Abstract
Morphological embryo classification is of great importance for many laboratory techniques, from basic research to the ones applied to assisted reproductive technology. However, the standard classification method for both human and cattle embryos, is based on quality parameters that reflect the overall morphological quality of the embryo in cattle, or the quality of the individual embryonic structures, more relevant in human embryo classification. This assessment method is biased by the subjectivity of the evaluator and even though several guidelines exist to standardize the classification, it is not a method capable of giving reliable and trustworthy results. Latest approaches for the improvement of quality assessment include the use of data from cellular metabolism, a new morphological grading system, development kinetics and cleavage symmetry, embryo cell biopsy followed by pre-implantation genetic diagnosis, zona pellucida birefringence, ion release by the embryo cells and so forth. Nowadays there exists a great need for evaluation methods that are practical and non-invasive while being accurate and objective. A method along these lines would be of great importance to embryo evaluation by embryologists, clinicians and other professionals who work with assisted reproductive technology. Several techniques shows promising results in this sense, one being the use of digital images of the embryo as basis for features extraction and classification by means of artificial intelligence techniques (as genetic algorithms and artificial neural networks). This process has the potential to become an accurate and objective standard for embryo quality assessment.
Keywords: Embryo quality assessment, morphological evaluation, artificial intelligence, mammalian embryo
INTRODUCTION
Since the development of the first successful techniques for assisted reproduction in mammals, it has become evident that there is a direct relationship between embryo quality and gestational success post embryo transfer (Lindner & Wright, 1983; Overström, 1996). Embryos morphologically classified as higher quality had higher successful gestation rates in domestic animals (Schneider et al., 1980; Tervit et al., 1980; Lindner & Wright, 1983) and in human patients (Balaban et al., 2000, 2006; Gardner & Schoolcraft., 1999). Although the direct relationship between embryo quality and success rate based on embryo grading is clear, it is still largely subjective due to low repetitiveness, with a high grading variance between embryologists (Lindner & Wright, 1983; Farin et al., 1995; Richardson et al., 2015). Thus, there is still great need for a system capable of categorizing embryos according to quality and according to viability and the capacity for successful gestations.
Currently, for morphological classification of cattle embryos, the usual approach is the grading within three quality ranks: Excellent or good (1), regular (2) or poor (3)(Bó & Mapletoft, 2013). This method is recommended by the International Embryo Transfer Society (IETS) over the deprecated four grading systems (Lindner & Wright, 1983), which separates excellent and good embryos, and it was common before studies had shown that there is not a significant difference in gestation rates between excellent and good embryos. However, it is noteworthy that the human eye is capable of distinguishing at least four morphological quality categories of embryos. Although the current grading system is simplified to only 3 possible ranks, the embryologist should be prepared to distinguish between excellent and good quality embryos, at one time both considered part of grade 1 in the IETS system.
In the case of human embryos, the prevailing system is the one proposed by Gardner & Schoolcraft (1999), although alternative grading systems exist (Dokras et al., 1993; Richardson et al., 2015). Altogether, the simpler grading systems (Dokras et al., 1993; Richardson et al., 2015) are more uniform and have a smaller variance between examiners. According to Balaban et al. (2006), the Gardner & Schoolcraft system, although more complex and with lower repetitiveness, results in higher predictive value for clinic pregnancy when compared to the proposal of Dokras et al. (1993). From this analysis derives an outcome that the more complex the system is, the more likely it is to grasp the biological reality of the grading system, here termed "embryo quality". Although a more straightforward system may have lower prediction accuracy, by reducing the amount of variables the system is less prone to differences between examiners, thus being more consistent.
A common factor between the systems described above is that all of them are based on the visual analysis of the embryo which is both subjective and qualitative and commonly done by stereomicroscopy. The technical quality assessment relies on the experience, attention to detail and systematic approach of the examiner on analyzing the embryo, from the more evident features as dead and extruded cells, or reduction of the percentage of viable cells to the more subtle characteristics that may influence embryo development such as irregularity of shape, heterogeneity of color, asynchrony between expected and encountered stage of development and the presence of vacuoles. On this classical approach of embryonic morphology, the variables are not measured in an objective form, resulting in low repeatability and subjectiveness of analysis (Bényei et al., 2006; van Loendersloot et al., 2014; Perkel et al., 2015; Richardson et al., 2015; Thompson et al., 2016). On this approach, a given embryo when analyzed by different examiners may be classified in different distinct degrees of quality (Farin et al., 1995, 1999; Chen et al., 2016). This variation between examiners is even more expressive between close quality grades as excellent/good and regular or regular and poor when compared to grades that are more distant, as excellent/good and poor (Farin et al., 1995). Additionally, the highest level of agreement between examiners occurs on the extreme classes (excellent or poor), being that the intermediate embryos are mostly responsible for the disagreement between examiners. Studies had also analyzed the effects of consecutive evaluations by the same person, so as to enable measuring the consistency (repeatability) of the evaluation (Arce et al., 2006; Paternot et al., 2009). Richardson et al. (2015) reported, for the classification of human embryos, a higher discrepancy between different examiners (K=0.63; Fleiss-Kappa statistic) than with the same examiner (K=0.71).
