Abstract
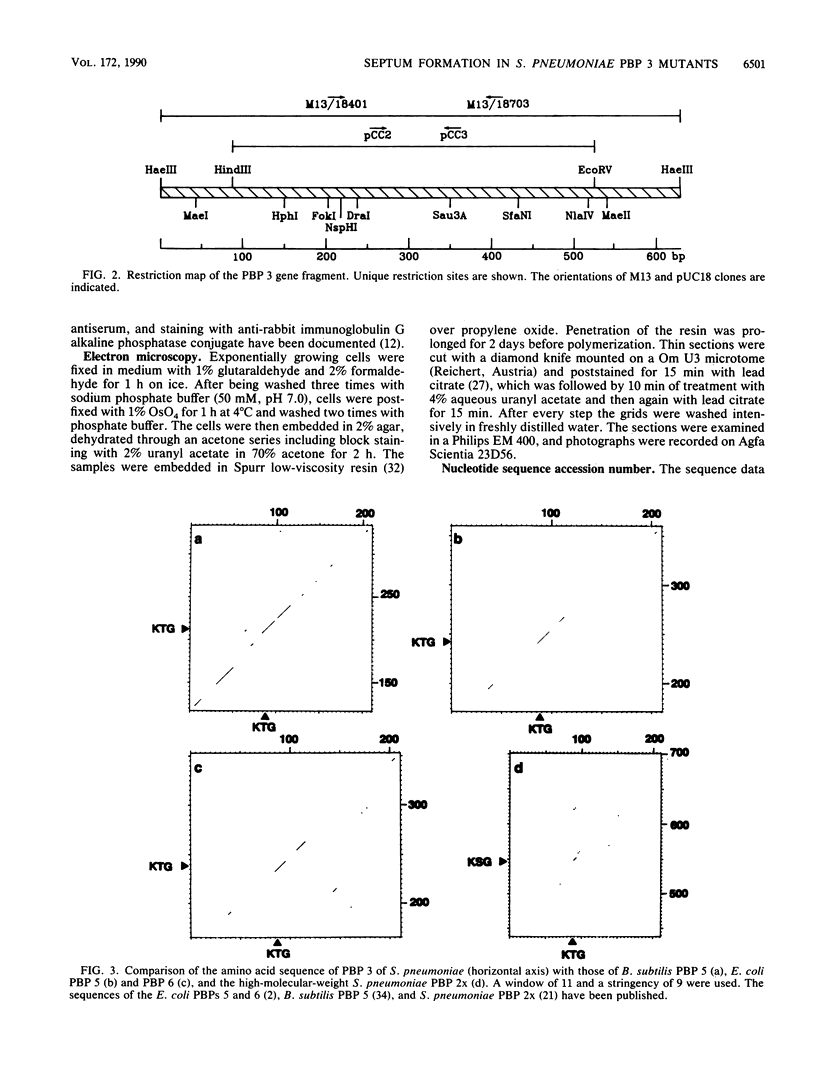
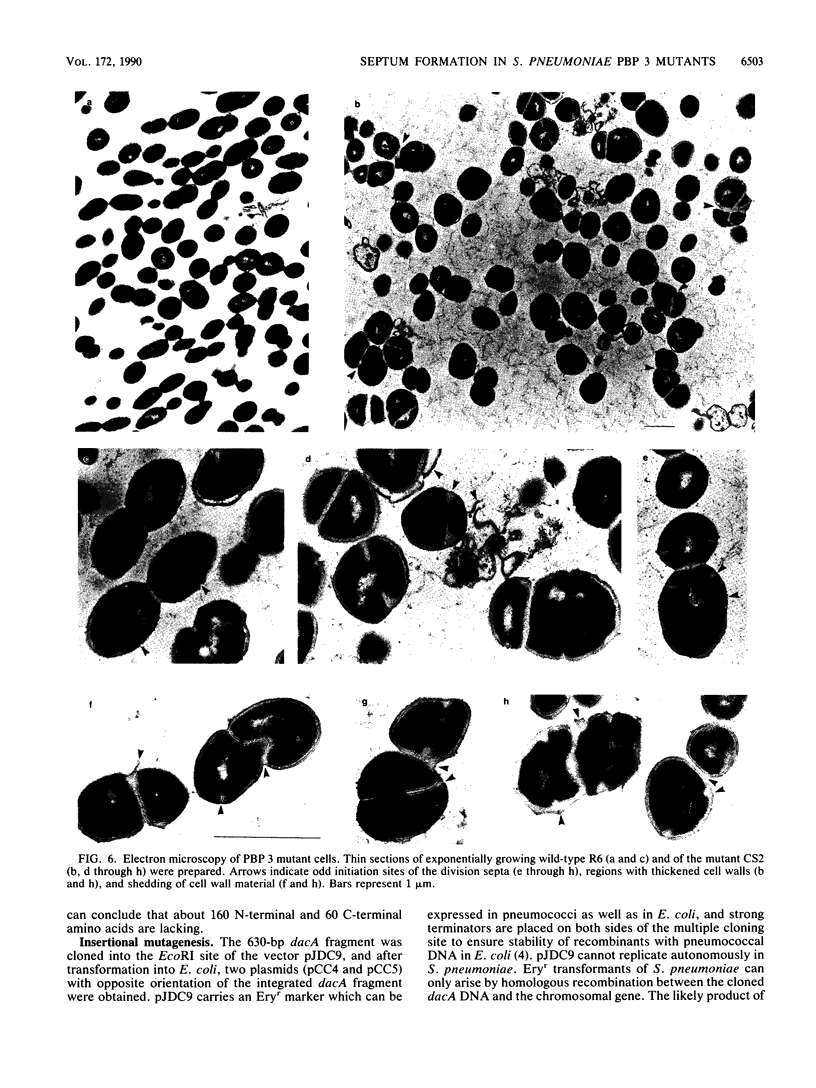
An internal 630-bp DNA fragment of the gene encoding penicillin-binding protein 3 (PBP 3) (dacA) of Streptococcus pneumoniae was identified in a lambda gt11 gene bank screened with anti-PBP 3 antiserum. The deduced 210-amino-acid sequence showed a high degree of homology to the low-molecular-weight PBPs 5 and 6 of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis PBP 5. Viable mutants lacking a C-terminal part of PBP 3 were obtained after a plasmid containing the dacA fragment was integrated into the PBP 3 gene by homologous recombination. The truncated PBP 3* was still active in terms of beta-lactam binding. Most PBP 3 was found in the growth medium, indicating that membrane anchoring of PBP 3 is provided by the C terminus, as has been shown for other D,D-carboxypeptidases. The mutant cells grew with a slower generation time than the wild type in the shape of irregular enlarged spheres. In addition, as revealed by electron microscopy, cell separation was severely affected, septa were found unevenly distributed at multiple sites within the cells, and the murein layer appeared variable in thickness.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broome-Smith J. K. Construction of a mutant of Escherichia coli that has deletions of both the penicillin-binding protein 5 and 6 genes. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Aug;131(8):2115–2118. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-8-2115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broome-Smith J. K., Ioannidis I., Edelman A., Spratt B. G. Nucleotide sequences of the penicillin-binding protein 5 and 6 genes of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1617–1617. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broome-Smith J. K., Spratt B. G. Deletion of the penicillin-binding protein 6 gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):904–906. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.904-906.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. D., Morrison D. A. Construction and properties of a new insertion vector, pJDC9, that is protected by transcriptional terminators and useful for cloning of DNA from Streptococcus pneumoniae. Gene. 1988 Apr 15;64(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90489-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellerbrok H., Hakenbeck R. Penicillin-binding proteins of Streptococcus pneumoniae: characterization of tryptic peptides containing the beta-lactam-binding site. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 2;144(3):637–641. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frère J. M., Joris B. Penicillin-sensitive enzymes in peptidoglycan biosynthesis. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1985;11(4):299–396. doi: 10.3109/10408418409105906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakenbeck R., Briese T., Ellerbrok H. Antibodies against the benzylpenicilloyl moiety as a probe for penicillin-binding proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1986 May 15;157(1):101–106. