Abstract
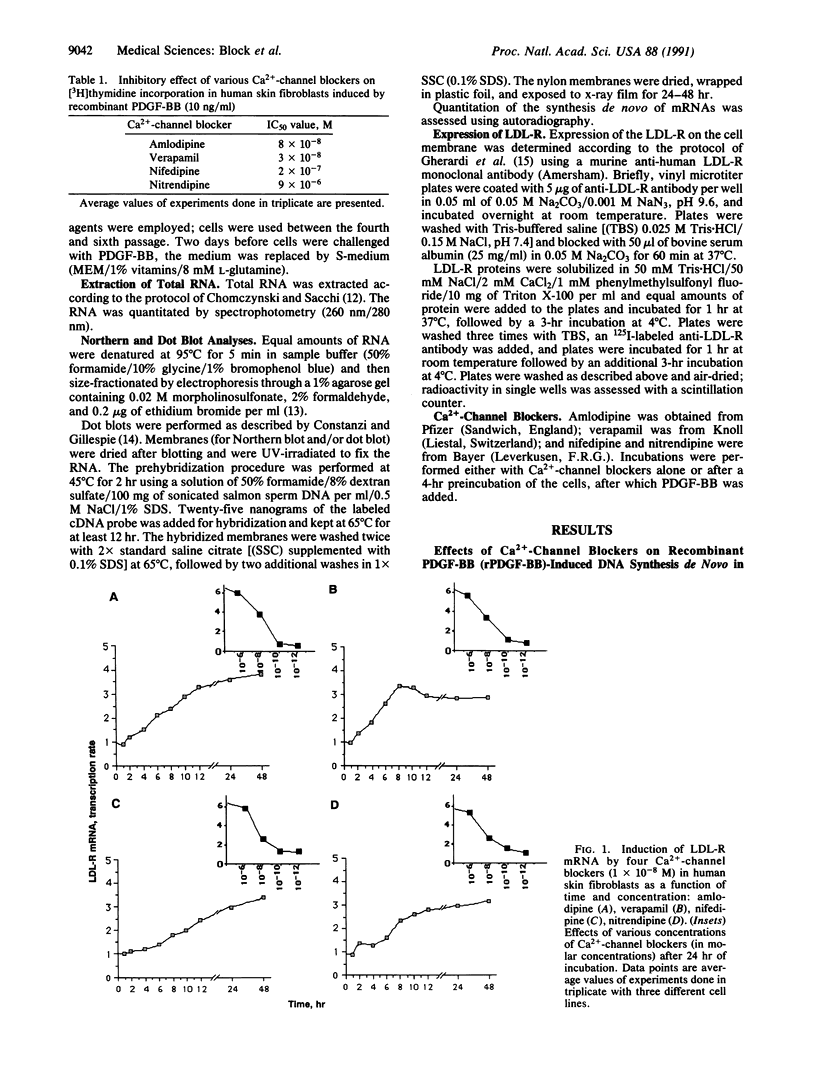
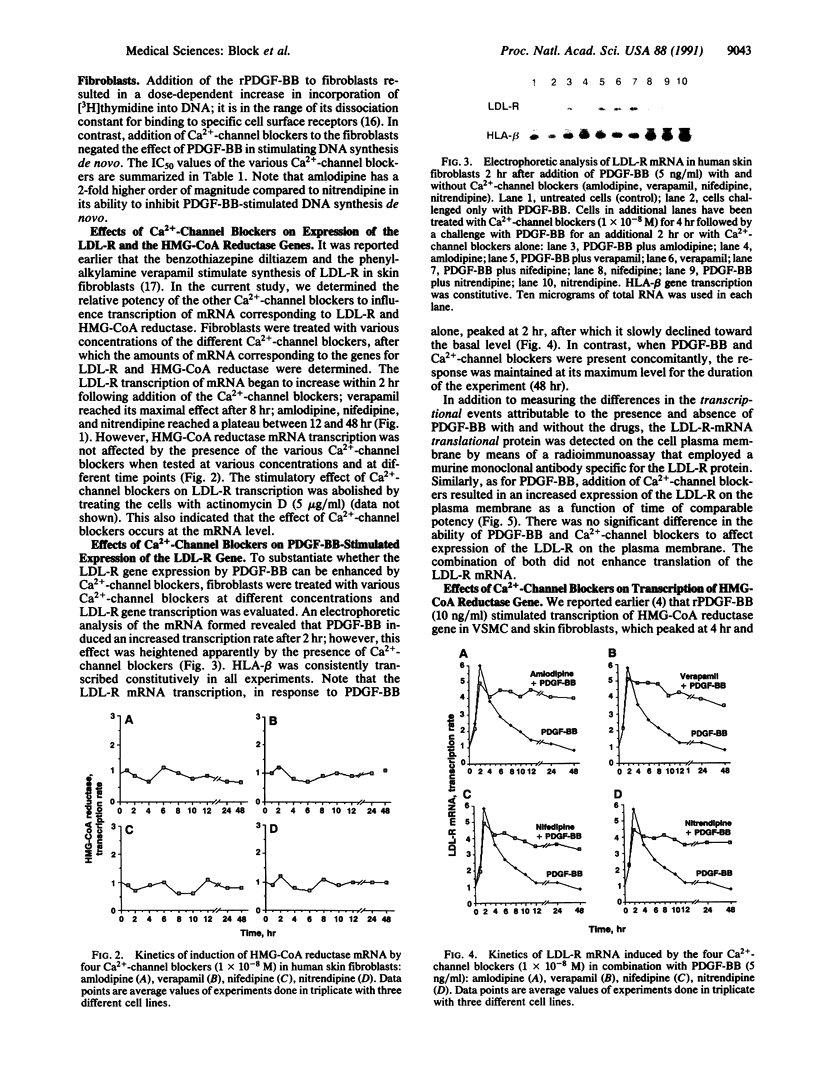
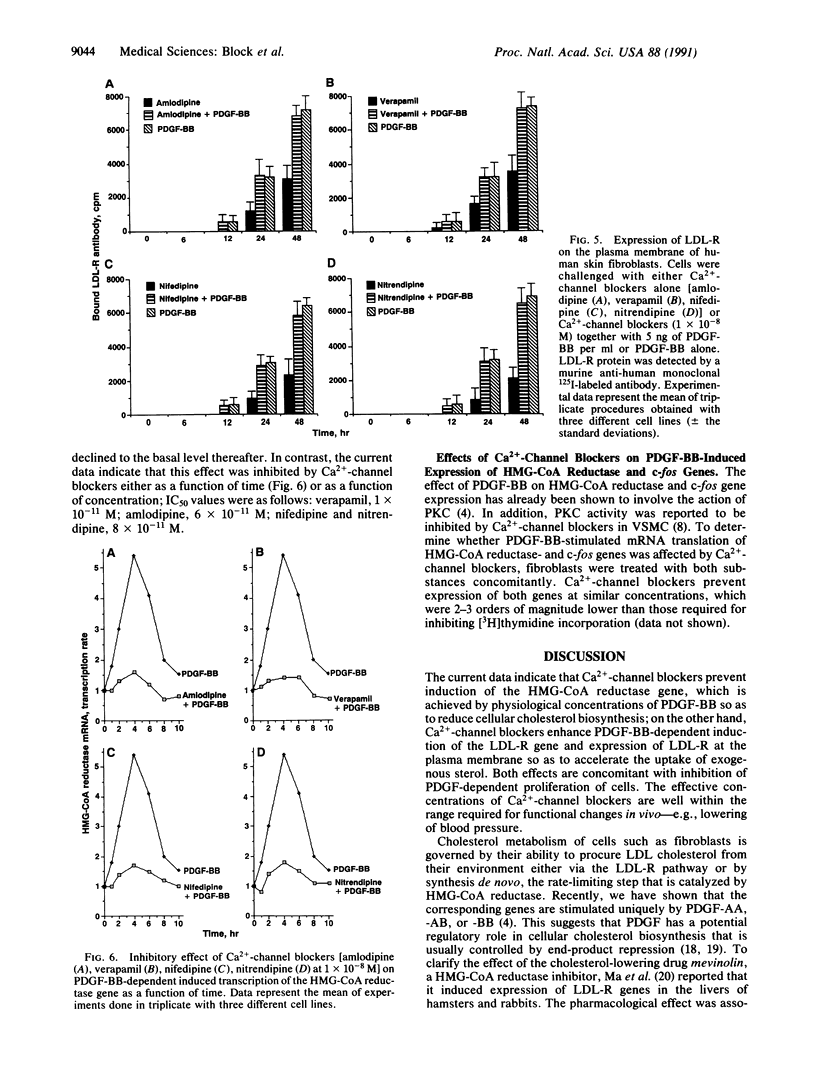
The effects of Ca(2+)-channel blockers (amlodipine, nifedipine, nitrendipine, and verapamil) on expression of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase (EC 1.1.1.88) and low density lipoprotein receptor (LDL-R) genes stimulated by recombinant platelet-derived growth factor BB isomer (PDGF-BB) were evaluated in human skin fibroblasts. The drugs enhanced expression of the LDL-R protein on the plasma membrane of the cells; in contrast, they inhibited expression of the HMG-CoA reductase gene. In addition, PDGF-BB-dependent stimulation of transcription of c-fos mRNA was inhibited also by the Ca(2+)-channel blockers. We conclude that PDGF-BB-dependent activation of the two genes is inhibited effectively by the Ca(2+)-channel blockers, at therapeutic concentrations, although they are unable to lower systemic cholesterol levels at these concentrations; however, they do modify responses of the two genes that are involved crucially in regulation of cellular cholesterol homeostasis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auwerx J. H., Chait A., Deeb S. S. Regulation of the low density lipoprotein receptor and hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase genes by protein kinase C and a putative negative regulatory protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1133–1137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block L. H., Emmons L. R., Vogt E., Sachinidis A., Vetter W., Hoppe J. Ca2+-channel blockers inhibit the action of recombinant platelet-derived growth factor in vascular smooth muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2388–2392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Lipoprotein metabolism in the macrophage: implications for cholesterol deposition in atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:223–261. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesterman C. N., Walker T., Grego B., Chamberlain K., Hearn M. T., Morgan F. J. Comparison of platelet-derived growth factor prepared from release products of fresh platelets and from outdated platelet concentrates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 15;116(3):809–816. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzi C., Gillespie D. Fast blots: immobilization of DNA and RNA from cells. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:582–587. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckardt H., Filipovic I., Hasilik A., Buddecke E. Calmodulin antagonists increase the amount of mRNA for the low-density-lipoprotein receptor in skin fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 15;252(3):889–892. doi: 10.1042/bj2520889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etingin O. R., Hajjar D. P. Calcium channel blockers enhance cholesteryl ester hydrolysis and decrease total cholesterol accumulation in human aortic tissue. Circ Res. 1990 Jan;66(1):185–190. doi: 10.1161/01.res.66.1.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipovic I., Buddecke E. Calcium channel blockers stimulate LDL receptor synthesis in human skin fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 14;136(3):845–850. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gherardi E., Brugni N., Bowyer D. E. Purification of low density lipoprotein receptor from liver and its quantification by anti-receptor monoclonal antibodies. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 15;253(2):409–415. doi: 10.1042/bj2530409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfraind T., Miller R., Wibo M. Calcium antagonism and calcium entry blockade. Pharmacol Rev. 1986 Dec;38(4):321–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Progress in understanding the LDL receptor and HMG-CoA reductase, two membrane proteins that regulate the plasma cholesterol. J Lipid Res. 1984 Dec 15;25(13):1450–1461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Bowen-Pope D., Seifert R., Hart C. E., Cooper J. A. Different effects of homo- and heterodimers of platelet-derived growth factor A and B chains on human and mouse fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3727–3735. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03256.