Seeking solution for the subjectivity of the morphological analysis, several alternative methods have been proposed (Overström, 1996; Hoshi, 2003; López-Damián et al., 2008; Held et al., 2012). Among them, the quality of in vitro growth of embryos, the integrity of blastomere membrane (Overström, 1996), analysis of embryo metabolism (Rondeau et al., 1995; Overström, 1996; Thompson et al., 2016), measurement of cellular respiration (Hoshi, 2003), electron-microscopy analysis (López-Damiánet et al., 2008) and zona pellucida birefringence index (Heldet et al., 2012). More recently, and specially for human embryos, there was a trend for methods that evaluate embryo kinetics and cleavage symmetry using time-lapse systems like EmbryoScope® or Primo VisionTM (Montag et al., 2013; Kovacs, 2014; VerMilyea et al., 2014). This kind of system allows the measurement of an index that stands as a guideline to aid embryologists on the selection of the best embryo for transfer in fertilization clinics. Nevertheless, for the in vitro production of cattle embryos, such a system is not widely used, mainly because of logistic limitations, the high operational cost and the reduced significance of evaluation for individual embryos. A distinct approach on early development is the classification by means of dedicated semi-automatic software (Santos Filho et al., 2012; Matos et al., 2014a), in a way that the analysis is not dependent on specific hardware. Table 1 shows a broader comparison among the different methods proposed for the morphological classification of human, cattle and murine embryos.
Table 1.
Studies addressing methods to evaluate mammalian embryos by non-invasive or invasive techniques.
| Authors | Technique | Nature | Species | Embryo stage | Compared to what traditional technique | On what parameters | Pros | Contras | Sample Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lindner & Wright, 1983 | Morphological assessment by stereomicroscopy | Noninvasive | Bovine | From morula to hatched blastocyst | Physiological parameters of devel-opment kinetics and pregnancy rates | Embryo stage and quality (excellent, good, fair and poor) on pregnan-cy rates | Embryo quality was a useful predictor of the pregnancy rate | Subjectivity of the embryo quality assessment; excellent and good qualities had no difference on pregnancy rate | 783 |
| Gardner & Schoolcraft, 1999 | Morphological assessment by stereomicroscopy | Noninvasive | Human | Blastocyst | Morphological aspects of the trophectoderm and inner cell mass | Blastocyst quality based on grades | Validated worldwide by embryologists and clinicians due its useful relation with pregnancy establishment | Does not cover all aspects of the aberrant morphology and it is limited to blastocyst stage | ND |
| Balaban et al., 2006 | Morphological assessment by stereomicroscopy | Noninvasive | Human | Blastocyst | Comparison between the Gardner and Dokras systems of evaluation | Clinical pregnancy, implantation rate and multiple pregnancies | Both systems were practical and accurate, good to predict blastocysts with high implantation potential and to limit the number of embryo transfer to avoid multiple pregnancies | Lack of a single and unified system and a standard to evaluate | 132 |
| Richardson et al., 2015 | Simplified method to evaluate blastocysts | Noninvasive | Human | Day 5 blastocyst | Traditional method to evaluate embryo morphology | New and simpli-fied method with less parameters to assess | Faster and easier than the traditional method (Gardner & Schoolcraft, 1999) with similar or better results than a more complex system | Method rarely used by clinicians | 80 |
| Shiku et al., 2001 | Scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM) | Noninvasive | Bovine | From morula to blastocyst | NA | Results showed that morulae with higher oxygen consumption were faster to develop into blastocysts. The method could be just a complement or to change the way how the embryo is chosen | Noninvasive technique that could be reliable to the embryo viability assessment and development | Not well established and worldwide acceptation | 19 |
| Braga et al., 2015 | Mass spectrometry to charac-terize (“fin-gerprint”) the culture medium conditioned by the embryo | Noninvasive | Human | Day 3 of culture | Spectroscopy | To identify potential embryo lipid biomarkers that are predictors to preview blastocyst formation | Promising approach to identify embryos that should be cultured until Day 5 or cryopreserved | 50 | |
| Yang et al., 2012 | Chromosomal screening by array Comparative Genomic Hybridization (aCGH) | Invasive | Human | Day 5 | NA | Together with morphological evaluation presented the best results | Produced clinical pregnancy more frequently and a lower abortion rate when compared to embryos chosen without a CGH | Demands skills from the embryologist and complex equipment to perform the invasive technique | 814 |
| Kropp et al., 2014 | Micro RNA (miRNA) profile | Noninvasive | Bovine and Human | Day 5 or 6 | NA | Potential to develop noninvasive biomarkers to predict embryo quality | Embryo quality related with some miRNA expression | Needs more studies and development of robust and accurate biomarkers | 216 (bovine embryos) |
| Kakourou et al., 2013 | Transcriptomic analysis | Invasive | Human | Blastocyst | NA | Results highlighted the importance of the hormones and their receptors but lack a physiologic comprehension of their role on the early development | Future analyses could identify new biomarkers that predict embryo development potential | Still an experimental method that needs more studies | 03 |
