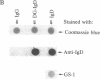
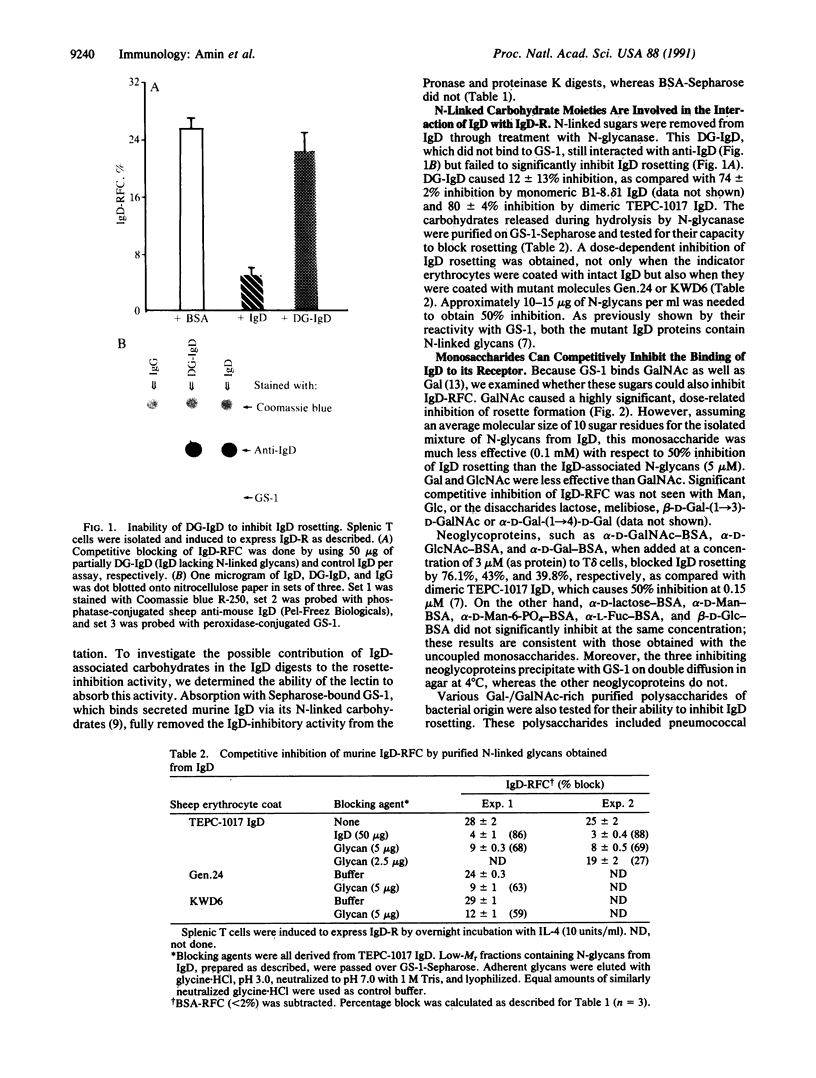
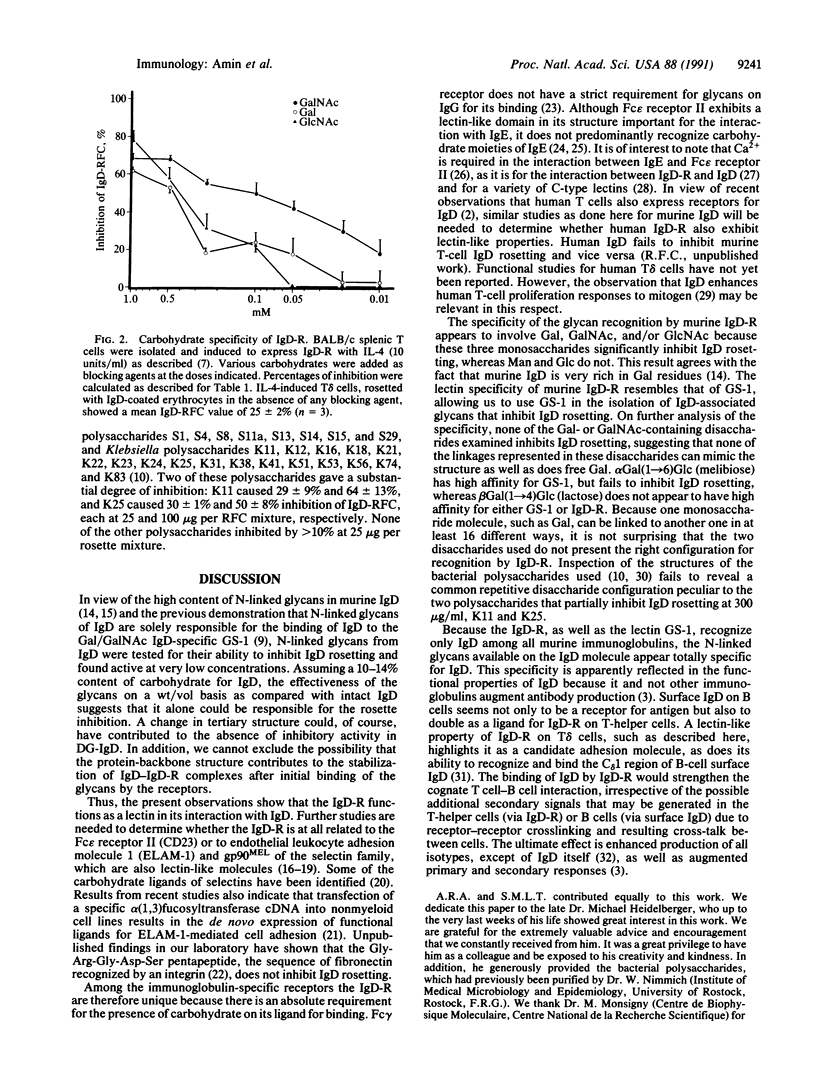
Abstract
IgD receptors on murine T cells have been reported in this issue [Tamma, S. M. L., Amin, A. R., Finkelman, F. D., Chen, Y.-W., Thorbecke, G. J. & Coico, R. F. (1991) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 9233-9237] to bind either the first or third constant region of the heavy-chain of IgD molecules--findings that could not be satisfactorily explained by IgD amino acid sequences. We now find that boiled IgD molecules or low-Mr fragments from protease-digested IgD still inhibit binding of IgD-coated erythrocytes to IgD receptors. This inhibitory activity can be absorbed with the murine IgD-binding lectin from Griffonia simplicifolia 1 (GS-1) immobilized on Sepharose. N-linked glycans, obtained from N-glycanase-treated IgD and purified by binding to GS-1-Sepharose, also inhibit rosette formation of T-helper cells bearing receptors for IgD with IgD- or mutant IgD-coated erythrocytes. Deglycosylated IgD, produced by treatment with N-glycanase, no longer binds to the lectin and fails to inhibit IgD rosetting. Binding of intact IgD to T cells is also competitively inhibited by N-acetylgalactosamine, galactose, N-acetylglucosamine, and neoglycoproteins containing these sugars. These results clearly show that N-linked glycans, present in both the first and third constant regions of the delta heavy-chain domains, are prerequisites for binding of IgD to IgD receptors.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amin A. R., Coico R. F., Finkelman F., Siskind G. W., Thorbecke G. J. Release of IgD-binding factor by T cells under the influence of interleukin 2, interleukin 4, or cross-linked IgD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9179–9183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amin A. R., Coico R. F., Thorbecke G. J. Characterization and regulation of T-cell IgD receptors and IgD-binding factor. Res Immunol. 1990 Jan;141(1):94–108. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(90)90110-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argon Y., Milstein C. Intracellular processing of membrane and secreted immunoglobulin delta-chains. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1627–1634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettler B., Maier R., Rüegg D., Hofstetter H. Binding site for IgE of the human lymphocyte low-affinity Fc epsilon receptor (Fc epsilon RII/CD23) is confined to the domain homologous with animal lectins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7118–7122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Stengelin S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Seed B. Endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1: an inducible receptor for neutrophils related to complement regulatory proteins and lectins. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1160–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.2466335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandley B. K., Swiedler S. J., Robbins P. W. Carbohydrate ligands of the LEC cell adhesion molecules. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):861–863. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90487-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger D. R., Regan D., Williams K., Leslie G. Human T-cell activation is augmented by monoclonal antibody to IgD. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;399:227–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coico R. F., Berzofsky J. A., York-Jolley J., Ozaki S., Siskind G. W., Thorbecke G. J. Physiology of IgD. VII. Induction of receptors for IgD on cloned T cells by IgD and interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 1;138(1):4–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coico R. F., Finkelman F., Swenson C. D., Siskind G. W., Thorbecke G. J. Exposure to crosslinked IgD induces receptors for IgD on T cells in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):559–563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coico R. F., Siskind G. W., Thorbecke G. J. Role of IgD and T delta cells in the regulation of the humoral immune response. Immunol Rev. 1988 Oct;105:45–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00765.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coico R. F., Tamma S. L., Bessler M., Wei C. F., Thorbecke G. J. IgD-receptor-positive human T lymphocytes. I. Modulation of receptor expression by oligomeric IgD and lymphokines. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 1;145(11):3556–3561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coico R. F., Xue B., Wallace D., Pernis B., Siskind G. W., Thorbecke G. J. T cells with receptors for IgD. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):744–746. doi: 10.1038/316744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drickamer K. Two distinct classes of carbohydrate-recognition domains in animal lectins. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9557–9560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidelberger M., Nimmich W. Immunochemical relationships between bacteria belonging to two separate families: pneumococci and Klebsiella. Immunochemistry. 1976 Jan;13(1):67–80. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90299-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikuta K., Takami M., Kim C. W., Honjo T., Miyoshi T., Tagaya Y., Kawabe T., Yodoi J. Human lymphocyte Fc receptor for IgE: sequence homology of its cloned cDNA with animal lectins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):819–823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieda C., Roche A. C., Delmotte F., Monsigny M. Lymphocyte membrane lectins. Direct visualization by the use of fluoresceinyl-glycosylated cytochemical markers. FEBS Lett. 1979 Mar 15;99(2):329–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80984-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Singer M. S., Yednock T. A., Dowbenko D., Fennie C., Rodriguez H., Nguyen T., Stachel S., Rosen S. D. Cloning of a lymphocyte homing receptor reveals a lectin domain. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):1045–1055. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90637-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J. B., Stoolman L. M., Nair R. P., Larsen R. D., Berhend T. L., Marks R. M. ELAM-1--dependent cell adhesion to vascular endothelium determined by a transfected human fucosyltransferase cDNA. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):475–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90444-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy L. A., Goldstein I. J. Five alpha-D-galactopyranosyl-binding isolectins from Bandeiraea simplicifolia seeds. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 10;252(13):4739–4742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim J. D., Amin A. R., Thorbecke G. J. A rapid one step purification procedure for murine IgD based on the specific affinity of Bandeiraea (Griffonia) simplicifolia-1 for N-linked carbohydrates on IgD. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Jul 3;130(2):243–250. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90054-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppard J. V., Hobbs S. M., Jackson L. E. Role of carbohydrate in binding of IgG to the Fc receptor of neonatal rat enterocytes. Mol Immunol. 1989 May;26(5):495–500. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90109-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards M. L., Katz D. H. The binding of IgE to murine Fc epsilon RII is calcium-dependent but not inhibited by carbohydrate. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2638–2646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelman M. H., van de Rijn M., Weissman I. L. Mouse lymph node homing receptor cDNA clone encodes a glycoprotein revealing tandem interaction domains. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1165–1172. doi: 10.1126/science.2646713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson C. D., Van Vollenhoven R. F., Xue B., Siskind G. W., Thorbecke G. J., Coico R. F. Physiology of IgD. IX. Effect of IgD on immunoglobulin production in young and old mice. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jan;18(1):13–20. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamma S. M., Amin A. R., Finkelman F. D., Chen Y. W., Thorbecke G. J., Coico R. F. IgD receptors on murine T-helper cells bind to Fd and Fc regions of immunoglobulin D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9233–9237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker P. W., Cheng H. L., Richards J. E., Fitzmaurice L., Mushinski J. F., Blattner F. R. Genetic aspects of IgD expression: III. Functional implications of the sequence and organization of the C delta gene. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;399:26–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilov R. G., Ploegh H. L. Biosynthesis of murine immunoglobulin D: heterogeneity of glycosylation. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Oct;12(10):804–813. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830121003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercelli D., Helm B., Marsh P., Padlan E., Geha R. S., Gould H. The B-cell binding site on human immunoglobulin E. Nature. 1989 Apr 20;338(6217):649–651. doi: 10.1038/338649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]