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09644.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakenbeck R., Ellerbrok H., Briese T., Handwerger S., Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding proteins of penicillin-susceptible and -resistant pneumococci: immunological relatedness of altered proteins and changes in peptides carrying the beta-lactam binding site. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Oct;30(4):553–558. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.4.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakenbeck R., Kohiyama M. Purification of penicillin-binding protein 3 from Streptococcus pneumoniae. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Oct;127(2):231–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakenbeck R., Tornette S., Adkinson N. F. Interaction of non-lytic beta-lactams with penicillin-binding proteins in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):755–760. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. E., Pratt J. M. Analysis of the membrane-binding domain of penicillin-binding protein 5 of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Sep;2(5):563–568. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joris B., Ghuysen J. M., Dive G., Renard A., Dideberg O., Charlier P., Frère J. M., Kelly J. A., Boyington J. C., Moews P. C. The active-site-serine penicillin-recognizing enzymes as members of the Streptomyces R61 DD-peptidase family. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 1;250(2):313–324. doi: 10.1042/bj2500313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACKS S., HOTCHKISS R. D. A study of the genetic material determining an enzyme in Pneumococcus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Apr 22;39:508–518. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90205-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laible G., Hakenbeck R. Penicillin-binding proteins in beta-lactam-resistant laboratory mutants of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Nov;1(3):355–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb01942.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laible G., Hakenbeck R., Sicard M. A., Joris B., Ghuysen J. M. Nucleotide sequences of the pbpX genes encoding the penicillin-binding proteins 2x from Streptococcus pneumoniae R6 and a cefotaxime-resistant mutant, C506. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1337–1348. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markiewicz Z., Broome-Smith J. K., Schwarz U., Spratt B. G. Spherical E. coli due to elevated levels of D-alanine carboxypeptidase. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):702–704. doi: 10.1038/297702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Yashouv-Gan Y., Nuchamovitz Y., Rozenhak S., Ron E. Z. Murein biosynthesis during a synchromous cell cycle of Escherichia coli B. J Bacteriol. 