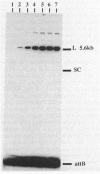
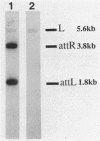
Abstract
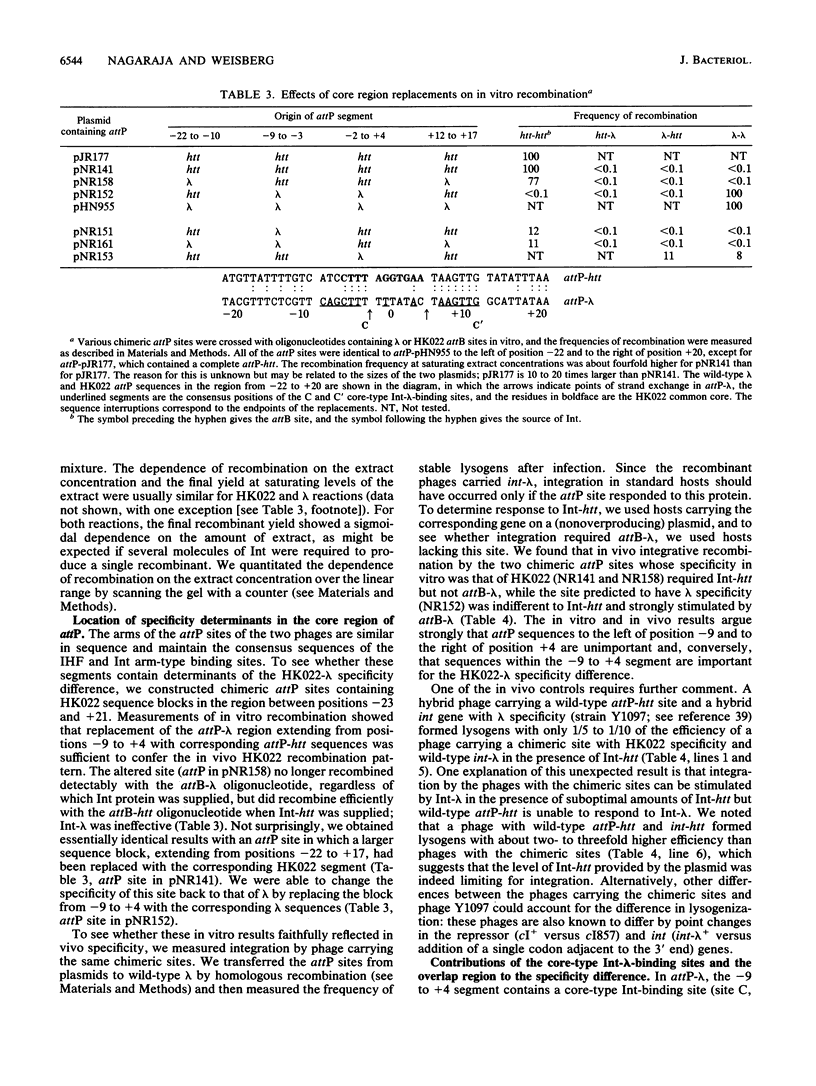
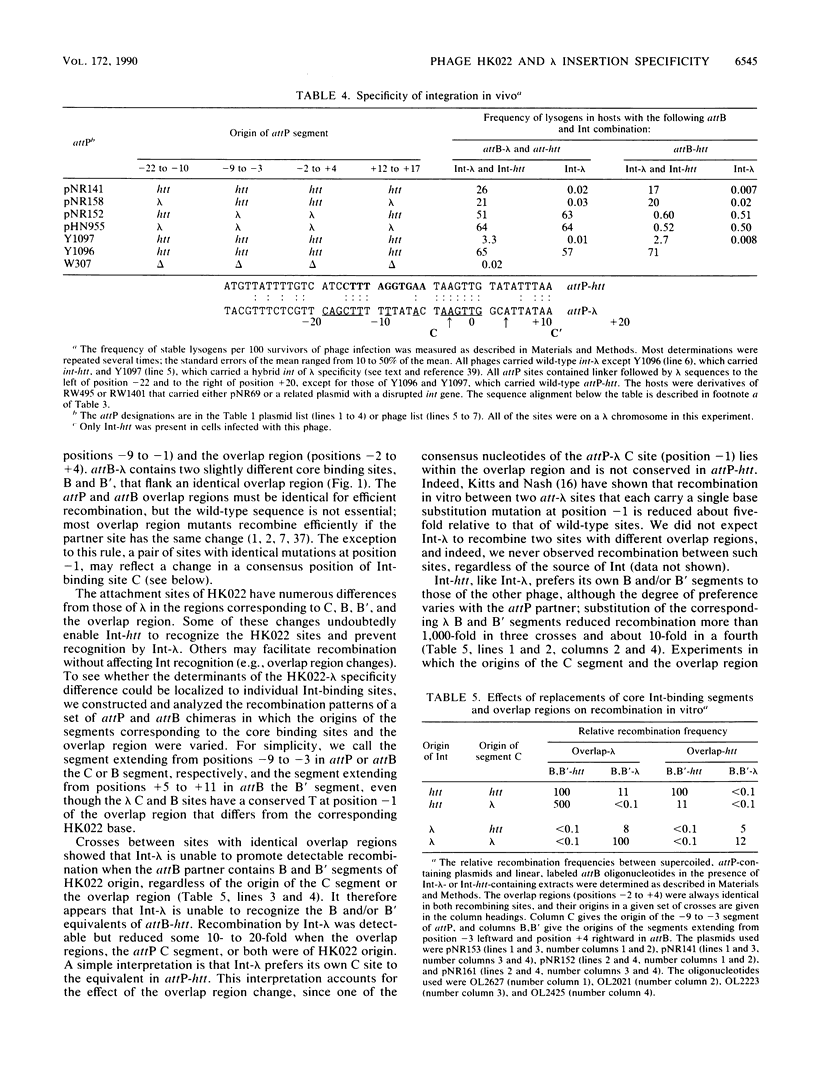
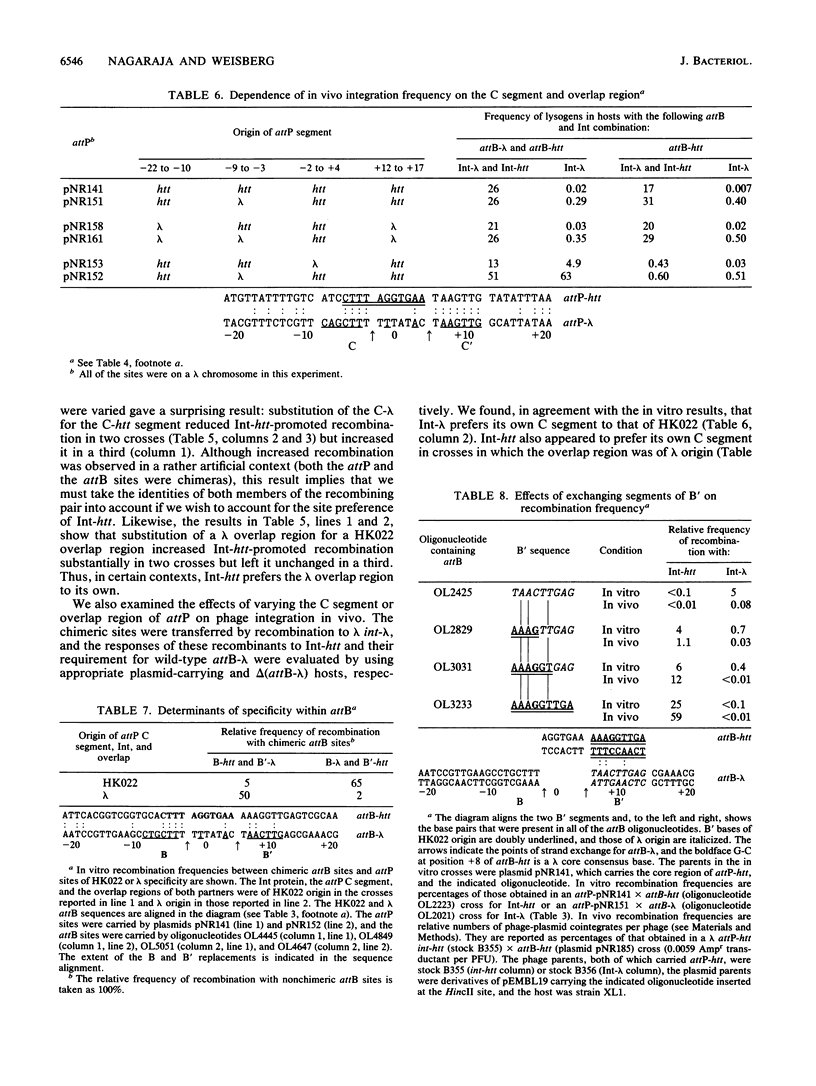
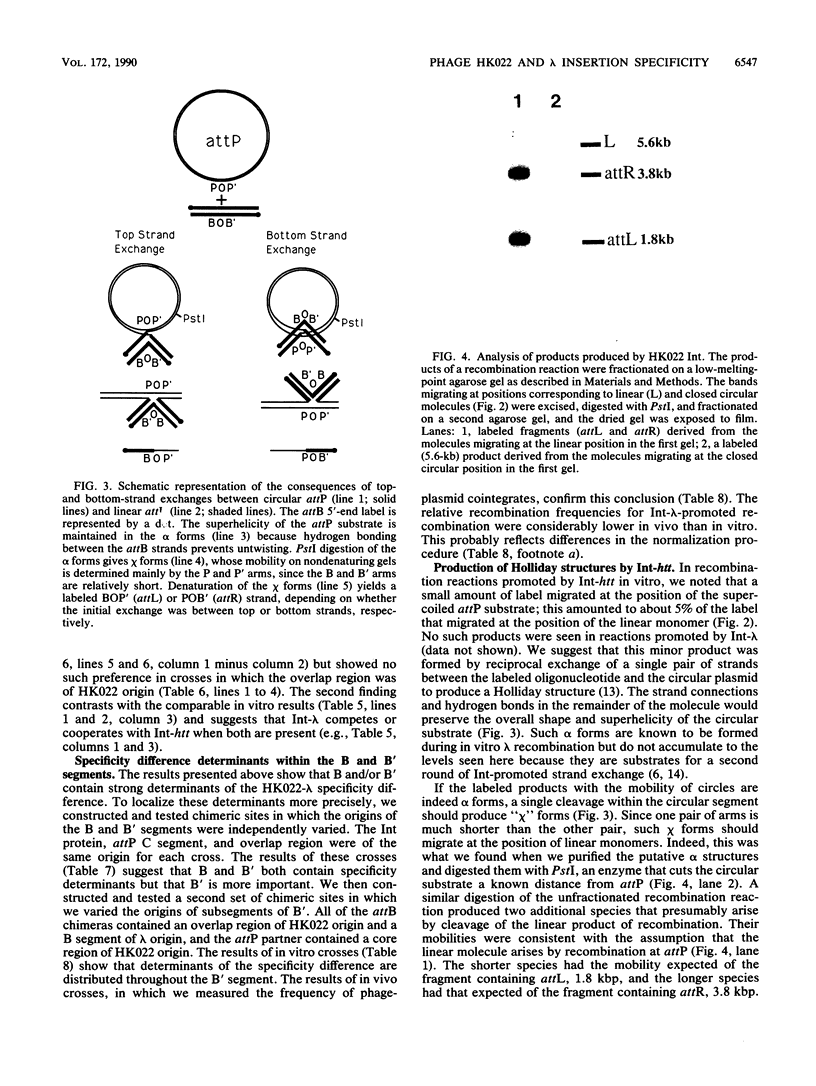
The Int proteins of bacteriophages HK022 and lambda promote recombination between phage and bacterial attachment sites. Although the proteins and attachment sites of the two phages are similar, neither protein promotes efficient recombination between the pair of attachment sites used by the other phage. To analyze this difference in specificity, we constructed and characterized chimeric attachment sites in which segments of one site were replaced with corresponding segments of the other. Most such chimeras recombined with appropriate partner sites in vivo and in vitro, and their differential responses to the Int proteins of the two phages allowed us to locate determinants of the specificity difference in the bacterial attachment sites and a central segment of the phage attachment sites. The location of these determinants encompasses three of the four core-type binding sites for lambda Int: C, B, and most importantly, B'. The regions corresponding to the C' core binding site and the arm-type binding sites of lambda Int play no role in the specificity difference and, indeed, are well conserved in the two phages. We found, unexpectedly, that the effect of replacement of an Int-binding region on the recombinational potency of one chimeric site was reversed by a change of partner. This novel context effect suggests that postsynaptic interactions affect the specificity of recognition of attachment sites by Int.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer C. E., Gardner J. F., Gumport R. I. Extent of sequence homology required for bacteriophage lambda site-specific recombination. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 20;181(2):187–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer C. E., Gardner J. F., Gumport R. I., Weisberg R. A. The effect of attachment site mutations on strand exchange in bacteriophage lambda site-specific recombination. Genetics. 1989 Aug;122(4):727–736. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.4.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L., Nash H. A. E. coli integration host factor binds to specific sites in DNA. