Abstract
Cytolysin, a two-component lanthipeptide comprising cytolysin S (CylLS″) and cytolysin L (CylLL″), is the only family member to exhibit lytic activity against mammalian cells, in addition to synergistic antimicrobial activity. A subset of the thioether crosslinks of CylLS″ and CylLL″ have LL-stereochemistry instead of the canonical DL-stereochemistry in all previously characterized lanthipeptides. The synthesis of a CylLS″ variant with DL stereochemistry is reported. Its antimicrobial activity was found to be decreased but not its lytic activity against red blood cells. Hence, the unusual LL-stereochemistry is not responsible for the lytic activity.
Graphical Abstract
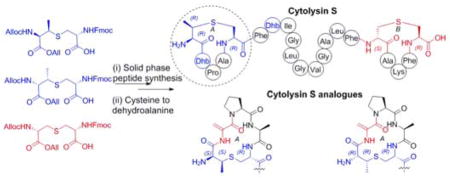
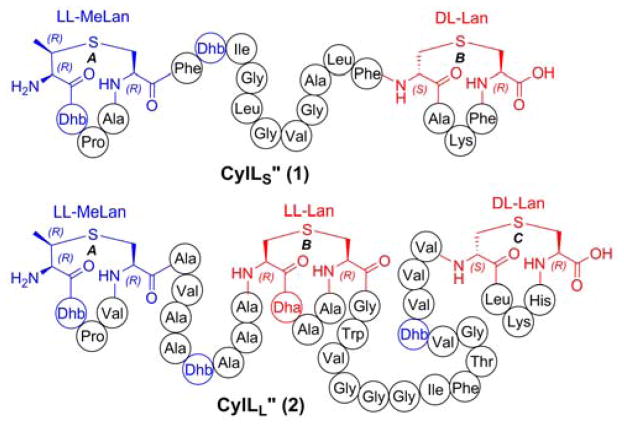
Lanthipeptides belong to the class of ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs) and bear lanthionine (Lan) and methyllanthionine (MeLan) structures as well as dehydroalanine (Dha) and dehydrobutyrine (Dhb) residues (Figure 1).1 Two-component lanthipeptides are an interesting subclass of lanthipeptides, in which two peptides synergistically act to provide antibacterial activity.2 Cytolysin is a two component lanthipeptide and comprises cytolysin S (CylLS″) and cytolysin L (CylLL″).3 In addition to exhibiting synergistic antimicrobial activity, cytolysin is the first and thus far only lanthipeptide shown to potently lyse mammalian cells.4 Cytolysin is responsible for the enhancement of enterococcal virulence and is produced by many clinical isolates of Enterococcus faecalis.5 Compared to most lanthipeptides, cytolysin exhibits unusual stereochemistry. This class of molecules generally contain Lan and MeLan with DL-stereochemistry, i.e. (2S,6R)-lanthionine and (2S,3S,6R)-methyllanthionine.6 In the case of cytolysin, the B ring of CylLS″ and the C ring of CylLL″ contain Lan with the canonical stereochemistry, but LL-stereochemistry (i.e. (2R,6R)-Lan and (2R,3R,6R)-MeLan) was observed for the A ring of CylLS″ and the A and B rings of CylLL″ (Figure 1).7 These observations suggested a possible correlation between the unique stereochemistry and the unusual lytic activity against mammalian cells. To test this hypothesis, we report the total synthesis of a diastereomer of cytolysin to investigate the effect of stereochemistry of the thioether crosslinks on the biological activity.
Figure 1.
Structures of cytolysin S and L. Lan and Dha (both de-rived from Ser) are shown in red, MeLan and Dhb (both derived from Thr) are in blue.