1978 May;134(2):458–461. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.2.458-461.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura Y., Suzuki H., Hirota Y., Park J. T. A mutant of Escherichia coli defective in penicillin-binding protein 5 and lacking D-alanine carboxypeptidase IA. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):531–534. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.531-534.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor C. G., Ashman L. K. Application of the nitrocellulose transfer technique and alkaline phosphatase conjugated anti-immunoglobulin for determination of the specificity of monoclonal antibodies to protein mixtures. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Oct 29;54(2):267–271. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt J. M., Jackson M. E., Holland I. B. The C terminus of penicillin-binding protein 5 is essential for localisation to the E. coli inner membrane. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2399–2405. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04510.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Cromie K. D. Penicillin-binding proteins of gram-negative bacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):699–711. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Deletion of the penicillin-binding protein 5 gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1190–1192. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1190-1192.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiraby J. G., Fox M. S. Marker discrimination and mutagen-induced alterations in pneumococcal transformation. Genetics. 1974 Jul;77(3):449–458. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.3.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. A., Roberts A. N., Johnstone K., Piggot P. J., Winter G., Ellar D. J. Reduced heat resistance of mutant spores after cloning and mutagenesis of the Bacillus subtilis gene encoding penicillin-binding protein 5. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):257–264. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.257-264.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Strominger J. L. Primary structure of the COOH-terminal membranous segment of a penicillin-sensitive enzyme purified from two Bacilli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):2067–2077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., Hakenbeck R., Tomasz A. In vivo interaction of beta-lactam antibiotics with the penicillin-binding proteins of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Oct;18(4):629–637. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.4.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyke A. W., Ward J. B., Hayes M. V., Curtis N. A. A role in vivo for penicillin-binding protein-4 of Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Oct;119(2):389–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]