extract.
Antioxidant assays
DPPH free radical scavenging assay, hydrogen peroxide scavenging assay, reducing power assay, metal chelating assay and β carotene-linoleic assay were used to assess the antioxidant potential of Aloe vera methanolic leaf extracts. Each experiment was done in triplicates and mean values were interpreted to conclude the results.
DPPH [(1, 1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl)] free radical scavenging activity
Antioxidant activity of A. vera extracts were measured in terms of hydrogen donating radical scavenging ability using the stable DPPH method of Zhu et al. [27]. The reaction was monitored as a color change from purple to pale yellow. A quantity of 1 ml (1 mg/ml) of Aloe vera extract was added to 2 ml of 0.5 mM DPPH solution in methanol and the reaction mixture was kept in the dark for 45 min. Absorbance was recorded at 517 nm against blank using a UV–Vis spectrophotometer. Ascorbic acid was used as a standard. The radical scavenging activity on DPPH was expressed as,
where A0 is the absorbance of control and A1 is the absorbance of sample extract or standard.
Hydrogen peroxide scavenging (H2O2) assay
The ability of extracts to scavenge hydrogen peroxide was estimated by following the method of Ruch et al. [28]. The extract was dissolved in a phosphate buffer at a concentration of 1 mg/ml. A quantity of 1 ml of extract was added to 3.4 ml of phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 7.4) followed by 600 µl of 400 mM H2O2. The solution was kept at room temperature for 40 min and absorption was measured at 230 nm. Ascorbic acid was used as control.
The percentage of hydrogen peroxide scavenging was calculated as follows:
where Ai was the absorbance of control and At was the absorbance of test samples.
Reducing power assay
The reductive potential of the extract was determined according to the method of Oyaizu [29]. Extracts and standard ascorbic acid (1 mg/ml) were mixed with 2.5 ml of phosphate buffer (0.2 M, pH 6.6) and 2.5 ml potassium ferricyanide (1% w/v). A quantity of 2.5 ml of chloroacetic acid (10% w/v) was added and the solution was centrifuged for 10 min at 3000 rpm. The upper layer solution of 2.5 ml was separated and mixed with 2.5 ml of distilled water and 0.5 ml of FeCl3 (0.1% w/v). Absorbance was measured at 700 nm. The increase in absorbance of the reaction mixture indicated reducing power of different A. vera accessions.
Metal chelating activity
The ability of the extract to chelate iron (II) was estimated based on the method of Dinis et al. with minimal modifications [30]. A quantity of 2 ml of extract at a concentration of 1 mg/ml was added with 0.25 ml of 250 mM FeCl2. The reaction was initiated by the addition of 0.25 ml of ferrozine. The mixture was shaken vigorously and left at room temperature for 10 min. Absorbance of the solution was measured spectrophotometrically at 562 nm. Methanol was used as blank and a control without extract was also included. The percentage of inhibition of Ferrozine-Fe2+ complex formation was calculated from:
where A0 is the absorbance of control and A1 is the absorbance of sample extract or standard.
Antioxidant activity in linoleic acid model system
The antioxidant activity of the extract was assayed based on the β carotene bleaching method developed by Velioglu et al. [12]. An amount of 1 mg β carotene was dissolved in 1 ml of chloroform, and was added with 40 mg of linoleic acid and 400 mg of Tween 80. Chloroform was evaporated with the help of rotary evaporator. Semisolid residue, left after chloroform evaporation was added with 100 ml distilled water with vigorous shaking. A quantity of 0.2 ml of the extract (1 mg/ml) was then added to 5 ml of the prepared solution. Absorbance was measured at zero time and after 60 min incubation at 50 °C. Solution without β carotene was used as blank. In β carotene-linoleic acid assay, the antioxidant capacity was determined by measuring the inhibition of the volatile organic compounds and the conjugated diene hydroperoxides arising from linoleic acid oxidation [31].
where A0 and A′0 are the absorbance at 0 min of the incubation for test sample and control, respectively, and At and A′t are the absorbance after incubation for 60 min for test sample and control, respectively.
Statistical analysis
All experiments were performed in triplicates. All values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) of three separate experiments using the computer programme Excel. Linear correlation between total phenolic content and different antioxidant assays were calculated to establish a relationship between phenol content and its antioxidant potential from different extracts. Correlation was calculated with the help of MS excel programme and SPSS 16.0 version.