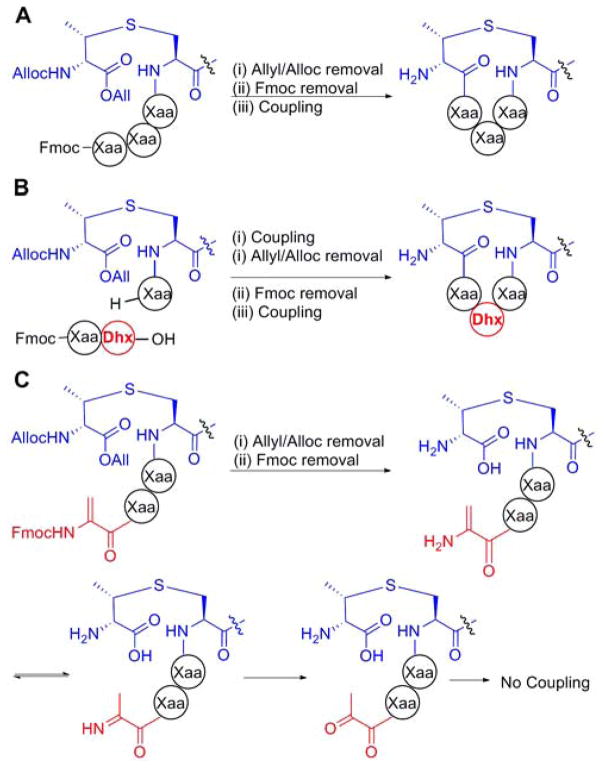
Synthesis of just five lanthipeptides or their variants has been reported thus far – nisin, lactosin S, both components of lacticin 3147, epilancin 15x, and lacticin 481.8 Four of these have been completed on solid phase utilizing an orthogonal protection scheme that allows on demand cyclization (Figure 2A). Cytolysin synthesis poses several challenges not present in these previously synthesized compounds. Firstly, the sequences of CylLS″ and CylLL″ are extremely hydrophobic, with only a single charged residue in each peptide (Figure 1). Hydrophobic peptides are prone to incomplete coupling during solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) because of inaccessibility of the reagents to the N-terminus of the elongating peptide chain.9 Secondly, the structures of cytolysins contain a dehydro amino acid in the second position within the thioether rings. Dehydro amino acids cannot be incorporated via the usual elongation methods of Fmoc SPPS because the enamine liberated upon Fmoc deprotection is very unreactive and would tautomerize to the imine followed by hydrolysis to the ketone, preventing further peptide coupling. Therefore, the traditional SPPS routes to lanthipeptides rely on preparation of short oligopeptides containing pre-installed dehydro amino acids (e.g. Figure 2B).8b–e Unfortunately, this strategy does not work with a dehydro amino acid incorporated at the second position of a Lan/MeLan-containing ring because the dehydro amino acid is the point of cyclization (Figure 2C). Synthesis of such a structure has not been accomplished thus far. We describe here the synthesis of cytolysin S as well as a diastereomer by introduction of the dehydro amino acid after cyclization.
Figure 2.
(A) Orthogonal protecting groups on a (methyl)lanthionine building block (DL-MeLan here) allow elongation and subsequent cyclization of a peptide. For alternative protecting group schemes, see 10 (B) Introduction of short oligopeptides containing dehydro amino acids (Dhx). (C) If the amine coupling partner for cyclization is a dehydro amino acid (Dha here), the low reactivity of the enamine promotes hydrolysis to the ketone preventing cyclization.
