Abstract
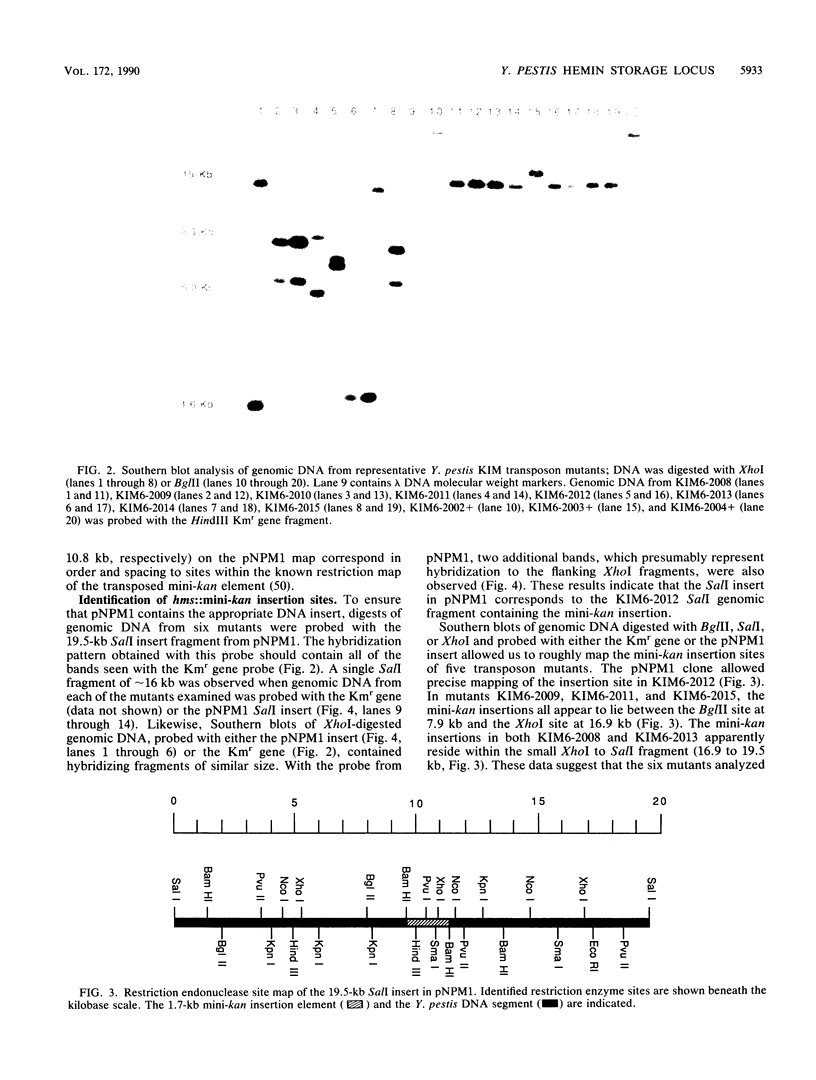
The temperature-dependent absorption of sufficient exogenous hemin or Congo red to form pigmented colonies of Yersinia pestis has been termed the pigmentation phenotype (Pgm+). Spontaneous mutation to a Pgm- phenotype results in the loss of a number of divergent physiological characteristics, including the ability to store hemin and to bind Congo red at 26 degrees C. In this study, we generated and isolated transposon insertion mutants that are hemin storage negative (Hms-) and therefore unable to form pigmented colonies. These mutations are due to single mini-kan insertions within a 19.5-kilobase (kb) SalI fragment of chromosomal DNA. Restriction site analysis of eight mutants identified a minimum of six potentially different insertion sites spanning an approximately 10-kb hemin storage (hms) locus. The 19.5-kb SalI fragment (containing approximately 18 kb of Y. pestis DNA and the mini-kan insert) was cloned from one of these mutants, KIM6-2012. By using this cloned fragment as a DNA probe, the mechanism of spontaneous mutation to a Pgm- phenotype was identified as a massive deletion event. The deletion spans at least 18 kb of genomic DNA in spontaneous Pgm- mutants from nine separate strains of Y. pestis. DNA adjacent to the mini-kan insert was used to identify a clone containing a wild-type hms locus. A spontaneous Pgm- mutant of Y pestis KIM containing this clone exhibits an Hms+ phenotype. The hms::mini-kan mutations and cloned wild-type hms locus generated in this study will greatly aid in identifying the function of hemin storage in Y. pestis.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRUBAKER R. R., SURGALLA M. J. Pesticins. I. Pesticinbacterium interrelationships, and environmental factors influencing activity. J Bacteriol. 1961 Dec;82:940–949. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.6.940-949.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., JACKSON S. The pigmentation of Pasteurella pestis on a defined medium containing haemin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Dec;37(6):570–576. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., JACKSON S. The virulence-enhancing effect of iron on nonpigmented mutants of virulent strains of Pasteurella pestis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Dec;37(6):577–583. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beesley E. D., Brubaker R. R., Janssen W. A., Surgalla M. J. Pesticins. 3. Expression of coagulase and mechanism of fibrinolysis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):19–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.19-26.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Gurion R., Shafferman A. Essential virulence determinants of different Yersinia species are carried on a common plasmid. Plasmid. 1981 Mar;5(2):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhoff H. A., Vinal A. C. Congo red medium to distinguish between invasive and non-invasive Escherichia coli pathogenic for poultry. Avian Dis. 1986 Jan-Mar;30(1):117–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Backman K. Plasmids of Escherichia coli as cloning vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:245–267. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. Mutation rate to nonpigmentation in Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1404–1406. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1404-1406.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. The Vwa+ virulence factor of yersiniae: the molecular basis of the attendant nutritional requirement for Ca++. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S748–S758. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carniel E., Mercereau-Puijalon O., Bonnefoy S. The gene coding for the 190,000-dalton iron-regulated protein of Yersinia species is present only in the highly pathogenic strains. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1211–1217. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1211-1217.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daskaleros P. A., Payne S. M. Congo red binding phenotype is associated with hemin binding and increased infectivity of Shigella flexneri in the HeLa cell model. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1393–1398. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1393-1398.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower W. J., Miller J. F., Ragsdale C. W. High efficiency transformation of E. coli by high voltage electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6127–6145. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber D. M., Brubaker R. R. Plasmids in Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):839–841. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.839-841.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber D. M., Fowler J. M., Brubaker R. R. Mutations to tolerance and resistance to pesticin and colicins in Escherichia coli phi. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):506–511. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.506-511.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goguen J. D., Yother J., Straley S. C. Genetic analysis of the low calcium response in Yersinia pestis mu d1(Ap lac) insertion mutants. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):842–848. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.842-848.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden J. W., Carrasco C. D., Mulligan M. E., Schneider G. J., Haselkorn R. Deletion of a 55-kilobase-pair DNA element from the chromosome during heterocyst differentiation of Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5034–5041. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5034-5041.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Collins J. A small cosmid for efficient cloning of large DNA fragments. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Yang G. C., Brubaker R. R. Specificity, induction, and absorption of pesticin. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):212–219. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.212-219.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys G. O., Willshaw G. A., Anderson E. S. A simple method for the preparation of large quantities of pure plasmid DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 2;383(4):457–463. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs W. R., Barrett J. F., Clark-Curtiss J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd In vivo repackaging of recombinant cosmid molecules for analyses of Salmonella typhimurium, Streptococcus mutans, and mycobacterial genomic libraries. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):101–109. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.101-109.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Blackmon B., Curtiss R., 3rd Loss of pigmentation in Shigella flexneri 2a is correlated with loss of virulence and virulence-associated plasmid. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):397–401. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.397-401.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monack D. M., Arico B., Rappuoli R., Falkow S. Phase variants of Bordetella bronchiseptica arise by spontaneous deletions in the vir locus. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1719–1728. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Finkelstein R. A. Detection and differentiation of iron-responsive avirulent mutants on Congo red agar. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):94–98. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.94-98.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. D., Brubaker R. R. Accumulation of iron by yersiniae. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1290–1298. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1290-1298.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. D., Brubaker R. R. Vwa+ phenotype of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):166–171. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.166-171.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. D., Harmon P. A., Bowmer W. S., Straley S. C. A low-Ca2+ response operon encodes the V antigen of Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):428–434. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.428-434.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prpic J. K., Robins-Browne R. M., Davey R. B. Differentiation between virulent and avirulent Yersinia enterocolitica isolates by using Congo red agar. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):486–490. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.486-490.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai T., Sasakawa C., Makino S., Kamata K., Yoshikawa M. Molecular cloning of a genetic determinant for Congo red binding ability which is essential for the virulence of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):476–482. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.476-482.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankaran K., Ramachandran V., Subrahmanyam Y. V., Rajarathnam S., Elango S., Roy R. K. Congo red-mediated regulation of levels of Shigella flexneri 2a membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2364–2371. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2364-2371.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa C., Kamata K., Sakai T., Murayama S. Y., Makino S., Yoshikawa M. Molecular alteration of the 140-megadalton plasmid associated with loss of virulence and Congo red binding activity in Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):470–475. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.470-475.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikkema D. J., Brubaker R. R. Outer membrane peptides of Yersinia pestis mediating siderophore-independent assimilation of iron. Biol Met. 1989;2(3):174–184. doi: 10.1007/BF01142557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikkema D. J., Brubaker R. R. Resistance to pesticin, storage of iron, and invasion of HeLa cells by Yersiniae. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):572–578. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.572-578.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodeinde O. A., Goguen J. D. Genetic analysis of the 9.5-kilobase virulence plasmid of Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2743–2748. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2743-2748.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker N. G., Fairweather N. F., Spratt B. G. Versatile low-copy-number plasmid vectors for cloning in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):335–341. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90172-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Bowmer W. S. Virulence genes regulated at the transcriptional level by Ca2+ in Yersinia pestis include structural genes for outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):445–454. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.445-454.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Brubaker R. R. Cytoplasmic and membrane proteins of yersiniae cultivated under conditions simulating mammalian intracellular environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1224–1228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Brubaker R. R. Localization in Yersinia pestis of peptides associated with virulence. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):129–135. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.129-135.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Cibull M. L. Differential clearance and host-pathogen interactions of YopE- and YopK- YopL- Yersinia pestis in BALB/c mice. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1200–1210. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1200-1210.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stugard C. E., Daskaleros P. A., Payne S. M. A 101-kilodalton heme-binding protein associated with congo red binding and virulence of Shigella flexneri and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli strains. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3534–3539. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3534-3539.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surgalla M. J., Beesley E. D. Congo red-agar plating medium for detecting pigmentation in Pasteurella pestis. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):834–837. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.834-837.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T., Brubaker R. R. In vivo comparison of avirulent Vwa- and Pgm- or Pstr phenotypes of yersiniae. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):895–900. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.895-900.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way J. C., Davis M. A., Morisato D., Roberts D. E., Kleckner N. New Tn10 derivatives for transposon mutagenesis and for construction of lacZ operon fusions by transposition. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):369–379. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]