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):707–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90478-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L., Nash H. A. The mechanism of phage lambda site-specific recombination: site-specific breakage of DNA by Int topoisomerase. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):795–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon T. S. Temperate coliphage HK022: virions, DNA, one-step growth, attachment site, and the prophage genetic map. J Gen Virol. 1981 Aug;55(Pt 2):487–492. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-55-2-487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L. W., Nash H., Weisberg R. A. Strand exchange in site-specific recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1363–1367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L. W., Weisberg R. A. An integration-proficient int mutant of bacteriophage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1-2):62–69. doi: 10.1007/BF00332725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L. W., Weisberg R. A. The red plaque test: a rapid method for identification of excision defective variants of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1976 Jul 1;72(1):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90319-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu P. L., Landy A. Resolution of synthetic att-site Holliday structures by the integrase protein of bacteriophage lambda. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):721–726. doi: 10.1038/311721a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Nash H. A. Nicking-closing activity associated with bacteriophage lambda int gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3760–3764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Nash H. A. An intermediate in the phage lambda site-specific recombination reaction is revealed by phosphorothioate substitution in DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):6839–6856. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Nash H. A. Bacteriophage lambda site-specific recombination proceeds with a defined order of strand exchanges. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):95–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90602-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Nash H. A. Homology-dependent interactions in phage lambda site-specific recombination. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):346–348. doi: 10.1038/329346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy A., Ross W. Viral integration and excision: structure of the lambda att sites. Science. 1977 Sep 16;197(4309):1147–1160. doi: 10.1126/science.331474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. C., Gumport R. I., Gardner J. F. Genetic analysis of bacteriophage lambda integrase interactions with arm-type attachment site sequences. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1529–1538. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1529-1538.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffatt B. A., Studier F. W. T7 lysozyme inhibits transcription by T7 RNA polymerase. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):221–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90563-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moitoso de Vargas L., Pargellis C. A., Hasan N. M., Bushman E. W., Landy A. Autonomous DNA binding domains of lambda integrase recognize two different sequence families. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):923–929. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Purification and properties of the bacteriophage lambda Int protein. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:210–216. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A., Robertson C. A. Heteroduplex substrates for bacteriophage lambda site-specific recombination: cleavage and strand transfer products. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3523–3533. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08518.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes-Düby S. E., Matsumoto L., Landy A. Site-specific recombination intermediates trapped with suicide substrates. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):779–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberto J., Weisberg R. A., Gottesman M. E. Structure and function of the nun gene and the immunity region of the lambdoid phage HK022. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jun 20;207(4):675–693. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90237-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richet E., Abcarian P., Nash H. A. Synapsis of attachment sites during lambda integrative recombination involves capture of a naked DNA by a protein-DNA complex. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90526-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richet E., Abcarian P., Nash H. A. The interaction of recombination proteins with supercoiled DNA: defining the role of supercoiling in lambda integrative recombination. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1011–1021. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90700-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Landy A. Bacteriophage lambda int protein recognizes two classes of sequence in the phage att site: characterization of arm-type sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7724–7728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Landy A. Patterns of lambda Int recognition in the regions of strand exchange. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90355-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisberg R. A., Enquist L. W., Foeller C., Landy A. Role for DNA homology in site-specific recombination. The isolation and characterization of a site affinity mutant of coliphage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 25;170(2):319–342. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80151-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagil E., Dolev S., Oberto J., Kislev N., Ramaiah N., Weisberg R. A. Determinants of site-specific recombination in the lambdoid coliphage HK022. An evolutionary change in specificity. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jun 20;207(4):695–717. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin S., Bushman W., Landy A. Interaction of the lambda site-specific recombination protein Xis with attachment site DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1040–1044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Massy B., Dorgai L., Weisberg R. A. Mutations of the phage lambda attachment site alter the directionality of resolution of Holliday structures. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1591–1599. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03543.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Massy B., Studier F. W., Dorgai L., Appelbaum E., Weisberg R. A. Enzymes and sites of genetic recombination: studies with gene-3 endonuclease of phage T7 and with site-affinity mutants of phage lambda. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:715–726. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]