Abstract
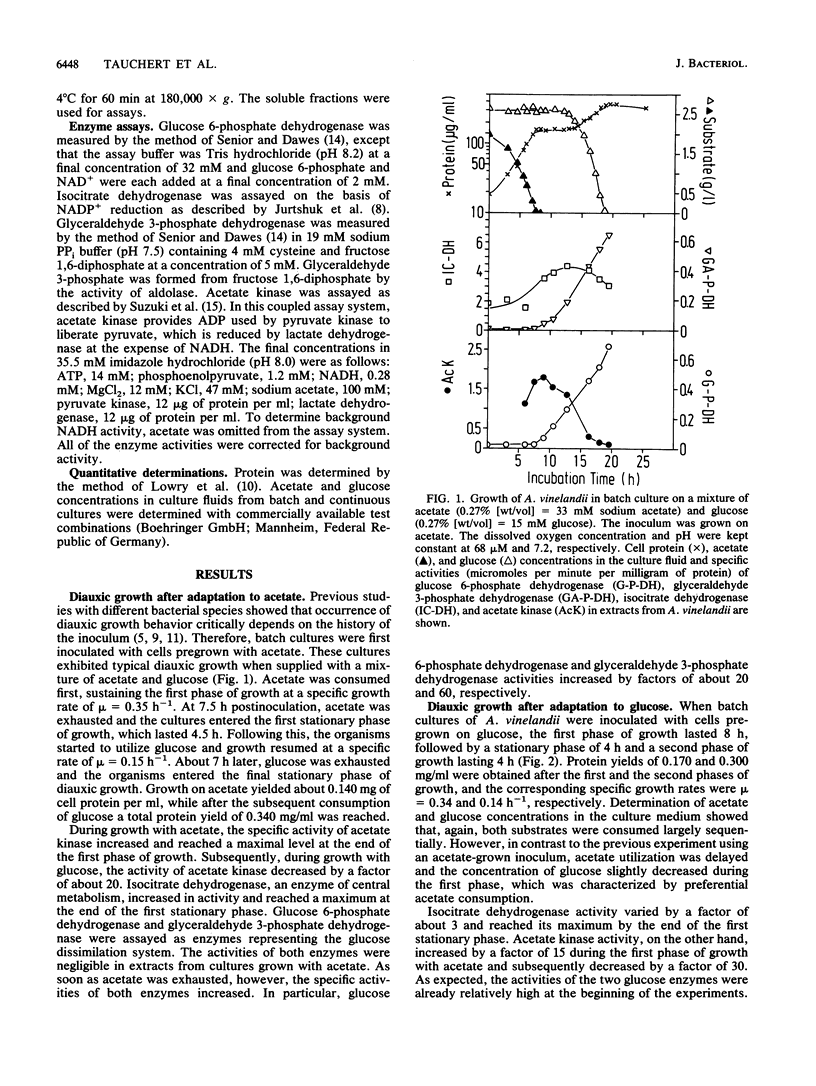
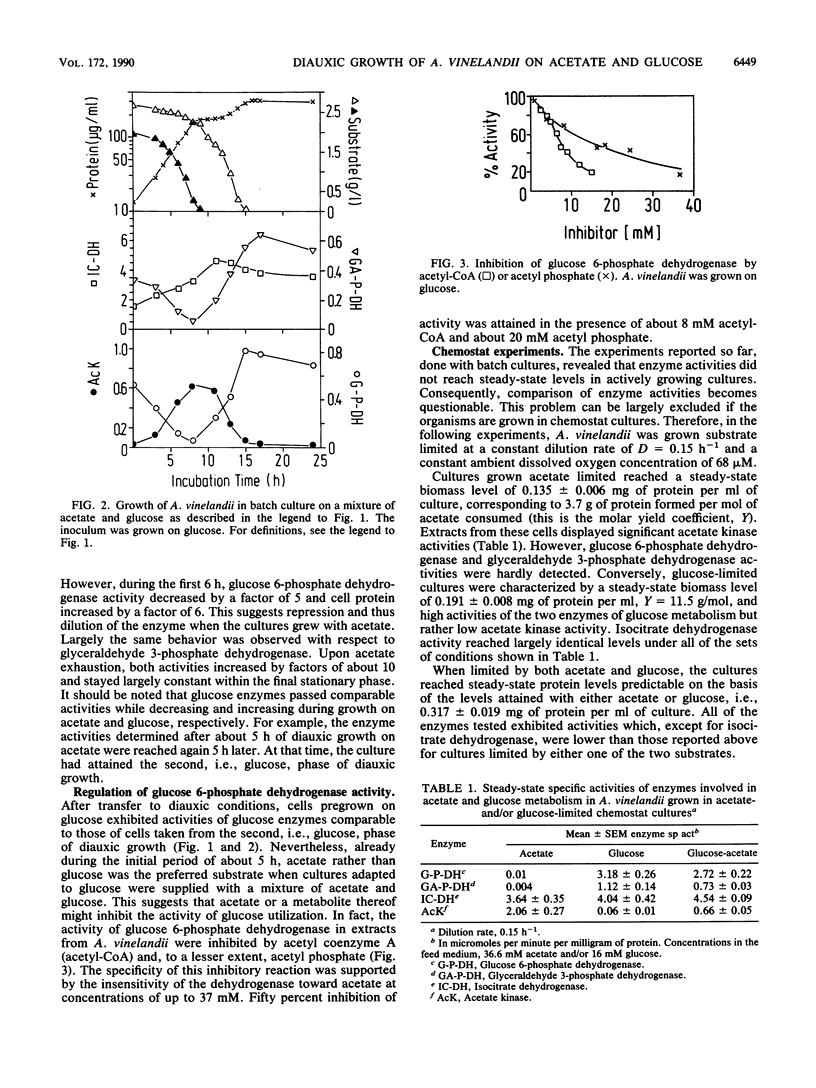
Batch cultures of Azotobacter vinelandii were inoculated with cells pregrown on either acetate or glucose. When they were subsequently grown on a mixture of acetate and glucose, typical diauxic growth was observed, with preferential uptake of acetate in the first and glucose in the second phase of growth. Extracts from acetate-pregrown cells exhibited high acetate kinase activity in the first phase of growth. This activity decreased and activities of the two glucose enzymes glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase increased in the second phase. Extracts from glucose-pregrown cells exhibited high initial activities of the two glucose enzymes, which decreased while acetate kinase activity increased in the first phase of growth. Again, in the second phase, activities of the two glucose enzymes increased and acetate kinase activity decreased. In any case, isocitrate dehydrogenase activity varied only slightly and unspecifically. The differences in enzyme activity and the constancy of isocitrate dehydrogenase were confirmed by experiments with either acetate- or glucose-limited chemostats. In chemostats in which both of the substrates were limiting, all of the enzymes displayed significant activities. Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity was inhibited by acetyl coenzyme A and acetyl phosphate but not by acetate. It is proposed that diauxic growth is based on the control of enzymes involved in acetate or glucose dissimilation by which acetate or its metabolites control the expression and activity of glucose enzymes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- George S. E., Costenbader C. J., Melton T. Diauxic growth in Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):866–871. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.866-871.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder W., Dijkhuizen L. Strategies of mixed substrate utilization in microorganisms. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Jun 11;297(1088):459–480. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurtshuk P., Barrera C. R., Manning S. The use of sephadex for the electrophoretic resolution and partial purification of beta-hydroxybutyric and isocitric dehydrogenases of Azotobacter vinelandii. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Apr;15(4):321–325. doi: 10.1139/m69-060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Ensign J. C. Alteration of glucose metabolism of Arthrobacter crystallopoietes by compounds which induce sphere to rod morphogenesis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):526–534. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.526-534.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch W. H., Franklin M. Effect of temperature on diauxic growth with glucose and organic acids in Pseudomonas fluorescens. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Aug 1;118(2):133–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00415721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenney D., Melton T. Isolation and characterization of ack and pta mutations in Azotobacter vinelandii affecting acetate-glucose diauxie. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):6–12. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.6-12.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior P. J., Dawes E. A. Poly- -hydroxybutyrate biosynthesis and the regulation of glucose metabolism in Azotobacter beijerinckii. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):55–66. doi: 10.1042/bj1250055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Nakajima H., Imahori K. Acetate kinase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Methods Enzymol. 1982;90(Pt E):179–185. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



