Abstract
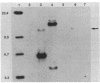
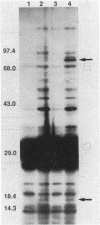
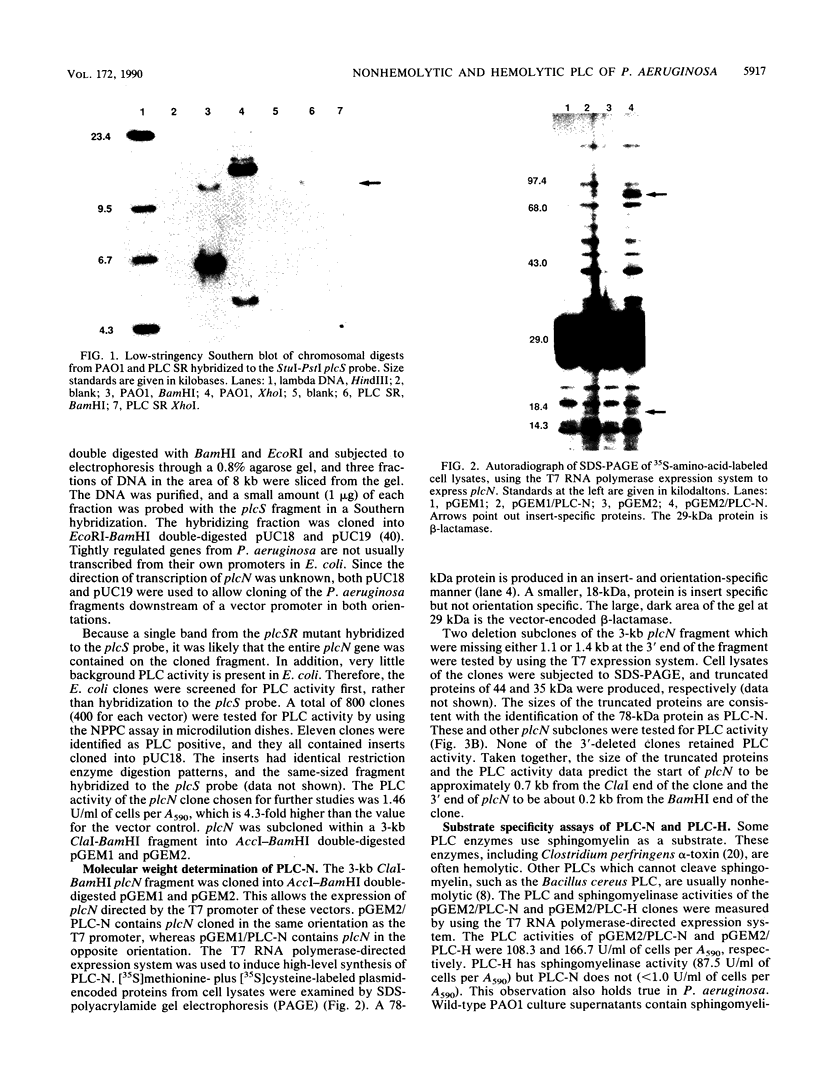
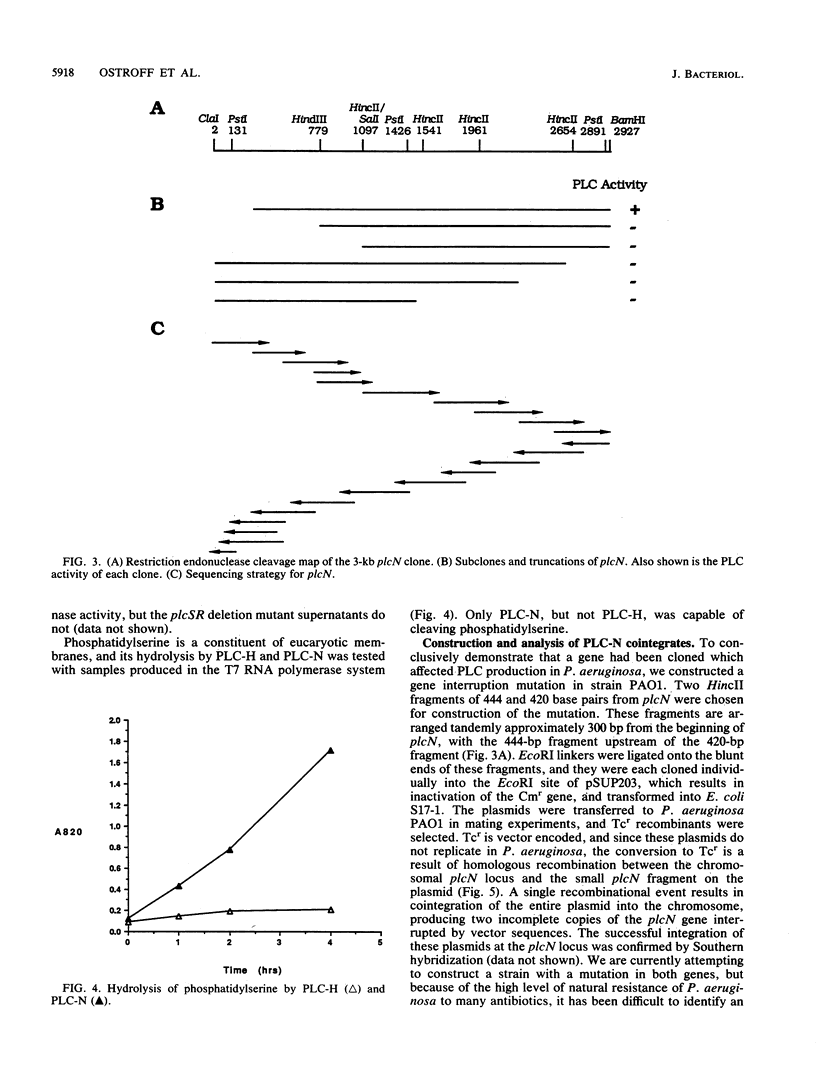
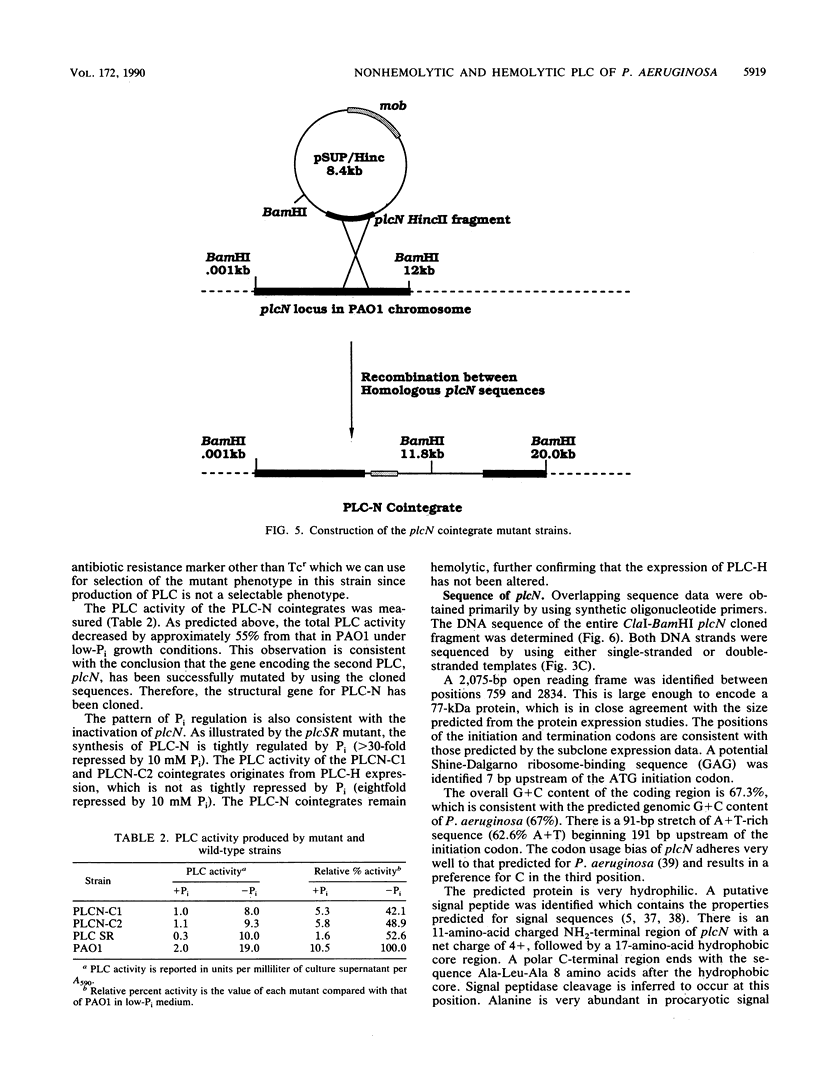
Pseudomonas aeruginosa produces two secreted phospholipase C (PLC) enzymes. The expression of both PLCs is regulated by Pi. One of the PLCs is hemolytic, and one is nonhemolytic. Low-stringency hybridization studies suggested that the genes encoding these two PLCs shared DNA homology. This information was used to clone plcN, the gene encoding the 77-kilodalton nonhemolytic PLC, PLC-N. A fragment of plcN was used to mutate the chromosomal copy of plcN by the generation of a gene interruption mutation. This mutant produces 55% less total PLC activity than the wild type, confirming the successful cloning of plcN. plcN was sequenced and encodes a protein which is 40% identical to the hemolytic PLC (PLC-H). The majority of the homology lies within the NH2 two-thirds of the proteins, while the remaining third of the amino acid sequence of the two proteins shows very little homology. Both PLCs hydrolyze phosphatidylcholine; however, each enzyme has a distinct substrate specificity. PLC-H hydrolyzes sphingomyelin in addition to phosphatidylcholine, whereas PLC-N is active on phosphatidylserine as well as phosphatidylcholine. These studies suggest structure-function relationships between PLC activity and hemolysis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berka R. M., Vasil M. L. Phospholipase C (heat-labile hemolysin) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: purification and preliminary characterization. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):239–245. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.239-245.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman K., Dougan G., Arbuthnott J. P. Cloning, and expression in Escherichia coli K-12, of the chromosomal hemolysin (phospholipase C) determinant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):909–915. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.909-915.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ESSELMANN M. T., LIU P. V. Lecithinase production by gramnegative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jun;81:939–945. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.6.939-945.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Silhavy T. J. Importance of secondary structure in the signal sequence for protein secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4599–4603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatt S., Dinur T., Barenholz Y. A spectrophotometric method for determination of sphingomyelinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 28;530(3):503–507. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90169-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore M. S., Cruz-Rodz A. L., Leimeister-Wächter M., Kreft J., Goebel W. A Bacillus cereus cytolytic determinant, cereolysin AB, which comprises the phospholipase C and sphingomyelinase genes: nucleotide sequence and genetic linkage. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):744–753. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.744-753.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant C. C., Vasil M. L. Analysis of transcription of the exotoxin A gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1112–1119. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1112-1119.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. L., Berka R. M., Vasil M. L. Phospholipase C regulatory mutation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa that results in constitutive synthesis of several phosphate-repressible proteins. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1221–1226. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1221-1226.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Krishnapillai V., Morgan A. F. Chromosomal genetics of Pseudomonas. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Mar;43(1):73–102. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.1.73-102.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. K., Boese-Marrazzo D. Production and properties of heat-stable extracellular hemolysin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1028–1033. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1028-1033.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurioka S., Matsuda M. Phospholipase C assay using p-nitrophenylphosphoryl-choline together with sorbitol and its application to studying the metal and detergent requirement of the enzyme. Anal Biochem. 1976 Sep;75(1):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90078-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren V., Ostroff R. M., Vasil M. L., Wretlind B. Genetic mapping of the structural gene for phospholipase C of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):1155–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.1155-1156.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lory S., Tai P. C. Characterization of the phospholipase C gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cloned in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1983 Apr;22(1):95–101. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane M. G., Knight B. C. The biochemistry of bacterial toxins: The lecithinase activity of Cl. welchii toxins. Biochem J. 1941 Sep;35(8-9):884–902. doi: 10.1042/bj0350884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hoy K., Krishnapillai V. Recalibration of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO chromosome map in time units using high-frequency-of-recombination donors. Genetics. 