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma P. T., Gil G., Südhof T. C., Bilheimer D. W., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Mevinolin, an inhibitor of cholesterol synthesis, induces mRNA for low density lipoprotein receptor in livers of hamsters and rabbits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8370–8374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehmet H., Nånberg E., Lehmann W., Murray M. J., Rozengurt E. Early signals in the mitogenic response of Swiss 3T3 cells: a comparative study of purified PDGF homodimers. Growth Factors. 1990;3(2):83–95. doi: 10.3109/08977199009108271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Bowen-Pope D. F., Raines E. W. Platelet-derived growth factor and its role in health and disease. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1990 Mar 12;327(1239):155–169. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1990.0051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Masuda J., Raines E. W., Gown A. M., Katsuda S., Sasahara M., Malden L. T., Masuko H., Sato H. Localization of PDGF-B protein in macrophages in all phases of atherogenesis. Science. 1990 May 25;248(4958):1009–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.2343305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. Platelet-derived growth factor. Lancet. 1989 May 27;1(8648):1179–1182. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92760-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M., Emmons L. R., Perruchoud A., Block L. H. Expressions of the low density lipoprotein receptor and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase genes are stimulated by recombinant platelet-derived growth factor isomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1888–1892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachinidis A., Locher R., Vetter W., Tatje D., Hoppe J. Different effects of platelet-derived growth factor isoforms on rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10238–10243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T. Signal transduction by the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1564–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.2538922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



