Abstract
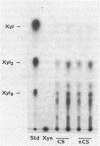
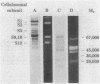
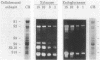
Xylanase activity of Clostridium thermocellum, an anaerobic thermophilic cellulolytic bacterium, was characterized. The activity was localized both in the cellulosome (the principal multienzyme, cellulose-solubilizing protein complex) and in noncellulosomal fractions. Each of these fractions contained at least four major polypeptide bands which contributed to the xylanolytic activity. In both cases, pH and temperature optima, product pattern, and other features of the xylanase activity were almost identical. The main difference was in the average molecular weights of the respective polypeptides which appeared responsible for the activity. In the noncellulosomal fraction, xylanases with Mrs ranging from 30,000 to 65,000 were detected. Distinct from these were the cellulosomal xylanases, which exhibited much larger Mrs (up to 170,000). The cellulosome-associated xylanases corresponded to known cellulosomal subunits, some of which also exhibited endoglucanase activity, and others which coincided with subunits which appeared to express exoglucanaselike activity. In contrast, the noncellulosomal xylanases hydrolyzed xylan exclusively. beta-Glucosidase and beta-xylosidase activities were shown to be the action of different enzymes; both were associated exclusively with the cell and were not components of the cellulosome. Despite the lack of growth on and utilization of xylan or its degradation products, C. thermocellum produces a highly developed xylanolytic apparatus which is interlinked with its cellulase system.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. K. Purification and specificity of cellobiose phosphorylase from Clostridium thermocellum. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 10;243(11):2899–2904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aït N., Creuzet N., Cattanéo J. Characterization and purification of thermostable beta-glucosidase from Clostridium thermocellum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 27;90(2):537–546. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91269-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Ben-Hur H., Wilchek M. Analysis of proteins and glycoproteins on blots. Methods Enzymol. 1990;184:415–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Kenig R., Lamed R. Adherence of Clostridium thermocellum to cellulose. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):818–827. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.818-827.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Lamed R. Ultrastructure of the cell surface cellulosome of Clostridium thermocellum and its interaction with cellulose. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):828–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.828-836.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. Protein biotinylation. Methods Enzymol. 1990;184:138–160. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)84268-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Béguin P. Detection of cellulase activity in polyacrylamide gels using Congo red-stained agar replicas. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jun;131(2):333–336. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claeyssens M., Van Tilbeurgh H., Tomme P., Wood T. M., McRae S. I. Fungal cellulase systems. Comparison of the specificities of the cellobiohydrolases isolated from Penicillium pinophilum and Trichoderma reesei. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 1;261(3):819–825. doi: 10.1042/bj2610819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freier Doris, Mothershed Cheryle P., Wiegel Juergen. Characterization of Clostridium thermocellum JW20. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jan;54(1):204–211. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.1.204-211.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grépinet O., Chebrou M. C., Béguin P. Purification of Clostridium thermocellum xylanase Z expressed in Escherichia coli and identification of the corresponding product in the culture medium of C. thermocellum. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4576–4581. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4576-4581.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. A., Sakajoh M., Halliwell G., Madia A., Demain A. L. Saccharification of Complex Cellulosic Substrates by the Cellulase System from Clostridium thermocellum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1125–1132. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1125-1132.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamed R., Setter E., Bayer E. A. Characterization of a cellulose-binding, cellulase-containing complex in Clostridium thermocellum. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):828–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.828-836.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie C. R., Yang R. C., Patel G. B., Bilous D., Narang S. A. Identification of three distinct Clostridium thermocellum xylanase genes by molecular cloning. Arch Microbiol. 1989;152(4):377–381. doi: 10.1007/BF00425176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno J. D., Bayer R. The limits of the ledger in public health promotion. Hastings Cent Rep. 1985 Dec;15(6):37–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray W. D. Symbiotic Relationship of Bacteroides cellulosolvens and Clostridium saccharolyticum in Cellulose Fermentation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Apr;51(4):710–714. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.4.710-714.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng T. K., Zeikus J. G. Comparison of Extracellular Cellulase Activities of Clostridium thermocellum LQRI and Trichoderma reesei QM9414. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Aug;42(2):231–240. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.2.231-240.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pétré D., Millet J., Longin R., Béguin P., Girard H., Aubert J. P. Purification and properties of the endoglucanase C of Clostridium thermocellum produced in Escherichia coli. Biochimie. 1986 May;68(5):687–695. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)80162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. K., Tan L. U., Saddler J. N. Multiplicity of beta-1,4-xylanase in microorganisms: functions and applications. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Sep;52(3):305–317. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.3.305-317.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]