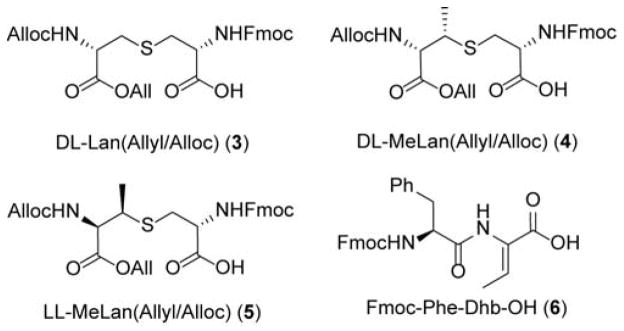
To minimize the problem of the high hydrophobicity of the cytolysins, we chose CylLS″ rather than CylLL″, as our synthetic target. In addition, the dehydrobutyrine in ring A of CylLS″ was substituted with a dehydroalanine (CylLS″-Dhb2Dha), which we envisioned could be accessed from a Cys. We first verified that this change would not alter the bioactivity of the peptide by preparing CylLS″-Dhb2Dha biosynthetically via co-expression of the precursor peptide CylLS-T2S with the lanthipeptide synthetase CylM in Escherichia coli using previously described methodology.7 Characterization of the product by tandem mass spectrometry and GC/MS analysis of derivatized amino acids after acid hydrolysis of CylLS″-Dhb2Dha demonstrated an LL-MeLan A-ring and a DL-Lan B-ring, identical to native CylLS″ (Figure S1).7 Purified CylLS″-Dhb2Dha was found to have very similar antimicrobial activity as that of native CylLS″ (Figure S2), thus making it a good target for synthesis. Hence, we set out to make both native CylLS″-Dhb2Dha and its diastereomer with a DL-MeLan A-ring instead of a LL-MeLan. The desired stereochemistry of the thioether crosslinks was preset in building blocks 3 and 4 (Figure 3).8e,11
Figure 3.
Building blocks used in SPPS of cytolysin analogues.
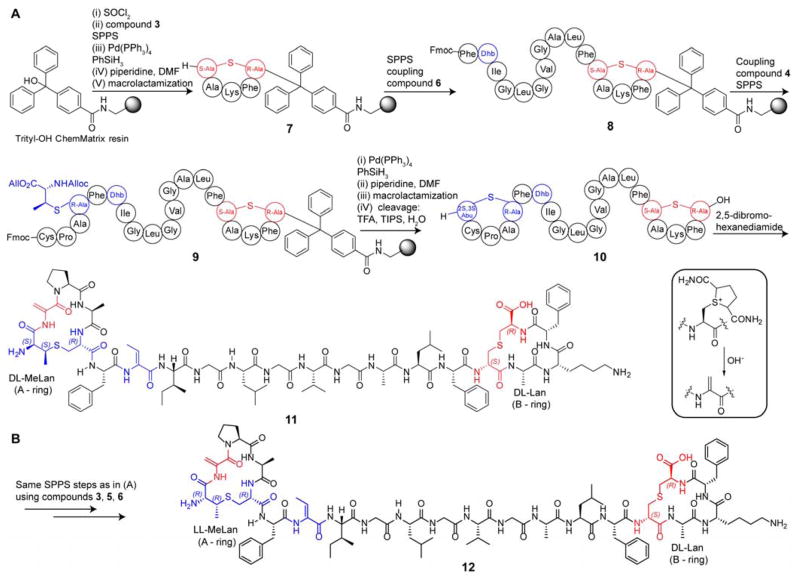
To aid in the synthesis of the hydrophobic peptide, polyethylene glycol (PEG) based ChemMatrix resin was employed instead of traditionally used polystyrene (PS) resin. ChemMatrix resin offers improved chemical stability, and owing to its polar nature, this resin does not interact as much with the side-chain protected peptides,12 which we felt was important given the hydrophobic nature of CylLS″. Additionally, ChemMatrix resin has enhanced swelling properties in a wide range of solvents, including solvents that minimize peptide self-association on the resin.12a A trityl group-containing linker to the resin was employed to prevent racemization of the C-terminal Lan residue. The bulky linker was also envisioned to improve the stability of the C-terminal Lan building block as C-terminal protected Cys residues often suffer from base-catalyzed elimination and subsequent β-piperidyl-alanine formation.13 The entire peptide was successfully synthesized on-resin. In place of the dehydroalanine residue in the second position within the MeLan A-ring of CylLS″-Dhb2Dha, a cysteine was incorporated as a convenient precursor to Dha.14 After cleavage of the peptide from the resin and purification, the peptide was reacted with 2,5-dibromohexanediamide, resulting in formation of a cyclic sulfonium intermediate at Cys2. As reported by Davis and co-workers,14a under basic conditions, elimination generates the desired dehydroalanine (Scheme 1, inset). The purity of the final compound 11 was confirmed by analytical high performance liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) (Figure S3). The desired stereochemistry of the thioether crosslinks in compound 11 was confirmed by gas chromatography coupled to MS analysis employing a chiral stationary phase (Figure S4). For direct comparison in bioactivity assays, CylLS″-Dhb2Dha with the natural LL-MeLan A-ring and DL-Lan B-ring (compound 12) was also synthesized (Scheme 1). This synthetic compound was expected to be identical to the biosynthetically accessed CylLS″-Dhb2Dha and thus was envisioned as a good control compound to assess the success of the synthetic procedure. For the synthesis of compound 12, similar synthetic steps were employed using synthetic building blocks 3, 5 and 6.