Results
Phytochemical screening
A wide range of various phytochemicals; alkaloids, glycosides, reducing sugars, phenolic compounds, steroids and terpenoids, flavonoids, tannins and saponin glycosides were tested with their appropriate protocols and reagents. The A. vera methanolic extracts showed presence of most of the phytochemicals tested; though amounts varied in the different accessions. The comparative presence of phytochemicals in the different crude extracts is depicted in Table 2.
Table 2.
Qualitative analyses of the phytochemical components of Aloe vera extracts
| Phytochemical analysis | Collection sites | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical constituents | Test reagent | Observation | 1. | 2. | 3. | 4. | 5. | 6. | 7. | 8. | 9. | 10. | 11. | 12. |
| Alkaloids | Mayer’s reagent | White ppt | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ |
| Glycosides | 10% Lead acetate solution |
White ppt | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Reducing sugar | Benedict’s solution | Reddish brown ppt | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ |
| Phenolic compounds | Ferric chloride solution | Green colour | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Steroids and terpenoids | Acetic anhydride and conc: H2SO4 | Pink colour | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | + | + | + | ++ | + | +++ | ++ |
| Flavonoids | Benzene FeCl3 | Yellow ppt | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Tannins | FeCl3 and 10% lead acetate | White ppt | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | + |
| Saponin glycosides | Distilled water | Frothing take place | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
+++ high, ++ medium, + low
Determination of total phenolics
The phenolic compounds are oxidized to phenolates by the reagent at alkaline pH in a saturated solution of sodium carbonate resulting in a blue complex. All accessions showed the presence of total phenols in crude extracts. Table 3 enlists the different TPC values obtained for all 12 accessions. The values ranged from 32.9 to 65.7 mg GAE per g of dry weight. Maximum values of TPC were obtained for Punjab, Jammu and Himachal accessions. Kerala, Telangana and West Bengal showed low TPC values as compared with other accessions.
Table 3.
Total phenolic contents of Aloe vera extracts
| Accession name | Total phenolic content (mg of GAE/g of extract) |
|---|---|
| Jammu | 63.2 ± 0.15 |
| Himachal Pradesh | 62.3 ± 0.26 |
| Haryana | 58.4 ± 0.35 |
| Panjab | 65.7 ± 0.30 |
| Rajasthan | 56.9 ± 0.23 |
| Gujarat | 54.6 ± 0.41 |
| Uttar Pradesh | 55.1 ± 0.15 |
| Madhya Pradesh | 52.5 ± 0.28 |
| West Bangal | 46.4 ± 0.76 |
| Telangana | 38.9 ± 0.35 |
| Goa | 53.4 ± 0.24 |
| Kerala | 32.9 ± 0.19 |
Antioxidant activity
The 12 crude extracts of A. vera were investigated for their antioxidant potential by using different methods and all assays showed the antioxidative potential of the extracts. All extracts showed significant antioxidant activity ranging from 56 to 80% with different climatic conditions showing significant differences on the antioxidant potential of the plant species.
DPPH free radical scavenging activity
The reduction capability of DPPH radical was determined by the decrease in absorbance at 517 nm induced by the antioxidants. The highest antioxidant capacity observed was 80%. Punjab, Himachal Pradesh and Haryana showed a high antioxidant capacities ranging from 75.54 to 80.2%. Telangana, Gujarat and West Bengal showed least antioxidant capacity ranging from 56.75 to 62.66%. Figure 2a shows the percentages of free radical scavenging activity of different aloe accessions. Ascorbic acid showed 96% radical scavenging activity.
Fig. 2.
