Abstract
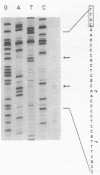
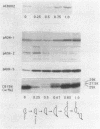
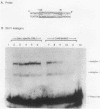
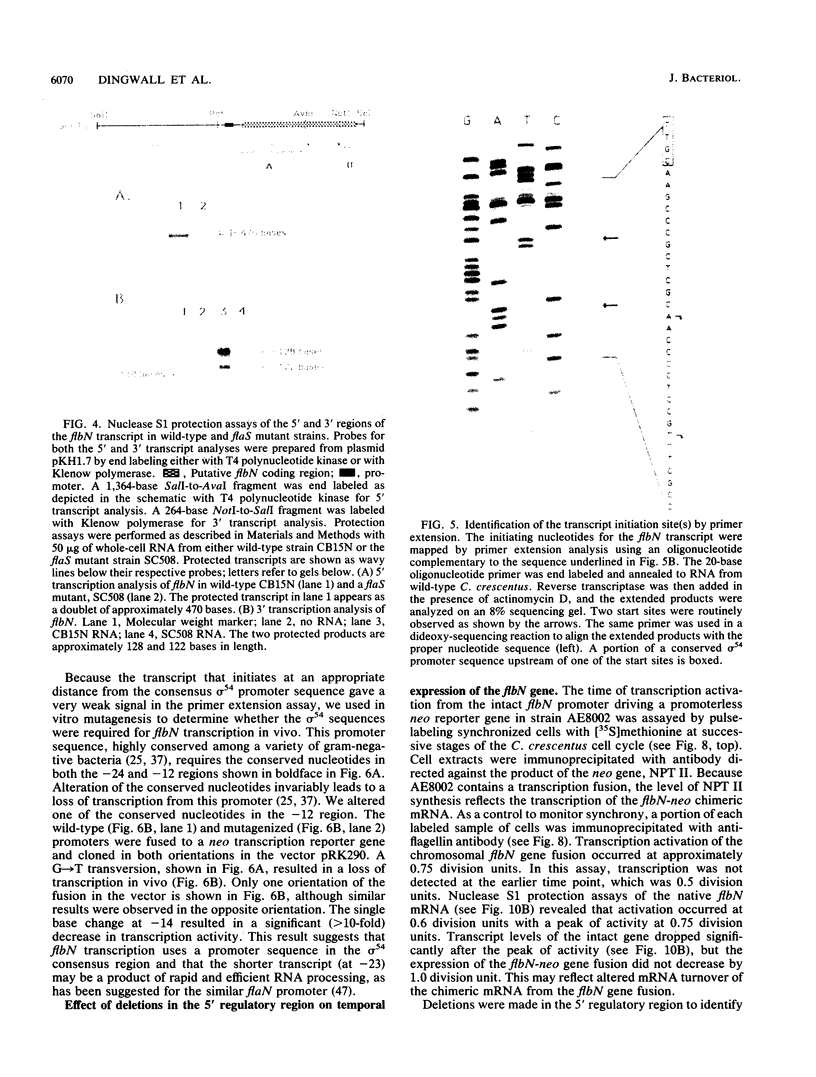
The genes that encode the components and regulatory proteins of the Caulobacter crescentus flagellum are transcribed at specific times in the cell cycle. One of these genes, flbN, is required early in the flagellar assembly process. The flbN gene was cloned and sequenced, and the time of transcription activation was determined. The derived amino acid sequence indicates that fibN encodes a 25-kilodalton protein with a cleavable leader peptide. The flbN-encoded protein has 30.8% identity with the protein encoded by the Salmonella typhimurium basal body L-ring gene, flgH. Site-directed mutagenesis and gel mobility shift assays identified a binding site at -100 from the transcription start site for a trans-acting protein, RF-2, that functions to partially activate flbN transcription at a defined time in the cell cycle. The RF-2 binding region is similar to a NifA binding site normally used in the activation of some sigma 54 promoters involved in nitrogen fixation in other bacteria. Transcription of a flbN-reporter gene fusion in an Escherichia coli background was dependent on the presence of a NifA transcription factor supplied by a plasmid-borne Rhizobium meliloti gene encoding NifA. A deletion or base changes in the RF-2 binding region eliminated expression of the flbN gene in E. coli even when a NifA protein was provided in trans, suggesting that a sigma 54 promoter with an upstream activator element is used by the C. crescentus flbN gene. A consensus sequence for a sigma 54 promoter was found at the appropriate distance 5' to one of two identified transcription start sites. Site-directed mutagenesis confirmed that a conserved nucleotide in this sigma 54 promoter consensus sequence was required for transcription. Deletion of the region 5' to the apparent sigma 54 promoter caused a complete loss of transcription activation. Transcription activation of flbN in C. crescentus involves the combination of several elements: the NifA-like site is required for full activation, and other sequence elements 5' to the promoter and 3' to the transcription start site are necessary for the correct time of transcription initiation.