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of (A) CylLS″-Dhb2Dha (DL-A ring, DL-B ring), and (B) CylLS″-Dhb2Dha (LL-A ring, DL-B ring).
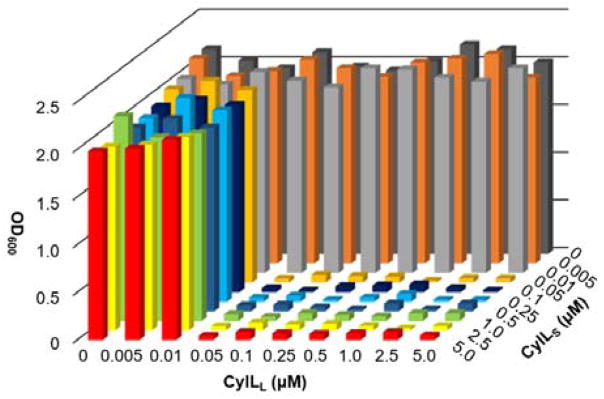
Antimicrobial activity was tested in combination with WT-CylLL″ against Lactococcus lactis HP and L. lactis CNRZ 481. None of the peptides displayed antimicrobial activity without its partner, and all CylLS″ peptides were active in combination with CylLL″ (Table 1). Isobolograms demonstrated that WT CylLL″ and CylLS″ act in 1:1 stoichiometry with a minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 0.05 μM for each component (Figure 4; Table 1). Expressed CylLS″-Dhb2Dha also acted with 1:1 stoichiometry but with a two-fold decrease in MIC (0.1 μM). Synthetic 12 exhibited identical antimicrobial activity as expressed CylLS″-Dhb2Dha, confirming the fidelity of the synthesis (Table 1, Figure S5). Conversely, diastereomer 11 exhibited decreased antimicrobial activity (Figure S5) when combined with CylLL″, as illustrated by a markedly smaller zone of growth inhibition and an MIC in liquid culture that was increased 10-fold (Table 1).
Table 1.
Minimal inhibitory concentrations of cytolysin and derivatives against L. lactis 481. n.a. not applicable
| entry | individual MIC (μM) | combined with CylLL″ MIC (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| CylLL″ | >50 | n.a. |
| CylLS″ | >50 | 0.05 |
| 11 | >50 | 1.0 |
| synthetic 12 | >50 | 0.1 |
| biosynthetic 12 | >50 | 0.1 |
Figure 4.
Antimicrobial activity assays of WT cytolysin against Lactococcus lactis 481. The isobologram demonstrates that the MIC of the combination of CylLL″ and CylLS″ is reached at 0.05 μM of each component, suggesting a 1:1 stoichiometry in the active species.