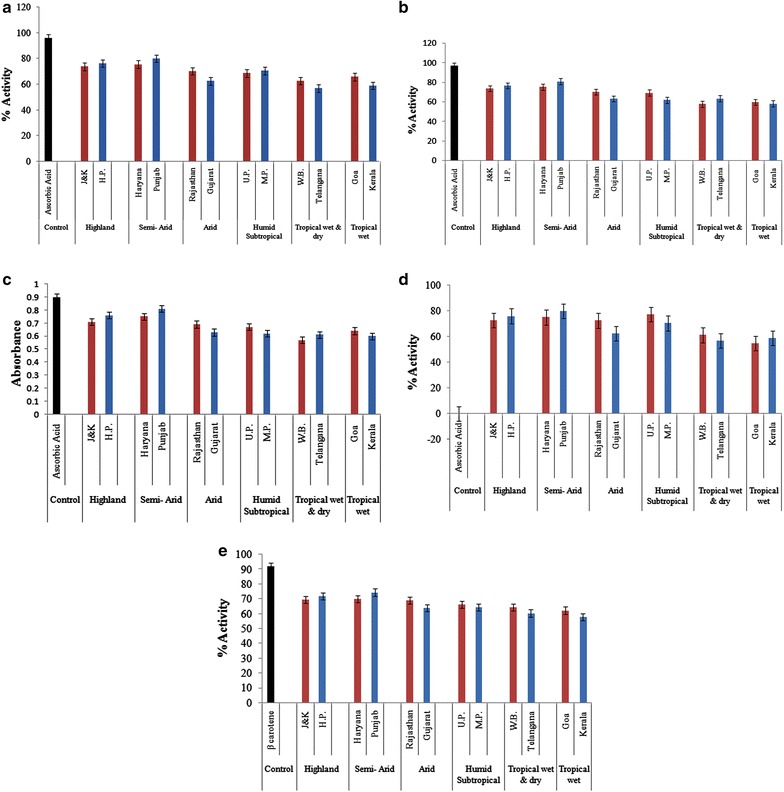
Antioxidant activity of Aloe vera accessions with control by using different assays. a Showing DPPH free radical scavenging activity of Aloe vera and ascorbic acid. b Showing hydrogen peroxide scavenging activity of Aloe vera and ascorbic acid. c Showing reducing power activity of Aloe vera and ascorbic acid. d Showing metal chelating activity of Aloe vera and ascorbic acid. e Showing reductive potential of Aloe vera leaf extracts assayed by β carotene-lenoleic acid assay
Hydrogen peroxide scavenging (H2O2) assay
Reduction potential of methanolic extracts of A. vera in H2O2 assay ranged from 58.54 to 81.10%. Reducing activity of ascorbic acid was 97%. Punjab, Telangana and Himachal Pradesh accessions showed maximum activity. These were followed by Haryana, Rajasthan and West Bengal accessions (Fig. 2b).
Reducing power assay
The data observed on the reducing power of the extracts contribute significantly towards the antioxidant effects. Punjab, Himachal Pradesh and Haryana had high absorbance values that indicate their greater reductive potential and electron donor ability for stabilizing free radicals. Other accessions also showed almost similar observations to H2O2 assay. Figure 2c represents activity of all extracts and ascorbic acid with respect to their absorbance values.
Metal chelating activity
In the presence of other chelating agents, the complex formation was disrupted with the result that the red colour of the complex was decreased. Ferrous ions are also commonly found in food systems and considered as prooxidants. Ferrozine form complexes with the ferrous ion, generating a violet color [32]. Punjab, Himachal Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh accessions showed high metal chelating activity. Kerala, Telangana and Goa showed least activity. Control ascorbic acid showed no activity. Activity of all extracts with respect to their absorbance values are represented in Fig. 2d.
Antioxidant activity in linoleic acid model system
Total antioxidant activities of the methanolic extracts of A. vera were determined using β carotene- linoleic acid model system. Figure 2e shows the reductive potential of A. vera leaf extracts assayed by β carotene-lenoleic acid assay. All extracts showed reductive potential. Antioxidant potential ranged from 59.60 to 74.4%. Maximum activity was observed for Punjab, Jammu, Haryana and Himachal Pradesh accessions and minimum activity was for Goa, Telangana and Kerala.
Correlation analysis
Satisfactory correlations have been reported reported between the parameters of antioxidant activity and the content of total phenols in different in vitro models, with different extracts of plant. Figure 3a–e illustrates the linear correlation between total phenols contents and antioxidant activity of different extracts. R2 values were 0.8025, 0.6407, 0.6534, 0.5209, 0.7729 for DPPH free radical scavenging assay, Hydrogen peroxide scavenging assay, Reducing power assay, metal chelating assay and β carotene-linoleic assay respectively. The matrices of linear correlation between total phenolic content and different antioxidant assays were analyzed (Table 4). They also showed good correlation with respect to each others.
Fig. 3.