| Farin et al., 1995 | Videotape assessment of embryo images | Noninvasive | Bovine | From morula to blastocyst | NA | Way to measure interembryologist agreement. Quality | Good to excellent agreement existed for classifying Day 7 embryos by stage and by extremes of quality grade (grades 1 and 4). It was proposed a simple grading criteia to maximize agreement among evaluators | There was poor agreement of evaluators by degree of abnormal morphology (Grades 2 and 3) | 40 |
| VerMilyea et al., 2014 | Timelapse | Noninvasive | Human | Day 1 to 3 | NA | Strong predic-tion of the clinical pregnancy when related to P2 (time between 1st and 2nd mitosis or 2 cellstage duration) and P3 (time between 2nd and 3rd mito-sis or 3 cell-stage duration) | Automatized predictive model | Not suitable to blastocyst evaluation | 375 |
| Milewski et al., 2015 | Timelapse | Noninvasive | Human | Day 5 | NA | Based on time of cell divisions (2 and 5 blastomeres) and inter-val between 2nd and 3rd divisions, it was proposed a multivariate predictive model | Evaluation of morphokinetics parameters could provide data encompassing a long time frame of embryo development. This is the main advantage of the method, i.e. the opportunity to observe the embryo almost continuously | The method considers only morphokinetic parameters - such as the relative and absolute times of cell division – on the impact of the embryo capacity to reach the blastocyst stage | 162 |
| Wong et al., 2010 | Image analysis algorithm | Noninvasive | Human | Day 2 | NA | First algorithm attempt to ebryo development automatized analysis. Could predict the blastocyst stage of develop-ment | Automatized analysis of parameters | Unable to discriminate parameters to predict the development up to blastocyst and its quality | 242 |
| Santos Filho et al., 2012 | Support Vector Machine | Noninvasive | Human | Blastocyst | NA | Potential method to automatized embryo classification discriminating quality parameters of inner cell mass and trophectoderm | Method based only on the blastocyst image (numerical data mined from it with more discrimina-tory parameters than visual morphology assessment by human beings) | Semiautomatic meth-od was obtained and a fully automatized meth-od should be achieved | 73 |
| van Loender-sloot et al., 2014 | Logistic regression | Noninvasive | Human | Day 3 | Embryonic morphology | Early cleavage, blastomere number on days 2 and 3, morphologic pointing and presence of a morula no Day 3 of culture | Method capable to distinguish embryos with high implantation potential from those with moderated or low potential | 6021 | |
| Chen et al., 2016 | Data mining to produce a computer assisted scoring system based on multivariable logistic regression and multivariate adaptative re-gression spline | Noninvasive | Human | Day 1,2 and 3 | Embryonic morphology | Point grading system | Improvement on the generalization of the current predictive models | Promising approach although still experimental | 871 |
| Matos et al., 2014a | Artificial neural network | Noninvasive | Mouse | Blastocyst | Embryonic morphology | To avoid the subjectivity of the assessment done by a human examiner | Classification systems fully based on software | Needs an embryologist to manually to obtain numerical parameters from the embryo image | 98 |
| Matsuura et al., 2010 | Blastocyst quality score | Noninvasive | Human | Blastocyst | NA | New pointing system | Numerical classifi-cation system based on the Gardner & Schoolcraft (1999) criteria | There is a requirement for a huge number of embryos to produce statistical significance | 220 |
| Tejera et al., 2012 | Oxygen consumption measurement | Noninvasive | Human | Day 3 | NA | Oxygen consump-tion rate was associated with potential implantation and embryo quality | Technique used as a complementary pa-rameter to determine the embryo to be chosen | Not useful to predict implantation rates. The causes of this lack of predictability is the clinical relevance of other variables that are related to embryo quality | 84 |
| Thompson et al., 2016 | Multi-spectral imaging to evaluate the endogenous auto fluores-cence | Noninvasive | Human and Bovine | Early embryo stages | Diversity of techniques | The authors are trying to correlate the observed pattern of auto fluorescence with metabolic profile of the embryo. The aim is to predict the embryo quality during development of early embryos | High resolution imag-ing (single embryo), real time and noninvasive method that could be associated with others (e.g., tra-ditional morphological evaluation) besides computer based techniques. It is a current promise to determine the intracellular met-abolic activity | Experimental technique under evaluation | ND |
| López-Damián et al., 2008 | Transmission electron microscopy | Lethal | Bovine | Blastocyst | NA | Demonstrated the sub-cellular varia-tion of the embryos classified as fair grade by optical light microscopy and by stereomi-croscopy | Validated the ac-curacy of the IETS proposed system of embryo classification | Unable to evaluate an embryo intended to be transferred to the uterus, just to validate the accuracy of a technique on subcellular aspects | 30 |
Legend: Nature - invasiveness of the technique employed; Embryo stage – range of stages where the embryo was suitable or was used in the study; Compared to what traditional technique – when it was the case - that a new proposed technique had its efficacy compared to a traditional and well established one; On what parameters – when there was such comparison, did it occur, if not the case, in what primary parameters the authors evaluated the embryos; Sample size – the quantity of embryos used on the study; NA – not available; ND – not determined.