The cytolysin S peptides were also tested in combination with CylLL″ for synergistic hemolytic activity against rabbit red blood cells. Both WT-CylLS″ and expressed CylLS″-Dhb2Dha exhibited very similar hemolytic activity. Surprisingly, 11 with a DL-MeLan A-ring and DL-Lan B-ring exhibited no decrease of hemolytic activity (Figure S6). This result shows that the influence of stereochemistry is different on the two activities of cytolysin. Similar findings were reported for mutants of cytolysin that affected antimicrobial and lytic activity differently.15
In summary, it appears that CylLS″ with the LL stereochemistry of the A-ring has evolved for optimal complementary with native CylLL″ with respect to antimicrobial activity. In CylLS″ with DL-stereochemistry of the A-ring, the synergy with native CylLL″ is clearly attenuated. Regarding the hemolytic activity, the stereochemistry of the A-ring of CylLS″ does not appear to be important. These findings further reinforce previous conclusions that these two activities have different structure-activity relationships.15 They are also consistent with the proposal that cytolysin evolved pre-dominantly for its antimicrobial activity since E. faecalis is mostly a commensal organism.16
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Patrick Knerr (UIUC) for providing Boc-Phe-Thr-OtBu and DL-Lan building block for initial studies. We thank Dr. Weixin Tang (UIUC) for providing Lan/MeLan synthetic standards. We thank Dr. Alexander V. Ulanov of the Metabolomics Center at UIUC for assistance with GC/MS analysis. This study was supported by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. A Bruker UltrafleXtreme MALDI TOF/TOF mass spectrometer was purchased in part with a grant from the National Institutes of Health (S10 RR027109).
Footnotes
Notes
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
The Supporting Information is available free of charge on the ACS Publications website.
Materials and experimental procedures, synthesis and characterization of small molecules and peptides, and biosynthesis of cytolysin analogues and bioactivity assays.
References
- 1.(a) Arnison PG, Bibb MJ, Bierbaum G, Bowers AA, Bugni TS, Bulaj G, Camarero JA, Campopiano DJ, Challis GL, Clardy J, Cotter PD, Craik DJ, Dawson M, Dittmann E, Donadio S, Dorrestein PC, Entian KD, Fischbach MA, Garavelli JS, Goransson U, Gruber CW, Haft DH, Hemscheidt TK, Hertweck C, Hill C, Horswill AR, Jaspars M, Kelly WL, Klinman JP, Kuipers OP, Link AJ, Liu W, Marahiel MA, Mitchell DA, Moll GN, Moore BS, Muller R, Nair SK, Nes IF, Norris GE, Olivera BM, Onaka H, Patchett ML, Piel J, Reaney MJT, Rebuffat S, Ross RP, Sahl HG, Schmidt EW, Selsted ME, Severinov K, Shen B, Sivonen K, Smith L, Stein T, Sussmuth RD, Tagg JR, Tang GL, Truman AW, Vederas JC, Walsh CT, Walton JD, Wenzel SC, Willey JM, van der Donk WA. Nat Prod Rep. 2013;30:108. doi: 10.1039/c2np20085f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Knerr PJ, van der Donk WA. Annu Rev Biochem. 2012;81:479. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060110-113521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lawton EM, Ross RP, Hill C, Cotter PD. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2007;7:1236. doi: 10.2174/138955707782795638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gilmore MS, Segarra RA, Booth MC, Bogie CP, Hall LR, Clewell DB. J Bacteriol. 1994;176:7335. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.23.7335-7344.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Coburn PS, Gilmore MS. Cell Microbiol. 2003;5:661. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-5822.2003.00310.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Jett BD, Huycke MM, Gilmore MS. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1994;7:462. doi: 10.1128/cmr.7.4.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chatterjee C, Paul M, Xie L, van der Donk WA. Chem Rev. 2005;5:633. doi: 10.1021/cr030105v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.