Full text
PDF





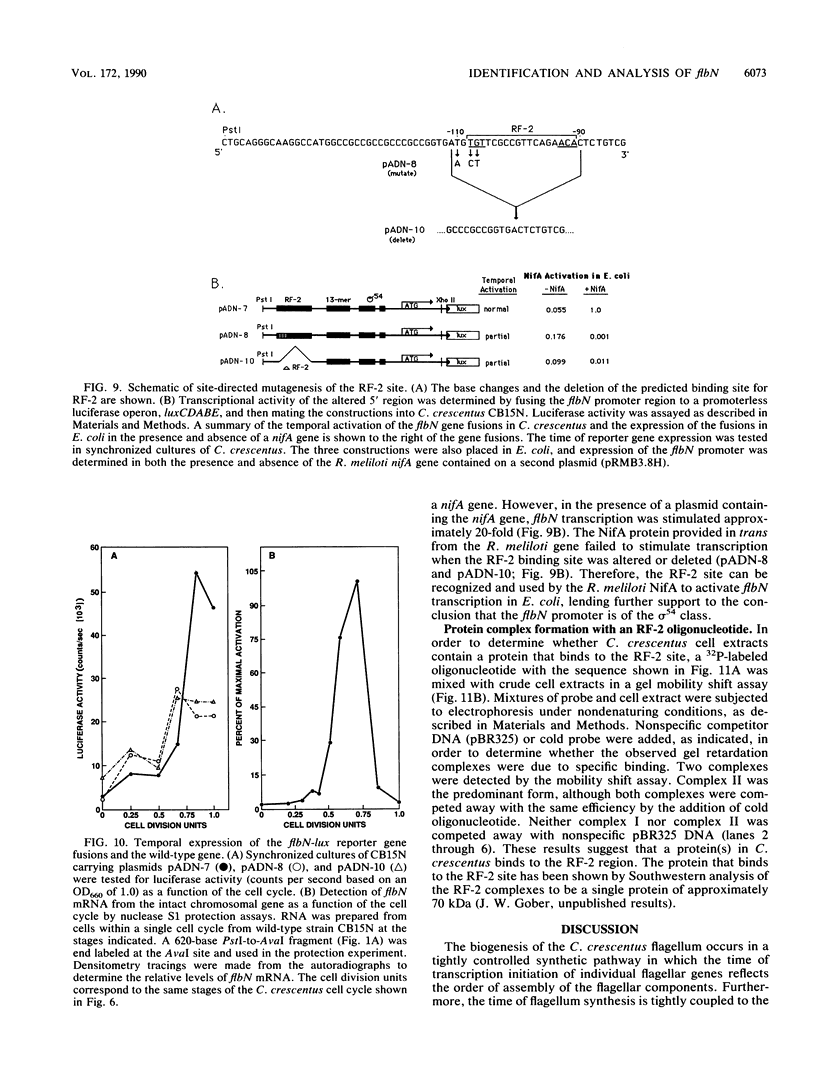



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnosti D. N., Chamberlin M. J. Secondary sigma factor controls transcription of flagellar and chemotaxis genes in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):830–834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellofatto V., Shapiro L., Hodgson D. A. Generation of a Tn5 promoter probe and its use in the study of gene expression in Caulobacter crescentus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1035–1039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun Y. V., Sanfaçon H., Breton R., Lapointe J. Closely spaced and divergent promoters for an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase gene and a tRNA operon in Escherichia coli. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of gltX, valU and alaW. J Mol Biol. 1990 Aug 20;214(4):845–864. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90340-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan R., Purucker M., Gomes S. L., Alexander W., Shapiro L. Analysis of the pleiotropic regulation of flagellar and chemotaxis gene expression in Caulobacter crescentus by using plasmid complementation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1341–1345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champer R., Bryan R., Gomes S. L., Purucker M., Shapiro L. Temporal and spatial control of flagellar and chemotaxis gene expression during Caulobacter cell differentiation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:831–840. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champer R., Dingwall A., Shapiro L. Cascade regulation of Caulobacter flagellar and chemotaxis genes. J Mol Biol. 1987 Mar 5;194(1):71–80. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90716-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras I., Shapiro L., Henry S. Membrane phospholipid composition of Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):1130–1136. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.1130-1136.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall A., Shapiro L. Rate, origin, and bidirectionality of Caulobacter chromosome replication as determined by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):119–123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely B., Croft R. H., Gerardot C. J. Genetic mapping of genes required for motility in Caulobacter crescentus. Genetics. 1984 Nov;108(3):523–532. doi: 10.1093/genetics/108.3.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely B., Ely T. W. Use of pulsed field gel electrophoresis and transposon mutagenesis to estimate the minimal number of genes required for motility in Caulobacter crescentus. Genetics. 1989 Dec;123(4):649–654. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.4.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely B., Gerardot C. J., Fleming D. L., Gomes S. L., Frederikse P., Shapiro L. General nonchemotactic mutants of Caulobacter crescentus. Genetics. 1986 Nov;114(3):717–730. doi: 10.1093/genetics/114.3.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evinger M., Agabian N. Envelope-associated nucleoid from Caulobacter crescentus stalked and swarmer cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):294–301. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.294-301.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Egelhoff T. T., Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Specific binding of proteins from Rhizobium meliloti cell-free extracts containing NodD to DNA sequences upstream of inducible nodulation genes. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):282–293. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederikse P. H., Shapiro L. An Escherichia coli chemoreceptor gene is temporally controlled in Caulobacter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4061–4065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gober J. W., Shapiro L. Integration host factor is required for the activation of developmentally regulated genes in Caulobacter. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1494–1504. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomes S. L., Gober J. W., Shapiro L. Expression of the Caulobacter heat shock gene dnaK is developmentally controlled during growth at normal temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3051–3059. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3051-3059.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomes S. L., Shapiro L. Differential expression and positioning of chemotaxis methylation proteins in Caulobacter. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 25;178(3):551–568. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90238-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gussin G. N., Ronson C. W., Ausubel F. M. Regulation of nitrogen fixation genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:567–591. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahnenberger K. M., Shapiro L. Organization and temporal expression of a flagellar basal body gene in Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4119–4124. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4119-4124.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirooka T., Rogowsky P. M., Kado C. I. Characterization of the virE locus of Agrobacterium tumefaciens plasmid pTiC58. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1529–1536. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1529-1536.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huo L., Martin K. J., Schleif R. Alternative DNA loops regulate the arabinose operon in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5444–5448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. J., Homma M., Macnab R. M. L-, P-, and M-ring proteins of the flagellar basal body of Salmonella typhimurium: gene sequences and deduced protein sequences. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3890–3900. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3890-3900.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. B., Dingwall A., Bryan R., Champer R., Shapiro L. Temporal regulation and overlap organization of two Caulobacter flagellar genes. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 5;205(1):71–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90365-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komeda Y. Fusions of flagellar operons to lactose genes on a mu lac bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):16–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.16-26.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komeda Y. Transcriptional control of flagellar genes in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1315–1318. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1315-1318.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S., Santero E., Keener J., Popham D., Weiss D. Expression of sigma 54 (ntrA)-dependent genes is probably united by a common mechanism. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):367–376. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.367-376.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsukake K., Ohya Y., Iino T. Transcriptional analysis of the flagellar regulon of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):741–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.741-747.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minchin S. D., Austin S., Dixon R. A. Transcriptional activation of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifLA promoter by NTRC is face-of-the-helix dependent and the activator stabilizes the interaction of sigma 54-RNA polymerase with the promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3491–3499. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08514.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minnich S. A., Newton A. Promoter mapping and cell cycle regulation of flagellin gene transcription in Caulobacter crescentus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1142–1146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morett E., Buck M. NifA-dependent in vivo protection demonstrates that the upstream activator sequence of nif promoters is a protein binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9401–9405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morett E., Cannon W., Buck M. The DNA-binding domain of the transcriptional activator protein NifA resides in its carboxy terminus, recognises the upstream activator sequences of nif promoters and can be separated from the positive control function of NifA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11469–11488. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin D. A., Newton A. Ntr-like promoters and upstream regulatory sequence ftr are required for transcription of a developmentally regulated Caulobacter crescentus flagellar gene. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3218–3227. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3218-3227.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin D., Minnich S., Chen L. S., Newton A. A set of positively regulated flagellar gene promoters in Caulobacter crescentus with sequence homology to the nif gene promoters of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):939–943. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90497-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müeller-Storm H. P., Sogo J. M., Schaffner W. An enhancer stimulates transcription in trans when attached to the promoter via a protein bridge. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):767–777. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90110-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton A., Ohta N., Ramakrishnan G., Mullin D., Raymond G. Genetic switching in the flagellar gene hierarchy of Caulobacter requires negative as well as positive regulation of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6651–6655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Mullin D. A., Ramakrishnan G., Newton A. Escherichia coli sigma 54 RNA polymerase recognizes Caulobacter crescentus flbG and flaN flagellar gene promoters in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):383–391. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.383-391.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta N., Chen L. S., Swanson E., Newton A. Transcriptional regulation of a periodically controlled flagellar gene operon in Caulobacter crescentus. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90261-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. Protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:615–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POINDEXTER J. S. BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES AND CLASSIFICATION OF THE CAULOBACTER GROUP. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Sep;28:231–295. doi: 10.1128/br.28.3.231-295.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasloske B. L., Drummond D. S., Frost L. S., Paranchych W. The activity of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa pilin promoter is enhanced by an upstream regulatory site. Gene. 1989 Sep 1;81(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90333-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santero E., Hoover T., Keener J., Kustu S. In vitro activity of the nitrogen fixation regulatory protein NIFA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7346–7350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenlein P. V., Gallman L. S., Ely B. Organization of the flaFG gene cluster and identification of two additional genes involved in flagellum biogenesis in Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1544–1553. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1544-1553.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro L., Mansour J., Shaw P., Henry S. Synthesis of specific membrane proteins is a function of DNA replication an phospholipid synthesis in Caulobacter crescentus. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 5;159(2):303–322. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90497-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szeto W. W., Zimmerman J. L., Sundaresan V., Ausubel F. M. A Rhizobium meliloti symbiotic regulatory gene. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1035–1043. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thöny B., Anthamatten D., Hennecke H. Dual control of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum symbiotic nitrogen fixation regulatory operon fixR nifA: analysis of cis- and trans-acting elements. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4162–4169. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4162-4169.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu H., Dingwall A., Shapiro L. Negative transcriptional regulation in the Caulobacter flagellar hierarchy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6656–6660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]