Still, no method thus far has been able to reach a definitive solution for the measurement of embryo quality, considering that many are still in experimental stage. Therefore, the research and development of techniques that prove to be fast, non-invasive and objective are fundamental in the development of any embryo grading system (Lindner & Gardner, 1983; Overström, 1996; Thompson et al., 2016). While for some methods the limiting factor is the high cost of implementation, preventing use on different species of mammals (time-lapse analysis, biopsy followed by pre-implantation genetic diagnosis) for others, the invasiveness - or even the lethality, as with the ultra-structural analysis (López-Damiánet et al., 2008) - is the crucial point. Thus, regardless of subjectivity, visual analysis of embryo morphology is still generally used to determine embryo quality.
Several authors recently proposed the use of mathematical and statistical tools for the analysis of embryo viability. Among the main researches, van Loendersloot et al. (2014) reported the use of multivariate logistic regression with eight predictive factors for the classification of embryos according to implantation potential. Such a model has shown a moderate discriminative capacity, being able to categorize embryos with high, moderate or low implantation potential. Nevertheless, we need to stress that the method also uses other variables rather than embryo morphology, such as physiological, endocrinological and metabolic parameters of the patient who will receive the embryo.
Chen et al. (2016) proposed the use of a computer-assisted scoring system (CASS). The system is supposed to have a higher discriminatory power for embryo selection, over the standard scoring system that has intrinsic examiner variability. The authors also used a multivariate logistic regression (LR) system, together with multivariate adaptive regression splines (MARS). The study had shown improvement on the predictive model when using the computer assisted scoring system associated with data mining.
Santos Filho et al. (2012) developed a system, by means of applied mathematics, capable of acting in a semi-automatic fashion on the interpretation and classification of human embryos. Such a proposal proved to be unique and managed to overcame an innovative challenge as no similar technique with comparable results exists. In this way, the fact that the process is not fully automated and only aimed at human embryo evaluation limits the diffusion of the methodology to other species and to practical routine laboratory work.
More recently, another group published research on embryo viability grading using image processing techniques based on the segmentation of blastomeres (Singh et al., 2014; Tian et al., 2014) or trophectoderm (Singh et al., 2015) from human embryos.
Artificial intelligence as a new way to approach the problem
Artificial intelligence (AI) techniques have the potential to develop objective, reproducible and non-invasive methodologies to predict embryo quality with high accuracy. The field of AI is very extensive, but some specific techniques as genetic algorithms (GA) along with artificial neural network (ANN) could be used to simulate an accurate predictive model (Takahashi et al., 2016).
GA is a search and optimization method inspired by genetic mechanisms and natural evolution. In GA a population of possible solutions is simulated for a determined problem, that is, a population of 'individuals' each one containing a possible solution. By an evolutionary process based on crossover, mutations and migrations, the individuals can converge to a better solution for the problem (Tanomaru, 1995). ANN is a technique based on how human neurons transmit and process information and it is indicated for the resolution of complex and nonlinear problems. Such neurons need to be exposed to training data (variables), in order to learn to generalize an output (i.e., a result) from a input dataset. Once properly trained, ANN is able to perform predictions from new input data to which it has never has access (Haykin, 1998; Zhang et al., 1998; Huang, 2009).
Initially proposed for mouse embryos (Matos et al., 2014a) and posteriorly applied in bovine blastocysts (Matos et al., 2014b), this potential method uses a process of automated extraction of information, from bi-dimensional digital images of embryos and, posteriorly, classifies them in quality grades, according to the specificity of each species. These two cases in particular used just blastocysts between the initial and expanded stages. The blastocyst stage is the standard in commercial procedures of bovine embryos transfers, produced in vitro, as well as has been increasingly used for clinical procedures in assisted human reproduction laboratories (Balaban et al., 2000; Hyttel et al., 2010).