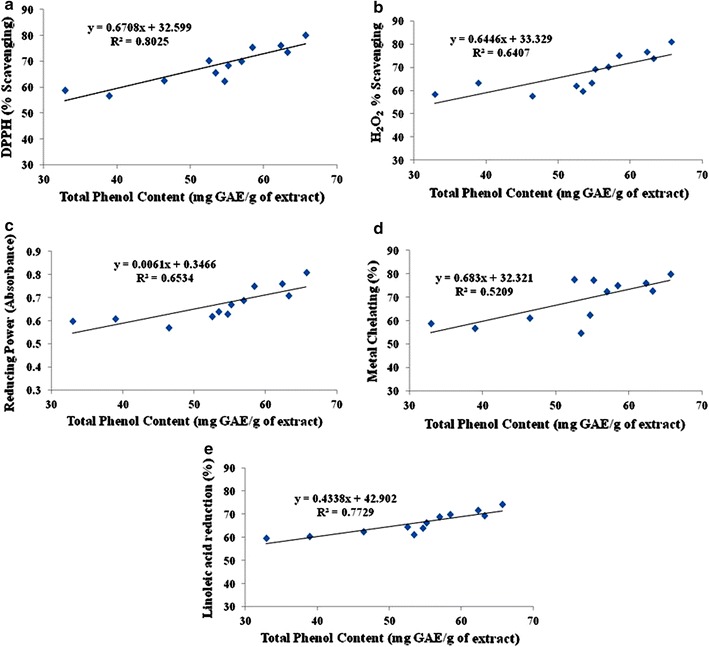
Linear correlation between total phenolic content and different antioxidant assays. a Showing linear correlation between total phenolic content and DPPH free radical scavenging activity. b Showing linear correlation between total phenolic content and hydrogen peroxide scavenging activity. c Showing linear correlation between total phenolic content and reducing power activity. d Showing linear correlation between total phenolic content and metal chelating activity. e Showing linear correlation between total phenolic content and β carotene linoleic acid assay
Table 4.
Linear correlation between total phenolic content and different antioxidant assays by using Pearson-correlations method
| Phenol | DPPH | H2O2 | Reducing power | Metal chelating | Linoleic reduction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenol | 1.000 | |||||
| DPPH | 0.895a | 1.000 | ||||
| H2O2 | 0.800a | 0.868a | 1.000 | |||
| Reducing power | 0.808a | 0.900a | 0.970a | 1.000 | ||
| Metal chelating | 0.721a | 0.853a | 0.772a | 0.719a | 1.000 | |
| Linoleic reduction | 0.879a | 0.938a | 0.952a | 0.935a | 0.846a | 1.000 |
aCorrelation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed)
Discussion
There are numbers of secondary metabolites found in plants which contribute significant biological activities [33]. Plant materials contain numerous types of antioxidants with varied activities [34, 35].
Aloe vera is a perennial succulent xerophyte originated in South Africa, although it is native to dry subtropical and tropical regions [36]. The plant species is are drought resistant and able to tolerate a wide range of climatic situations. Hot humid conditions along with high rainfall are the most suitable [37].
Phytochemical analysis of plants is commercially important being great interest of pharmaceutical industries for the production of new drugs to cure various diseases [38]. Our study showed the presence of various medicinally important phytoconstituents from the different A. vera accessions in good amount, and hence rationalizes the use of this plant species as an herbal remedy. Extracts having high phenolic content also showed good antioxidant activity. Linear correlation analyzed between the total phenolic content and the different antioxidant assays by using Pearson-correlations method showed the significant correlation at 0.01 levels (2-tailed). Previous studies also have concluded that there was a significant linear correlation between total phenolic content and antioxidant potential [39, 40].
Our study emphasizes the antioxidant potential of Aloe vera methanolic leaf extracts. Previous studies on A. vera stated that the plant contains substantial amounts of antioxidants including α-tocopherol (vitamin E), carotenoids, ascorbic acid (vitamin C), flavonoids, and tannins [41]. Glutathione peroxidase activity, superoxide dismutase enzymes and a phenolic antioxidant were found to be present in A. vera gel, which may be responsible for these antioxidant effects [42]. Methanolic extract induced the best extraction yield and more complex composition of phenolics [43]. The methanol extracts of A. vera were also screened previously for their in vitro antioxidant activity, and extracts exhibited good antioxidant activity [44]. Potent antioxidative compounds like Aloe barbendol, Aloe emodin, barbaloin A and Aloe chrysone have been isolated from methanolic extracts of A. vera. [45]. Biological activities of A. vera may be due to the synergistic action of these compounds, rather than from a single defined component [46].
