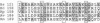Abstract
The levanase operon in Bacillus subtilis is expressed from a -12, -24 promoter and transcription is stimulated by the regulator LevR, which contains a domain homologous with the central domain of the NifA and NtrC family of regulators. We isolated mutants defective in the expression of the levanase operon. These strains contain mutations that define a gene, called sigL, located between cysB and sacB on the genetic map. The sigL gene was cloned and sequenced. It encodes a polypeptide containing 436 residues with a molecular weight of 49,644. The amino acid sequence of SigL is homologous with all sigma 54 factors from Gram-negative bacteria, including Rhizobium meliloti (32% identity) and Klebsiella pneumoniae (30% identity). B. subtilis sigL mutants have a pleiotropic phenotype: (i) the transcription of the levanase operon is strongly reduced and (ii) in minimal medium lacking ammonia, sigL mutants cannot grow when arginine, ornithine, isoleucine, or valine is the sole nitrogen source. These results indicate that the sigL gene encodes an equivalent of the sigma 54 factor in B. subtilis, to our knowledge, the first of this type to be identified in Gram-positive bacteria.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson M. R., Fisher S. H. Identification of genes and gene products whose expression is activated during nitrogen-limited growth in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):23–27. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.23-27.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. R., Wray L. V., Jr, Fisher S. H. Regulation of histidine and proline degradation enzymes by amino acid availability in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4758–4765. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4758-4765.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd I. B., Egan J. B. Improved detection of helix-turn-helix DNA-binding motifs in protein sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5019–5026. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Débarbouillé M., Martin-Verstraete I., Klier A., Rapoport G. The transcriptional regulator LevR of Bacillus subtilis has domains homologous to both sigma 54- and phosphotransferase system-dependent regulators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2212–2216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. H., Rosenkrantz M. S., Sonenshein A. L. Glutamine synthetase gene of Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gassel M., Alonso J. C. Expression of the recE gene during induction of the SOS response in Bacillus subtilis recombination-deficient strains. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1269–1276. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kullik I., Fritsche S., Knobel H., Sanjuan J., Hennecke H., Fischer H. M. Bradyrhizobium japonicum has two differentially regulated, functional homologs of the sigma 54 gene (rpoN). J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1125–1138. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1125-1138.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunst F., Debarbouille M., Msadek T., Young M., Mauel C., Karamata D., Klier A., Rapoport G., Dedonder R. Deduced polypeptides encoded by the Bacillus subtilis sacU locus share homology with two-component sensor-regulator systems. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5093–5101. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5093-5101.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S., Santero E., Keener J., Popham D., Weiss D. Expression of sigma 54 (ntrA)-dependent genes is probably united by a common mechanism. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):367–376. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.367-376.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepesant J. A., Kunst F., Lepesant-Kejzlarová J., Dedonder R. Chromosomal location of mutations affecting sucrose metabolism in Bacillus subtilis Marburg. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;118(2):135–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00267084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lereclus D., Arantès O., Chaufaux J., Lecadet M. Transformation and expression of a cloned delta-endotoxin gene in Bacillus thuringiensis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jul 15;51(1):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90511-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Verstraete I., Débarbouillé M., Klier A., Rapoport G. Levanase operon of Bacillus subtilis includes a fructose-specific phosphotransferase system regulating the expression of the operon. J Mol Biol. 1990 Aug 5;214(3):657–671. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90284-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin I., Debarbouille M., Klier A., Rapoport G. Induction and metabolite regulation of levanase synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):1885–1892. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.1885-1892.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin I., Débarbouillé M., Ferrari E., Klier A., Rapoport G. Characterization of the levanase gene of Bacillus subtilis which shows homology to yeast invertase. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jun;208(1-2):177–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00330439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick M. J., Gibbins J. R. The nucleotide sequence of the nitrogen-regulation gene ntrA of Klebsiella pneumoniae and comparison with conserved features in bacterial RNA polymerase sigma factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7607–7620. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick M., Gibbins J., Toukdarian A. The nucleotide sequence of the sigma factor gene ntrA (rpoN) of Azotobacter vinelandii: analysis of conserved sequences in NtrA proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(2):323–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00325701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano Y., Tanaka E., Kato C., Kimura K., Horikoshi K. The complete nucleotide sequence of the glutamine synthetase gene (glnA) of Bacillus subtilis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jan 1;48(1):81–86. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90151-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronson C. W., Nixon B. T., Albright L. M., Ausubel F. M. Rhizobium meliloti ntrA (rpoN) gene is required for diverse metabolic functions. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2424–2431. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2424-2431.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasse-Dwight S., Gralla J. D. Role of eukaryotic-type functional domains found in the prokaryotic enhancer receptor factor sigma 54. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):945–954. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90269-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier H. J., Brown S. W., Hirschi K. D., Nomellini J. F., Sonenshein A. L. Regulation of Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase gene expression by the product of the glnR gene. J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 5;210(1):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch M. A., Aronson A. I., Brown S. W., Schreier H. J., Sonenhein A. L. Sequence of the Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase gene region. Gene. 1988 Nov 30;71(2):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan M. A., Yasbin R. E., Young F. E. New shuttle vectors for Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli which allow rapid detection of inserted fragments. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90161-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thöny B., Hennecke H. The -24/-12 promoter comes of age. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;5(4):341–357. doi: 10.1016/0168-6445(89)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trieu-Cuot P., Courvalin P. Nucleotide sequence of the Streptococcus faecalis plasmid gene encoding the 3'5"-aminoglycoside phosphotransferase type III. Gene. 1983 Sep;23(3):331–341. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]