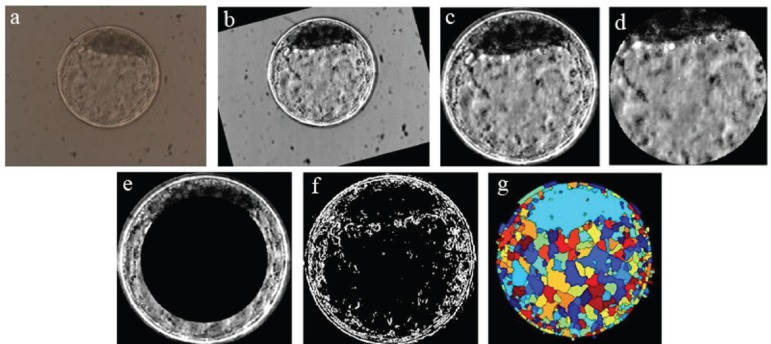
In a paper published by Matos et al. (2014b), blastocyst digital images were captured by optic microscopy without the use of dye while maintaining embryo exposure lower than 30 seconds, using techniques of digital image processing (Gonzalez & Woods, 2008) for information standardization and interpretation. Once the embryo was properly standardized and isolated of its background (in an automated mode), it was possible to do a segmentation step, that is, the extraction of several numeric variables contained in the digital image. Thus, these variables obtained were used as input to the ANN system. The objective of the information extraction is to obtain a numeric vector, which represents the original image. Several algorithms work independently in this process, providing the input variables to the ANN. Therefore, we used techniques such as Hough transform (Atherton & Kerbyson, 1999) to determine embryo circularity, texture analysis (Haralick et al., 1973; Tuceryan & Jain, 1998; Soille, 2013; Sonka et al., 2014) using the Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix(GLCM) classification method (Hu et al., 2008; Siqueira et al., 2013) and the Watershed transform (Beucher, 1992), that proposes a morphologic approach to the problem of image segmentation, by its interpretation as being surfaces, in which the grey levels of each pixel determines the altitude of a given region (Körbes, 2010). Figure 1 ilustrates the sequence of steps used to process a digital image from an in vitro produced bovine blastocyst.
Figure 1.
Ilustrates the sequence of steps required to process a digital image from an in vitro produced bovine blastocyst. a) original image as obtained by optic microscopy; b) standardization of bright and positioning of the inner cell mass (ICM) at 12 o’clock; c) segmentation of the embryo itself (by Hough transform) and elimination of background; d) segmentation of ICM and blastocoel by elimination of the zona pellucida and trophectoderm; e) elimination of inner area of the image “c” to highlight the trophectoderm and part of the ICM; f) binary form of image “c” after gradient calculation; g) visualization of the image after Watershed transform.
All the possible information from the digital images of bovine blastocysts was extracted, and 36 variables were obtained to define the embryo (i.e., the mathematic representation of the main features of the digital image). After a co-linearity analysis, these 36 variables were reduced to 24, which were used as the input data for ANN. After training, these variables made up the GA population. This has undergone the natural evolution process (containing the crossover, mutation and migration events) which determined the most suitable ANN for the embryos classification.
In results obtained recently (not published) of our research group, and involving 126 images of bovine blastocysts, after three experienced embryologists analysed the images, the results were applied to the GA technique associated to ANN. As the network output standard (template) was used, the mode value of the classification was made by the embryologists. Seventy percent of the sample was utilized for training and 15% for ANN validation leaving 15% for testing the system. The result in a blind test with the 15% remaining resulted in 84% correct in exact classification of embryos, that is, the ANN classified with the same mode value given by the trained embryologists. In this blind test there were no detected critic error in evaluation by ANN, that is, the cases in which ANN classified the image in a grade than the one rated by the examiners (e.g., the examiners classified the image as excellent and the ANN as poor). Therefore, we consider the accuracy of the applied method for embryo classification as satisfactory, showing to be a promising technique with potential for clinical application.
Our study, which is still in the experimental stage and in collaboration with the world's largest company of bovine embryo in vitro production (In Vitro Brasil, Mogi Mirim, SP, Brazil), is protected by a national patent application filling with INPI (BR102012031953-5; Matos et al., 2016) and international with WIPO (PCT-BR2013-000506; Matos et al., 2014c), in which both were done together with Agência Unesp de Inovação (AUIN). This is, to our knowledge, the only other registered invention engaged in embryo selection (Loewke & Suraj, 2014). However, our invention differs from Loewke & Suraj's (2014), by the use of a time-lapse image acquisition system for determining embryo quality, which is based on the kinetics and symmetry of embryo cleavage. We infer that both classification systems are not mutually exclusive. The kinetic evaluation and symmetry as well as the blastocyst image by ANN could be made available in hardware by time-lapse video equipment.
