Abstract
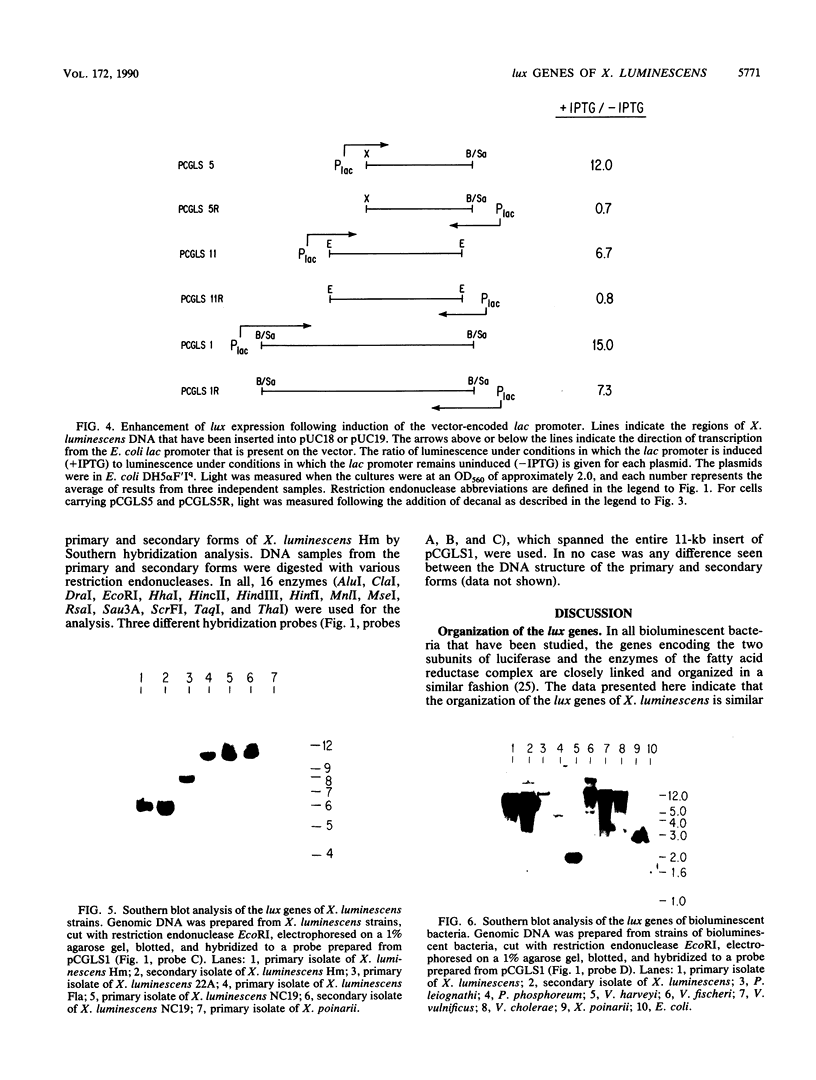
The lux genes of Xenorhabdus luminescens, a symbiont of the nematode Heterorhabditis bacteriophora, were cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. The expression of these genes in E. coli was qualitatively similar to their expression in X. luminescens. The organization of the genes is similar to that found in the marine luminous bacteria. Hybridization studies with the DNA that codes for the two subunits of luciferase revealed considerable homology among all of the strains of X. luminescens and with the DNA of other species of luminous bacteria, but none with the nonluminous Xenorhabdus species. Gross DNA alterations such as insertions, deletions, or inversions do not appear to be involved in the generation of dim variants known as secondary forms.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhurst R. J. Antibiotic activity of Xenorhabdus spp., bacteria symbiotically associated with insect pathogenic nematodes of the families Heterorhabditidae and Steinernematidae. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Dec;128(12):3061–3065. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-12-3061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akhurst R. J., Boemare N. E. A numerical taxonomic study of the genus Xenorhabdus (Enterobacteriaceae) and proposed elevation of the subspecies of X. nematophilus to species. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jul;134(7):1835–1845. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-7-1835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. H., Ogden R. C., Abelson J. N., Baldwin T. O., Nealson K. H., Simon M. I., Mileham A. J. Cloning of the Vibrio harveyi luciferase genes: use of a synthetic oligonucleotide probe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):120–123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colepicolo P., Cho K. W., Poinar G. O., Hastings J. W. Growth and luminescence of the bacterium Xenorhabdus luminescens from a human wound. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2601–2606. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2601-2606.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couche G. A., Gregson R. P. Protein inclusions produced by the entomopathogenic bacterium Xenorhabdus nematophilus subsp. nematophilus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5279–5288. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5279-5288.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delong E. F., Steinhauer D., Israel A., Nealson K. H. Isolation of the lux genes from Photobacterium leiognathi and expression in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;54(2-3):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90488-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Nealson K., Silverman M. Bacterial bioluminescence: isolation and genetic analysis of functions from Vibrio fischeri. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Silverman M. Identification of genes and gene products necessary for bacterial bioluminescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4154–4158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton G. L., Nunn D. N., Lidstrom M. E. Molecular cloning of a malyl coenzyme A lyase gene from Pseudomonas sp. strain AM1, a facultative methylotroph. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):718–723. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.718-723.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurlbert R. E., Xu J., Small C. L. Colonial and Cellular Polymorphism in Xenorhabdus luminescens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 May;55(5):1136–1143. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.5.1136-1143.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illarionov B. A., Protopopova M. V., Karginov V. A., Mertvetsov N. P., Gitelson J. I. Nucleotide sequence of part of Photobacterium leiognathi lux region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9855–9855. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jablonski E., DeLuca M. Studies of the control of luminescence in Beneckea harveyi: properties of the NADH and NADPH:FMN oxidoreductases. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 21;17(4):672–678. doi: 10.1021/bi00597a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini J. A., Boylan M., Soly R. R., Graham A. F., Meighen E. A. Cloning and expression of the Photobacterium phosphoreum luminescence system demonstrates a unique lux gene organization. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14308–14314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M., Showalter R., Silverman M. Identification of a locus controlling expression of luminescence genes in Vibrio harveyi. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2406–2414. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2406-2414.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray N. E., Brammar W. J., Murray K. Lambdoid phages that simplify the recovery of in vitro recombinants. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jan 7;150(1):53–61. doi: 10.1007/BF02425325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nealson K. H., Hastings J. W. Bacterial bioluminescence: its control and ecological significance. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Dec;43(4):496–518. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.4.496-518.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. H., Schmidt T. M., Nealson K. H. Identification of an anthraquinone pigment and a hydroxystilbene antibiotic from Xenorhabdus luminescens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1602–1605. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1602-1605.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riendeau D., Meighen E. Co-induction of fatty acid reductase and luciferase during development of bacterial bioluminescence. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):12060–12065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt T. M., Bleakley B., Nealson K. H. Characterization of an Extracellular Protease from the Insect Pathogen Xenorhabdus luminescens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Nov;54(11):2793–2797. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.11.2793-2797.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt T. M., Kopecky K., Nealson K. H. Bioluminescence of the insect pathogen Xenorhabdus luminescens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2607–2612. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2607-2612.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]