Five different methods were employed for determining antioxidant potential of Aloe vera leaf extracts. DPPH radical scavenging method is an extensive procedure to evaluate the free radical scavenging ability of various samples [47]. The effect of antioxidants on DPPH radical scavenging was supposed to be due to their hydrogen- donating ability. Hydrogen peroxide is generally not very reactive, but it can sometimes be toxic to cell because it can give rise to hydroxyl radicals in the cells. Thus, the removal of H2O2 is essential for antioxidant defence in cell or food systems. In general, the reducing properties are associated with the presence of reductones, which have been shown to exert antioxidant action through breaking the free radical chain by donating a hydrogen atom [48, 49]. In the reducing power assay, the presence of reductants in the sample would result in the reduction of Fe3+ to Fe2+ by donating an electron [50]. Metal chelating activity is based on chelation of Fe2+ ions in a quantitative manner by the reagent ferrozine, which results to the formation of a complex with Fe2+ ions [51]. So the chelating ability influences other scavenging activities of free radicals which protect the organisms against oxidative damage. Mechanism of β carotene bleaching is a free radical mediated phenomenon resulting from the formation of hydroperoxides from linoleic acid oxidation. The presence of antioxidant extracts can hinder the extent of β carotene bleaching by acting on the linoleate- free radical and other formations of free radicals in the system [52, 53].
India is characterized by strong temperature and rainfall variations along with other different environmental and climatic fluctuations in different seasons [54]. Phytochemical composition of plants is greatly influenced by different agro-climatic conditions. According to previous findings it was suggested that environmental temperature plays a significant role on antioxidant activity evaluation and it is more pronounced in cold weather [55]. Therefore, we collected the plant material in the winter season (Jan–Feb 2013). In the present study we also found that the extracts of highland and semi-arid zones possess maximum antioxidant potential. Accessions from Tropical zones showed least antioxidant activity in all assays. A. vera can grow in almost all types of environmental conditions but there are several factors that can affect the quality and quantity of a particular constituent. Previous studies state that phytochemical composition of plants is influenced by a variety of environmental factors including the geography, climate, soil type, sun exposure, grazing stress, seasonal changes etc. [56–58].
Aloe vera is a cold sensitive plant. During stress more phytochemicals are produced in plants to withstand the adverse conditions. Studies conducted on plants in stress conditions showed higher production of flavonoids, anthocyanins and mucilaginous substances [59]. Our previous finding on antimicrobial activity and quantification of aloe- emodin on the same A. vera extracts also supports the present statement [60].
Report by Sanders [61], describing that an increase in unsaturated fatty acids is generally associated with cooler climates leading to production of antioxidants for a self- defense system against environmental stress, supports our present findings to suggest pronounced effects of environmental temperature on the different A. vera extracts. Lower temperature leads to higher production of phenolics and vice versa [62]. Plants from hilly areas are thought to be more important from nutritional and dietary points of view [63]. A. vera is found to grow in hot humid and high rainfall conditions, so semi- arid conditions having low rainfall are also not favorable for the plant. Although, soil texture and climatic conditions of semi-arid region is normally most suitable for majority of plant crops, Aloe genus however is an exception. In present study, accessions from colder regions showed the good antioxidant activity, supporting the statement that more phytochemicals are produced in plants under stress [64]. Consequently, phytochemical content can vary with growing environmental conditions. From the present work, it could be concluded that agro- climatic locations along with temperature and rainfall have significant effects on the A. vera plant phytoconstituents and its antioxidant potential. However, there is still a need to investigate the effects of soil properties and other related biotic and abiotic factors.
Conclusion
The present study showed that A. vera is a promising source of bioactive phenol which has a good antioxidant activity. The study demonstrated that the total phenolic content and antioxidant activity were higher in A. vera plants grown in Northern India in comparison to Southern India. Phytochemical analysis in relation to their activity from different climatic regions can help in selecting places for mass production of this plant species to enhance its pharmaceutical and marketing values. The present work tries to establish a correlation between phytochemicals, TPC and antioxidant activity of A. vera from different agro-climatic zones of India and have found that climatic zones showed significant effect on all these parameters. Our study emphasizes that north Indian climatic conditions are more suitable for the antioxidant potential of A. vera. Good antioxidant properties of the Aloe could be considered for applications in food, medicine and cosmetic industries.
Authors’ contributions
SK made major contribution to data collection, experimental work and drafted the manuscript. AY has made significant involvement in the interpretation of data and revising the manuscript. MY participated in the design of the study and performed the statistical analysis. JPY conceived of the study, and participated in its design and coordination and helped to draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
Financial Assistance from UGC, New Delhi in the form of UGC-SAP Grant (No. F.3-20/2012, SAP II) and UGC-BSR fellowship is gratefully acknowledged.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets supporting the results of this article are included in the article.