CONCLUSION
In light of the multiple current attempts to develop a precise non-invasive system for embryo classification, this is still an ongoing process. Clinicians and researchers are waiting for a system that is non-invasive, objective and accurate, for prediction and with high reproducibility. The most promising alternatives seems to be the ones that take into account the metabolites used by the embryo and obtained by analysis of the conditioned culture medium, the use of applied mathematics and statistics with the classificatory system or dedicated software for the analysis of kinetics, symmetry or morphology of the embryo. In the absence of a robust and well-established system, the majority of embryologists will continue to rely on the conventional classification system that, despite its inaccuracies, it still bears some predictive power for successful implantation and the ability to classify embryos morphologically. However, no matter how new technologies may be developed, they cannot currently surpass human evaluation with years of clinical experience on the ultimate assessment of embryo quality.
Finally, we foresee the possibility of an artificial intelligence system, similar to the one described before, but not limited only to the morphological analysis of the embryo. Theoretically, it is possible to adapt the system for the direct prediction of successful embryo implantation, once the variables that describe the physiological, endocrinological and metabolic environment of the recipient are included on the machine learning algorithms.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the financial support from FAPESP (06/06491-2, 11/06179-7, 12/20110-2 and 12/50533-2) and the UNESP Agency for Innovation (AUIN). Also, we thank all those involved, directly or indirectly, in the project of automated assessment of digital images of embryos: collaborators from In Vitro Brazil and from the laboratories of Applied Mathematics and Embryo Micromanipulation from the Department of Biological Science, FCL/Assis, UNESP.
Footnotes
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
No conflict of interest have been declared.
REFERENCES
- Arce JC, Ziebe S, Lundin K, Janssens R, Helmgaard L, Sørensen P. Interobserver agreement and intraobserver reproducibility of embryo quality assessments. Hum Reprod. 2006;21:2141–2148. doi: 10.1093/humrep/del106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton TJ, Kerbyson DJ. Size invariant circle detection. Image Vision Comput. 1999;17:795–803. [Google Scholar]
- Balaban B, Urman B, Sertac A, Alatas C, Aksoy S, Mercan R. Blastocyst quality affects the success of blastocyst-stage embryo transfer. Fertil Steril. 2000;74:282–287. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(00)00645-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balaban B, Yakin K, Urman B. Randomized comparison of two different blastocyst grading systems. Fertil Steril. 2006;85:559–563. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2005.11.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bényei B, Komlósi I, Pécsi A, Pollot G, Marcos CH, Campos AO, Lemes MP. The effect of internal and external factors on bovine embryo transfer results in a tropical environment. Anim Reprod Sci. 2006;93:268–279. doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2005.07.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beucher S. The watershed transformation applied to image segmentation. Scanning Microsc Suppl. 1992;6:299–314. [Google Scholar]
- Bó G, Mapletoft R. Evaluation and classification of bovine embryos. Anim Reprod. 2013;54:344–348. [Google Scholar]
- Braga DPAF, Setti AS, Cabral EC, Eberlin M, Loturco EG, Borges E., Jr Non-Invasive Prediction of Blastocyst Formation by Day Three Embryo Culture Medium Mass Spectrometry Lipid Fingerprinting. JBRA Assisted Reproduction. 2015;19:119–124. doi: 10.5935/1518-0557.20150027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen F, Neubourg DD, Debrock S, Peeraer K, D'Hooghe T, Spiessens C. Selecting the embryo with the highest implantation potential using a data mining based prediction model. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2016;14:10–10. doi: 10.1186/s12958-016-0145-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dokras A, Sargent IL, Barlow DH. Human blastocyst grading: an indicator of developmental potential? Hum Reprod. 1993;8:2119–2127. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a137993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farin PW, Britt JH, Shaw DW, Slennig BD. Agreement among evaluators of bovine embryos produced in vivo or in vitro. Theriogenology. 1995;44:339–349. doi: 10.1016/0093-691x(95)00189-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner DK, Schoolcraft WB. In virto culture of human blastocyst. In: Janson R, Mortimer D, editors. Towards Reproductive Certainty: Infertility and Genetics Beyond. Carnforth: Parthenon Press; 1999. pp. 378–388. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez RC, Woods RE, editors. Digital Image Processing. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice Hall; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Haralick RM, Shanmugam K, Dinstein I, editors. Textural Features for Image Classification. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern. 1973;3:610–621. [Google Scholar]
