Figure 1.
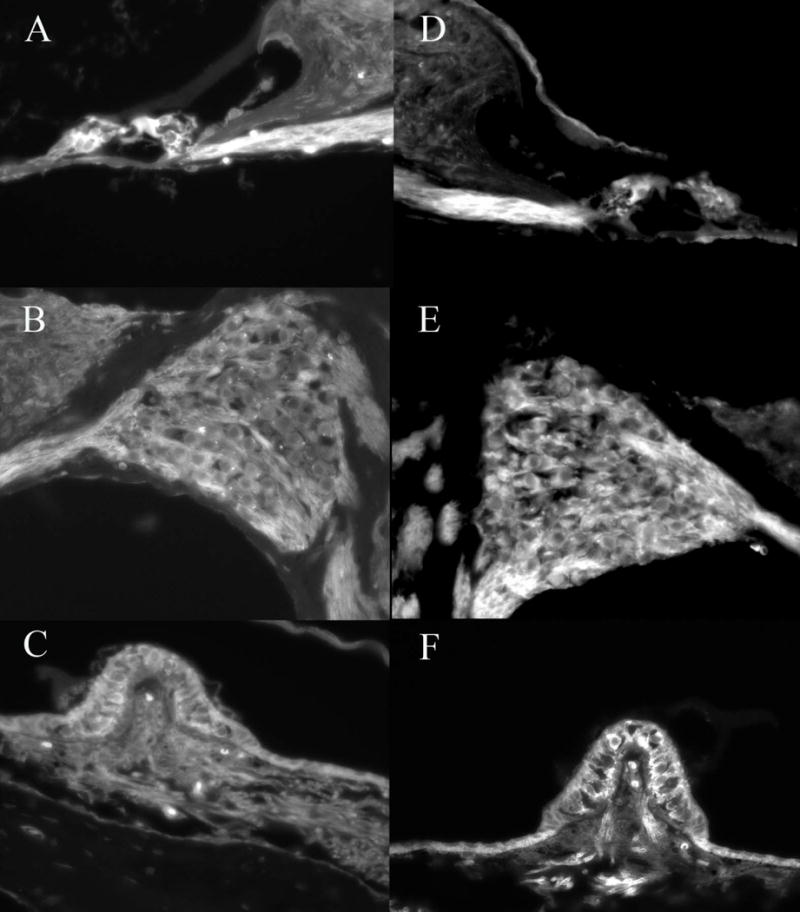
Delivery of Adf to the basal turn of the mouse cochlea resulted in expression of GFP in the inner and outer hair cells (A), auditory neurons (B) and supporting as well as sensory cells in the vestibular system (C). Ablation of CAR and integrin binding capacity results in similar GFP distribution patterns (E,F,G). No clear differences in GFP intensity or distribution were noted with any of the capsid ablated vectors when used in high concentration. This demonstrates that integrin binding or CAR binding is not necessary for entry of the vector into the cells of the inner ear and suggests that secondary vector entry mechanisms exist.