1987 Apr;115(4):611–618. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.4.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostroff R. M., Vasil M. L. Identification of a new phospholipase C activity by analysis of an insertional mutation in the hemolytic phospholipase C structural gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4597–4601. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4597-4601.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostroff R. M., Wretlind B., Vasil M. L. Mutations in the hemolytic-phospholipase C operon result in decreased virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 grown under phosphate-limiting conditions. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1369–1373. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1369-1373.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard A. E., Vasil M. L. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a phosphate-regulated gene encoding a secreted hemolysin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):291–298. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.291-298.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen B. F., Tai P. C., Pritchard A. E., Vasil M. L. Nucleotide sequences and expression in Escherichia coli of the in-phase overlapping Pseudomonas aeruginosa plcR genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4602–4607. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4602-4607.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titball R. W., Hunter S. E., Martin K. L., Morris B. C., Shuttleworth A. D., Rubidge T., Anderson D. W., Kelly D. C. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the alpha-toxin (phospholipase C) of Clostridium perfringens. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):367–376. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.367-376.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasil M. L., Berka R. M., Gray G. L., Nakai H. Cloning of a phosphate-regulated hemolysin gene (phospholipase C) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):431–440. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.431-440.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasil M. L., Chamberlain C., Grant C. C. Molecular studies of Pseudomonas exotoxin A gene. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):538–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.538-548.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. E., Iglewski B. H. Codon usage in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9323–9335. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. How signal sequences maintain cleavage specificity. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 25;173(2):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90192-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]