- Haykin S, editor. Neural networks. A comprehensive foundation. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Held E, Mertens EM, Mohammadi-Sangcheshmeh AM, Salilew-Wondim D, Bessenfelder U, Havlicek V, Herrler A, Tesfaye D, Schellander K, Hölker M. Zona pellucida birefringence correlates with developmental capacity of bovine oocytes classified by maturational environment, COC morphology and G6PDH activity. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2012;24:568–579. doi: 10.1071/RD11112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi H. In vitro production of bovine embryos and their application for embryo transfer. Theriogenology. 2003;59:675–685. doi: 10.1016/s0093-691x(02)01247-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y, Zhao C, Wang H. Directional Analysis of Texture Images Using Gray Level Co-Occurrence Matrix. Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Pacific-Asia Workshop on Computational Intelligence and Industrial Application. 2008;2:277–281. [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. Advances in Artificial Neural Networks - Methodological Development and Application. Algorithms. 2009;2:973–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Hyttel P, Sinowatz F, Vejlsted M. Essentials of Domestic Animal Embryology. Elsevier; Toronto: Saunders; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kakourou G, Jaroudi S, Tulay P, Heath C, Serhal P, Harper JC, Sengupta SB. Investigation of gene expression profiles before and after embryonic genome activation and assessment of functional pathways at the human metaphase II oocyte and blastocyst stage. Fertil Steril. 2013;99:803–814. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2012.10.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Körbes A, Lotufo RA. On Watershed Transform: Plateau Treatment and Influence of the Different Definitions in Real Applications; Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Systems, Signals and Image Processing, Signals and Image Processing; 2010. pp. 376–379. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs P. Embryo selection: the role of time-lapse monitoring. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2014;12:124–124. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-12-124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropp J, Salih S, Khatib H. Expression of microRNAs in bovine and human pre-implantation embryo culture media. Front Genet. 2014;5:91–91. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner G, Wright RW., Jr Bovine embryo morphology and evaluation. Theriogenology. 1983;20:407–416. doi: 10.1016/0093-691x(83)90201-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loendersloot L, Welya M van, Veena F van der, Bossuyt P, Repping S. Selection of embryos for transfer in IVF: ranking embryos based on their implantation potential using morphological scoring. Reprod Biomed Online. 2014;29:222–230. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2014.04.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewke KE, Suraj V. In vitro embryo blastocyst prediction methods. G01N 33/50 20060101 G01N033/50; A61B 17/435 20060101 A61B017/435. US20140017717 A1. May 31 16, 2013. Jan 31 16, 2014. [06/05/16]. Available at: http://www.google.ch/patents/US20140017717. [Google Scholar]
- López-Damián EP, Galina CS, Merchant H, Cedilo-Peláez C, Aspron M. Assessment of Bos taurus embryos comparing stereoscopic microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. J Cell Anim Biol. 2008;2:72–78. [Google Scholar]
- Matos FD, Rocha JC, Nogueira MFG. A method using artificial neural networks to morphologically assess mouse blastocyst quality. J Anim Sci Technol. 2014a;56:15–15. doi: 10.1186/2055-0391-56-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matos FD, Nogueira MFG, Rocha JC. Artificial intelligence meets the same challenges as humans in morphological classification of bovine blastocysts. Abstract of Proceedings of the 28th Annual Meeting of the Brazilian Embryo Technology Society (SBTE). A209 Supporting Biotechnologies: Cryopreservation and Cryobiology, Image Analysis and Diagnosis, Molecular Biology and "Omics". Anim Reprod. 2014b;11:489–489. [Google Scholar]
- Matos FD, Nogueira MFG, Rocha JC. Universidade Estadual Paulista Júlio de Mesquita Filho US Pat. WO2014089647. Method for determining embryo viability and quality. G01N 33/483 (2006.01), A61D 19/00 (2006.01), C12N 5/073 (2010.01), G06T 1/40 (2006.01) 2014c Jun 19; 22 nov. 2013.