(a) Tang W, van der Donk WA. Nat Chem Biol. 2013;9:157. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Tang W, Jiménez-Osés G, Houk KN, van der Donk WA. Nat Chem. 2015;7:57. doi: 10.1038/nchem.2113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Tang W, Thibodeaux GN, van der Donk WA. ACS Chem Biol. 2016;11:2438. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.6b00397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.(a) Fukase K, Kitazawa M, Sano A, Shimbo K, Fujita H, Horimoto S, Wakamiya T, Shiba T. Tetrahedron Lett. 1988;29:795. [Google Scholar]; (b) Ross AC, Liu H, Pattabiraman VR, Vederas JC. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;132:462. doi: 10.1021/ja9095945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Liu W, Chan ASH, Liu H, Cochrane SA, Vederas JC. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:14216. doi: 10.1021/ja206017p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Knerr PJ, van der Donk WA. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:7648. doi: 10.1021/ja302435y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Knerr PJ, van der Donk WA. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135:7094. doi: 10.1021/ja4014024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.(a) Ludwick AG, Jelinski LW, Live D, Kintanar A, Dumais JJ. J Am Chem Soc. 1986;108:6493. [Google Scholar]; (b) Masuda K, Ooyama H, Shikano K, Kondo K, Furumitsu M, Iwakoshi-Ukena E, Ukena K. J Pep Sci. 2015;21:454. doi: 10.1002/psc.2756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.(a) Carrillo AK, VanNieuwenhze MS. Org Lett. 2012;14:1034. doi: 10.1021/ol2034806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) García-Reynaga P, Carrillo AK, VanNieuwenhze MS. Org Lett. 2012;14:1030. doi: 10.1021/ol203399x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Bregant S, Tabor AB. J Org Chem. 2005;70:2430. doi: 10.1021/jo048222t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Mothia B, Appleyard AN, Wadman S, Tabor AB. Org Lett. 2011;13:4216. doi: 10.1021/ol201548m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Narayan RS, VanNieuwenhze MS. Org Lett. 2005;7:2655. doi: 10.1021/ol0507930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Martin NI. J Org Chem. 2009;74:946. doi: 10.1021/jo802415c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.(a) Ross AC, Liu H, Pattabiraman VR, Vederas JC. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:462. doi: 10.1021/ja9095945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Pattabiraman VR, McKinnie SMK, Vederas JC. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2008;47:9472. doi: 10.1002/anie.200802919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Zhu X, Schmidt, Richard R. Eur J Org Chem. 2003;2003:4069. [Google Scholar]
- 12.(a) García-Martín F, Quintanar-Audelo M, García-Ramos Y, Cruz LJ, Gravel C, Furic R, Côté S, Tulla-Puche J, Al-bericio F. J Comb Chem. 2006;8:213. doi: 10.1021/cc0600019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) García-Martín F, White P, Steinauer R, Côté S, Tulla-Puche J, Albericio F. Biopolymers. 2006;84:566. doi: 10.1002/bip.20564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.(a) Eritja R, Martin JPZ, Walker PA, Lee TD, Legesse K, Albericio F, Kaplan BE. Tetrahedron. 1987;43:2675. [Google Scholar]; (b) Lukszo J, Patterson D, Albericio F, Kates S. Lett Pept Sci. 1996;3:157. [Google Scholar]
- 14.(a) Chalker JM, Gunnoo SB, Boutureira O, Gerstberger SC, Fernandez-Gonzalez M, Bernardes GJL, Griffin L, Hailu H, Schofield CJ, Davis BG. Chem Sci. 2011;2:1666. [Google Scholar]; (b) Morrison PM, Foley PJ, Warriner SL, Webb ME. Chem Comm. 2015;51:13470. doi: 10.1039/c5cc05469a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cox CR, Coburn PS, Gilmore MS. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2005;6:77. doi: 10.2174/1389203053027557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Van Tyne D, Martin MJ, Gilmore MS. Toxins. 2013;5:895. doi: 10.3390/toxins5050895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.