Consent to publish
All authors consent to publish the article.
Contributor Information
Sandeep Kumar, Email: skkundu785@gmail.com.
Amita Yadav, Email: amita.yadav86@gmail.com.
Manila Yadav, Email: manila.yadav@gmail.com.
Jaya Parkash Yadav, Email: yadav1964@rediffmail.com.
References
- 1.Uttara B, Singh AV, Zamboni P, Mahajan RT. Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: a review of upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2009;7:65–74. doi: 10.2174/157015909787602823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lobo V, Patil A, Phatak A, Chandra N. Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: impact on human health. Pharmacogn Rev. 2010;4(8):118–126. doi: 10.4103/0973-7847.70902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tiwari AK. Anti-oxidants: new generation therapeutic base for treatment of polygenic disorders. Curr Sci. 2004;86:1092–1102. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Freidovich I. Fundamental aspects of reactive oxygen species, or what’s the matter with oxygen? Ann NY Acad Sci. 1999;893:13–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb07814.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Fang YZ, Yang S, Wu G. Free radicals, antioxidants, and nutrition. Nutrition. 2002;18:872–879. doi: 10.1016/S0899-9007(02)00916-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ramassamy C. Emerging role of polyphenolic compounds in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases: a review of their intracellular targets. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006;545(1):51–64. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.06.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yadav M, Yadav A, Yadav JP. In vitro antioxidant activity and total phenolic content of endophytic fungi isolated from Eugenia jambolana Lam. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2014;7(1):256–261. doi: 10.1016/S1995-7645(14)60242-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Halliwell B. How to characterize an antioxidant: an update. Biochem Soc Symp. 1995;61:73–101. doi: 10.1042/bss0610073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Shahidi F, Zhong Y. Novel antioxidants in food quality preservation and health promotion. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol. 2010;112:930–940. doi: 10.1002/ejlt.201000044. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cai Y, Sun M, Corke H. Antioxidant activity of betalains from plants of the amaranthaceae. J Agric Food Chem. 2003;51(8):2288–2294. doi: 10.1021/jf030045u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cotelle N, Bernier JL, Catteau JP, Pommery J, Wallet JC, Gaydou EM. Antioxidant properties of hydroxyflavones. Free Rad Bio Med. 1996;20(1):35–43. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(95)02014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Velioglu YS, Mazza G, Gao L, Oomah BD. Antioxidant activity and total phenolics in selected fruits, vegetables, and grain products. J Agric Food Chem. 1998;46(10):4113–4117. doi: 10.1021/jf9801973. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zheng W, Wang SY. Antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds in selected herbs. J Agric Food Chem. 2001;49(11):5165–5170. doi: 10.1021/jf010697n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Eggli U. Illustrated handbook of succulent plants. Monocotyledons. Berlin: Springer; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Eshun K, Qian H. Aloe vera: a valuable ingredient for the food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic industriesda review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2004;44:91–96. doi: 10.1080/10408690490424694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Boudreau MD, Beland FA. An evaluation of the biological and toxicological properties of Aloe barba- densis (Miller), Aloe vera. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 2006;24(1):103–154. doi: 10.1080/10590500600614303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rishi P, Rampuria A, Tewari R, Koul A. Phyto-modulatory potentials of Aloe vera against Salmonella OmpR-mediated inflammation. Phytother Res. 2008;22(8):1075–1082. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wintola OA, Afolayan AJ. Phytochemical constituents and antioxidant activities of the whole leaf extract of Aloe ferox Mill. Pharmaco Mag. 2011;7(28):325–333. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.90414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Langmead L, Makins RJ, Rampton DS. Anti-inflammatory effects of Aloe vera gel in human colorectal mucosa in vitro. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004;19:521–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.01874.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jayaprakasha GK, Singh RP, Sakariah KK. Antioxidant activity of grape seed (Vitis vinifera) extracts on peroxidation models in vitro. Food Chem. 2001;73:285–290. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(00)00298-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tan ZJ, Li FF, Xu XL. Isolation and purification of Aloe anthraquinones based on an ionic liquid/salt aqueous two-phase system. Separ Sci Technol. 2011;98:150–157. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kumar S, Yadav JP. Ethnobotanical and pharmacological properties of Aloe vera: a review. J Med Plants Res. 2014;48(8):1387–1398. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Harborne JB. Phytochemical methods: a guide to modern techniques of plant analysis. 3. London: Chapman and Hall Limited; 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Karunyadevi S, Arun N, Surekha V. Screening of phytochemical compounds, antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of Aloe vera and Arkaa. Adv Biotec. 2009;9(6):38–43. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Dewanto V, Xianzhong W, Adom KK, Liu RH. Thermal processing enhances the nutritional value of tomatoes by increasing total antioxidant activity. J Agric Food Chem. 2002;50(10):3010–3014. doi: 10.1021/jf0115589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Halliwel B, Guttridge JM. Free radicals in biology and medicine. 2. London: Clarendon Press; 1989. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhu K, Zhou H, Qian H. Antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities of wheat germ protein hydrolysates (WGPH) prepared with alcalase. Process Biochem. 2006;41(6):1296–1302. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2005.12.029. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ruch RJ, Cheng SJ, Klaunig JE. Prevention of cytotoxicity and inhibition of intercellular communication by antioxidant catechins isolated from Chinese green tea. Carcinogenesis. 1989;10(6):1003–1008. doi: 10.1093/carcin/10.6.1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Oyaizu M. Studies on products of browning reaction: antioxidative activities of browning reaction prepared from glucosamine. Jpn J Nutr. 1986;44(6):307–315. doi: 10.5264/eiyogakuzashi.44.307. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Dinis TC, Madeira VM, Almeida LM. Action of phenolic derivatives (acetaminophen, salicylate, and 5- aminosalicylate) as inhibitors of membrane lipid peroxidation and as peroxyl radical scavengers. Arch Biochem Biophy. 1994;315(1):161–169. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1994.1485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yen GC, Chang YC, Su SW. Antioxidant activity and active compounds of rice koji fermented with Aspergillus candidus. Food Chem. 2003;83(1):49–54. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(03)00035-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Guo T, Wei L, Sun J, Hou CL, Fan L. Antioxidant activities of extract and fractions from Tuber indicum Cooke & Massee. Food Chem. 2011;127:1634–1640. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.02.030. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Xiong YQ. Aloe. Beijing: Agricultural Press; 2002. pp. 53–54. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Leong LP, Shui G. An investigation of antioxidant capacity of fruits in Singapore markets. Food Chem. 2002;76:69–75. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(01)00251-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Nagai T, Inove R, Inove H, Suzuki N. Preparation and antioxidant properties of water extract of propolis. Food Chem. 2003;80:29–33. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(02)00231-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Reynolds T, Dweck AC. Aloe vera gel leaf: a review update. J Ethnopharmacol. 1999;68(1–3):3–37. doi: 10.1016/S0378-8741(99)00085-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Manvitha K, Bidya B. Aloe vera: a wonder plant its history, cultivation and medicinal uses. J Pharmacogn Phytochem. 2014;2(5):85–88. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Radha MH, Laxmipriya NP. Evaluation of biological properties and clinical effectiveness of Aloe vera. JTCM. 2015;5:21–26. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2014.10.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wadood A, Ghufran M, Jamal SB, Naeem M, Khan A, Ghaffer R, et al. Phytochemical analysis of medicinal plants occurring in local area of Mardan. Biochem Anal Biochem. 2013;2:144. doi: 10.4172/2161-1009.1000144. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sultana B, Anwar F, Przybylski R. Antioxidant activity of phenolic components present in barks of Azadirachta indica, Terminalia arjuna, and Eugenia jambolana Lam. trees. Food Chem. 2007;104(3):1106–1114. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.01.019. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hamman JH. Composition and applications of Aloe vera leaf gel. Molecules. 2008;2008(13):1599–1616. doi: 10.3390/molecules13081599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Haritha K, Ramesh B, Saralakumari D. Effect of Aloe vera gel on antioxidant enzymes in streptozotocin-induced cataractogenesis in male and female Wistar rats. J Acute Med. 2014;4(1):38–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jacme.2014.01.005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Pop RM, Csernatoni F, Ranga F, Fetea F, Socaciu C. HPLC-UV Analysis coupled with chemometry to identify phenolic biomarkers from medicinal plants, used as ingredients in two food supplement formulas. Bull UASVM Food Sci Technol. 2013;70(2):99–107. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lopez A, de Tangil MS, Orellana OV, Ramirez AS, Rico M. Phenolic constituents, antioxidant and preliminary antimycoplasmic activities of leaf skin and flowers of Aloe vera (L.) Burm. f. (syn. A. barbadensis Mill.) from the Canary Islands (Spain) Molecules. 2013;18:4942–4954. doi: 10.3390/molecules18054942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Lee H, Guo Y, Ohta M, Xiong L, Stevenson B, Zhu JK. LOS2, a genetic locus acquired for cold responsive gene transcription encodes a bifunctional enolase. EMBO J. 2002;21:2692–2702. doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.11.2692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Dagne E, Bisrat D, Viljoen A, Van Wyk BE. Chemistry of Aloe species. Curr Org Chem. 2000;4:1055–1078. doi: 10.2174/1385272003375932. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Brand-Williams W, Cuvelier ME, Berset C. Use of free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT-Food Sci Technol. 1995;28(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/S0023-6438(95)80008-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Meir S, Kanner J, Akiri B, Hadas SP. Determination and involvement of aqueous reducing compounds in oxidative defense systems of various senescing leaves. J Agr Food Chem. 1995;43:1813–1819. doi: 10.1021/jf00055a012. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Schimada VL, Fujikawa K, Yahara K, Nakamura T. Antioxidative properties of xanthan on the autoxidation of soyabean oil in cyclodextrin emulsion. J Agr Food Chem. 1992;40:945–948. doi: 10.1021/jf00018a005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Saritha V, Anilakumar KR, Khanum F. Antioxidant and antibacterial activity of Aloe vera gel extracts. Inter J Pharma Biol Arch. 2010;1(4):376–384. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Yamaguchi F, Ariga T, Yoshimira Y, Nakazawa H. Antioxidant and anti-glycation of gcarcinol from Garcinia indica fruit rind. J Agri Food Chem. 2000;48:180–185. doi: 10.1021/jf990845y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kammoun M, Miladi S, Ben Ali Y, Damak M, Gargouri Y, Bezzine S. In vitro study of the PLA2 inhibition and antioxidants activities of Aloe vera leaf skin extracts. Lipids Health Dis. 2011;10:30. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Mammadov R, Ili P, Vaizogullar H. Antioxidant activity and total phenolic content of Gagea fibrosa and Romulea ramiflora. Iran J Chem Chem Eng. 2011;30(3):57–62. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Krishnarajua AV, Rao TVN, Sundararajua D, Vanisreeb M, Tsayb H, Subbaraju GV. Assessment of bioactivity of India medicinal plants using Brine Shrimp (Artemia salina) Lethality Assay. Int J Appl Sci Eng. 2005;3(2):125–134. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Iqbal S, Bhanger MI. Effect of season and production location on antioxidant activity of Moringa oleifera leaves grown in Pakistan. J Food Comp Anal. 2006;19:544–551. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2005.05.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Ganskopp D, Bohnert D. Mineral concentration dynamics among 7 northern Great Basin grasses. J Range Manage. 2003;56:174–184. doi: 10.2307/4003902. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Khan ZI, Ashraf M, Valeem EE. Forage mineral status evaluation: the influence of pastures. Pak J Bot. 2006;38:1043–1054. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Hussain J, Khan AL, Rehman N, Zainullah Hussain ST, Khan F, et al. Proximate and nutrient analysis of selected medicinal plant species of Pakistan. Pak J Nutr. 2009;8(5):620–624. doi: 10.3923/pjn.2009.620.624. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kaplan F, Kopka J, Sung DY, Zhao W, Popp M, Porat R, Guy CL. Transcript and metabolite profiling during cold acclimation of Arabidopsis reveals an intricate relationship of cold-regulated gene expression with modifications in metabolite content. Plant J. 2007;50:967–981. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Kumar S, Yadav M, Yadav A, Yadav JP. Comparative analysis of antimicrobial activity of methanolic extracts of Aloe vera and quantification of aloe- emodin collected from different climatic zones of India. ACMicrob. 2015;6(2):1–10. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Sanders TH. Peanut triacylglycerols: effect of season and production location. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1982;59(8):346–351. doi: 10.1007/BF02541017. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kumar S, Budhwar L, Yadav A, Yadav M, Yadav JP. Phytochemical screening and antibacterial activity of Aloe vera collected from different climatic regions of India. Nat Prod J. 2016;6:73–82. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Anwar F, Manzoor M, Bajwa J. Antioxidant activity of solvent extracts of strawberry using various antioxidant assay. Pak J Anal Chem. 2004;5(2):28–37. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Chalker-Scott L. Environmental significance of anthocyanins in plant stress responses. Photochem Photobiol. 1999;70(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1999.tb01944.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets supporting the results of this article are included in the article.