- Matos FD, Nogueira MFG, Rocha JC. Universidade Estadual Paulista Júlio de Mesquita Filho . Método para determinação da viabilidade e qualidade de embriões. C12N 5/0604. C12N 5/073. BR 10 2012 031953 5 A2. 2016. Mar 08, 2016. 14 dez. 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura K, Hayashi N, Takiue C, Hirata R, Habara T, Naruse K. Blastocyst quality scoring based on morphologic grading correlates with cell number. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:1135–1137. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milewski R, Kuć P, Kuczyńska A, Stankiewicz B, Łukaszuk K, Kuczyński W. A predictive model for blastocyst formation based on morphokinetic parameters in time-lapse monitoring of embryo development. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2015;32:571–579. doi: 10.1007/s10815-015-0440-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montag M, Toth B, Strowitzki T. New approaches to embryo selection. Reprod Biomed Online. 2013;27:539–546. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2013.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overström E. In vitro assessment of embryo viability. Theriogenology. 1996;45:3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Paternot G, Devroe J, Debrock S, D'Hooghe TM, Spiessens C. Intra- and inter-observer analysis in the morphological assessment of early-stage embryos. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2009;7:105–105. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-7-105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkel KJ, Tscherner A, Merrill C, Lamarre J, Madan P. The ART of Selecting the Best Embryo: A Review of Early Embryonic Mortality and Bovine Embryo Viability Assessment Methods. Mol Reprod Dev. 2015;82:822–838. doi: 10.1002/mrd.22525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson A, Brearley S, Ahitan S, Chamberlain S, Davey T, Zujovic L, Hopkisson J, Campbell B, Raine-Fenning N. A clinically useful simplified blastocyst grading system. Reprod Biomed Online. 2015;31:523–530. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2015.06.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rondeau M, Guay P, Goffa AK, Cooke GM. Assessment of embryo potential by visual and metabolic evaluation. Theriogenology. 1995;44:351–366. doi: 10.1016/0093-691x(95)00190-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos E, Filho, Noble JA, Poli M, Griffiths T, Emerson G, Wells D. A method for semi-automatic grading of human blastocyst microscope images. Hum Reprod. 2012;27:2641–2648. doi: 10.1093/humrep/des219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider HJ, Castleberry RS, Griffin JL. Commercial aspects of bovine embryo transfer. Theriogenology. 1980;13:73–85. doi: 10.1016/0093-691x(80)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiku H, Shiraishi T, Ohya H, Matsue T, Abe H, Hoshi H, Kobayashi M. Oxygen consumption of single bovine embryos probed by scanning electrochemical microscopy. Anal Chem. 2001;73:3751–3758. doi: 10.1021/ac010339j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A, Saeedi P, Buonassisi J. Automatic blastomere detection in day 1 to day 2 human embryo images using partitioned graphs and ellipsoids; IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP); 2014. pp. 917–921. [Google Scholar]
- Singh A, Au J, Saeedi P, Havelock J. Automatic Segmentation of Trophectoderm in Microscopic Images of Human Blastocysts. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2015;62:382–393. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2014.2356415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siqueira FR, Schwartz WR, Predrini H. Multi-scale gray level co-occurrence matrices for texture description. Neurocomputing. 2013;120:336–345. [Google Scholar]
- Soille P, editor. Morphological Image Analysis, Principles and Applications. Springer Science & Business Media; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sonka M, Hlavac V, Boyle R, editors. Image processing, analysis, and machine vision. Cengage Learning Engineering; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi MB, Rocha JC, Núñez EGF. Optimization of artificial neural network by genetic algorithm fordescribing viral production from uniform design data. Process Biochem. 2016;51:422–430. [Google Scholar]
- Tanomaru J. Motivação, fundamentos e aplicações de algoritmos genéticos; Proceedings of the II Congresso Brasileiro de Redes Neurais; II Escola de Redes Neurais; 1995. pp. 331–411. [Google Scholar]
- Tejera A, Herrero J, Viloria T, Romero JL, Gamiz P, Meseguer M. Time-dependent O2 consumption patterns determined optimal time ranges for selecting viable human embryos. Fertil Steril. 2012;98:843–857. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2012.06.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tervit H, Cooper MW, Goold PG, Haszard GM. Non-surgical embryo transfer in cattle. Theriogenology. 1980;13:63–71. doi: 10.1016/0093-691x(80)90015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson JG, Brown HM, Sutton-McDowall ML. Measuring embryo metabolism to predict embryo quality. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2016;28:41–50. doi: 10.1071/RD15340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuceryan M, Jain AK. Texture Analysis. In: Chen CH, Pau LF, Wang PSP, editors. Handbook of Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision. Word Scientific Publishing; 1998. pp. 207–248. [Google Scholar]
- VerMilyea MD, Tanb L, Anthonya JT, Conaghanc J, Ivanid K, Gvakhariae M, Boostanfarf R, Bakerg VL, Surajb V, Chenb AA, Mainigia M, Coutifarisa C, Shenb S. Computer-automated time-lapse analysis results correlate with embryo implantation and clinical pregnancy: A blinded, multi-centre study. Reprod Biomed Online. 2014;29:729–736. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2014.09.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong CC, Loewke KE, Bossert NL, Behr B, De Jonge CJ, Baer TM, Pera RAR. Non-invasive imaging of human embryos before embryonic genome activation predicts development to the blastocyst stage. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28:1115–1121. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z, Liu J, Collins GS, Salem SA, Liu X, Lyle SS, Peck AC, Sills ES, Salem RD. Selection of single blastocysts for fresh transfer via standard morphology assessment alone and with array CGH for good prognosis IVF patients: results from a randomized pilot study. Mol Cytogenet. 2012;5:24–24. doi: 10.1186/1755-8166-5-24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang G, Patuwo BE, Hu MY. Forecasting with artificial neural networks: The state of the art. Int J Forecast. 1998;14:35–62. [Google Scholar]