Abstract
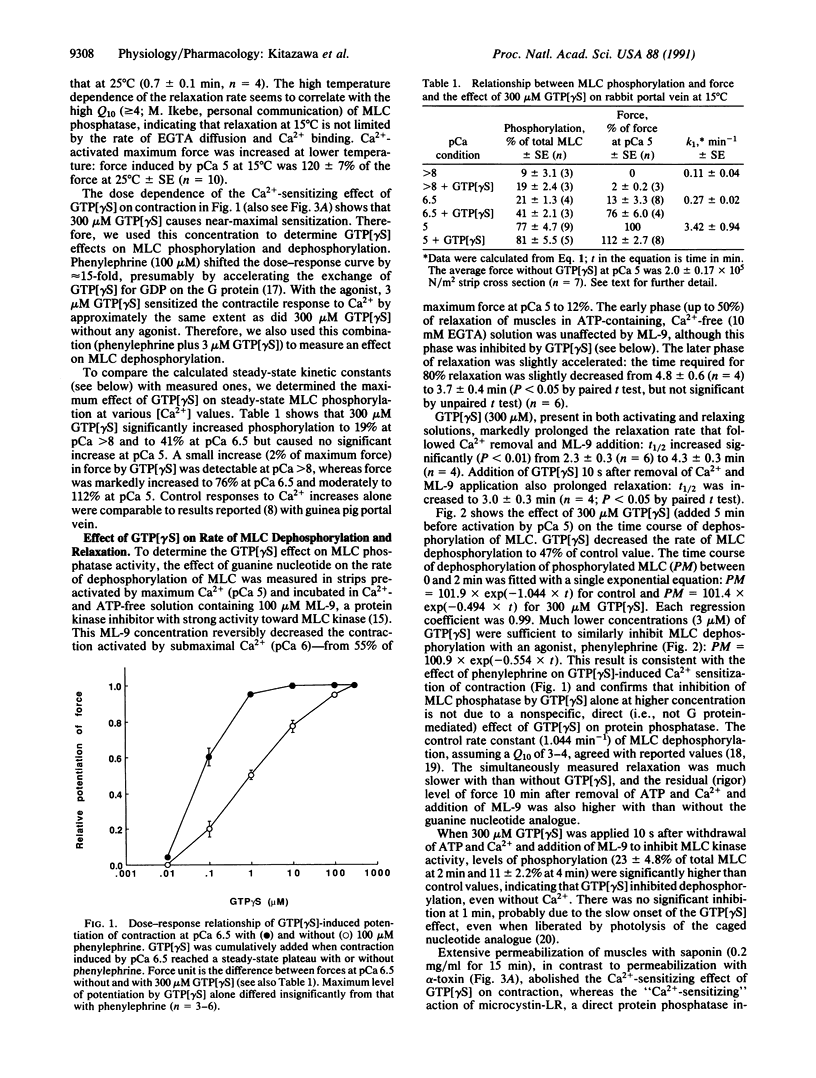
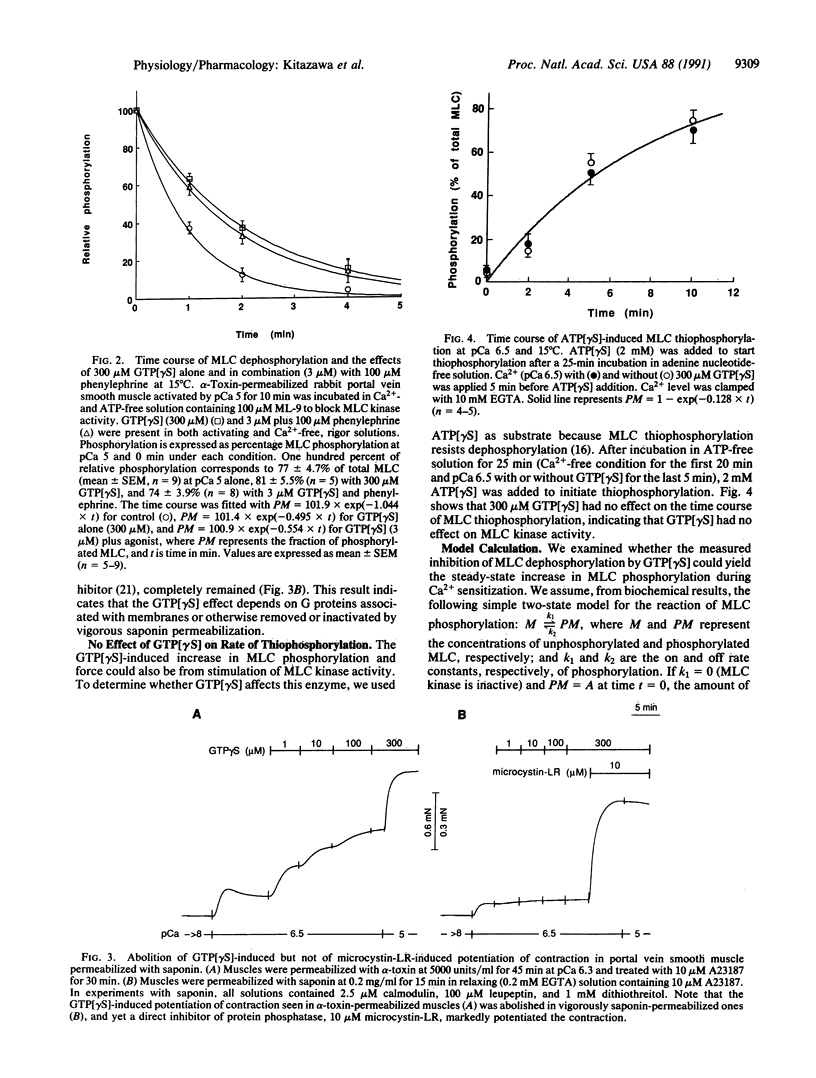
The mechanism of G protein-mediated sensitization of the contractile apparatus of smooth muscle to Ca2+ was studied in receptor-coupled alpha-toxin-permeabilized rabbit portal vein smooth muscle. To test the hypothesis that Ca2+ sensitization is due to inhibition of myosin light-chain (MLC) phosphatase activity, we measured the effect of guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate and phenylephrine on the rate of MLC dephosphorylation in muscles preactivated with Ca2+ and incubated in Ca(2+)- and ATP-free solution containing 1-(5-chloronaphthalene-1-sulfonyl)-1H-hexahydro-1,4-diazepine (ML-9) to block MLC kinase activity. Guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate alone (300 microM) or in combination (3 microM) with phenylephrine decreased the rates of relaxation and dephosphorylation of MLC to about half of control values; this inhibition is sufficient to account for maximal G protein-mediated Ca2+ sensitization of MLC phosphorylation. The rate of thiophosphorylation of MLC with adenosine 5'-[gamma-thio]-triphosphate was not affected by guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate. We suggest that inhibition of protein phosphatase(s) by G protein(s) may have important regulatory functions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley A. B., Morgan K. G. Alterations in cytoplasmic calcium sensitivity during porcine coronary artery contractions as detected by aequorin. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:437–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy P., Hoar P. E., Kerrick W. G. Irreversible thiophosphorylation and activation of tension in functionally skinned rabbit ileum strips by [35S]ATP gamma S. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11148–11153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driska S. P., Stein P. G., Porter R. Myosin dephosphorylation during rapid relaxation of hog carotid artery smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 1):C315–C321. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.2.C315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman A. M., Lin W. H., Osterhout D. J., Bennett M. K., Kennedy M. B., Krebs E. G. Phosphorylation of smooth muscle myosin by type II Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Mol Cell Biochem. 1990 Sep 3;97(1):87–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00231704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Itoh T., Kubota Y., Kuriyama H. Effects of guanosine nucleotides on skinned smooth muscle tissue of the rabbit mesenteric artery. J Physiol. 1989 Jan;408:535–547. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeberle J. R., Sutton T. A., Trockman B. A. Phosphorylation of two sites on smooth muscle myosin. Effects on contraction of glycerinated vascular smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4424–4429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himpens B., Casteels R. Measurement by Quin2 of changes of the intracellular calcium concentration in strips of the rabbit ear artery and of the guinea-pig ileum. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Jan;408(1):32–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00581837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himpens B., Kitazawa T., Somlyo A. P. Agonist-dependent modulation of Ca2+ sensitivity in rabbit pulmonary artery smooth muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Sep;417(1):21–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00370764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himpens B., Matthijs G., Somlyo A. P. Desensitization to cytoplasmic Ca2+ and Ca2+ sensitivities of guinea-pig ileum and rabbit pulmonary artery smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1989 Jun;413:489–503. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa T., Chijiwa T., Hagiwara M., Mamiya S., Saitoh M., Hidaka H. ML-9 inhibits the vascular contraction via the inhibition of myosin light chain phosphorylation. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;33(6):598–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamm K. E., Stull J. T. Activation of smooth muscle contraction: relation between myosin phosphorylation and stiffness. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):80–82. doi: 10.1126/science.3754063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamm K. E., Stull J. T. Myosin phosphorylation, force, and maximal shortening velocity in neurally stimulated tracheal smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 1):C238–C247. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.249.3.C238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazawa T., Gaylinn B. D., Denney G. H., Somlyo A. P. G-protein-mediated Ca2+ sensitization of smooth muscle contraction through myosin light chain phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1708–1715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazawa T., Kobayashi S., Horiuti K., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Receptor-coupled, permeabilized smooth muscle. Role of the phosphatidylinositol cascade, G-proteins, and modulation of the contractile response to Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5339–5342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazawa T., Somlyo A. P. Desensitization and muscarinic re-sensitization of force and myosin light chain phosphorylation to cytoplasmic Ca2+ in smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1291–1297. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91589-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKintosh C., Beattie K. A., Klumpp S., Cohen P., Codd G. A. Cyanobacterial microcystin-LR is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A from both mammals and higher plants. FEBS Lett. 1990 May 21;264(2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80245-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. P., Morgan K. G. Stimulus-specific patterns of intracellular calcium levels in smooth muscle of ferret portal vein. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:155–167. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mrwa U., Hartshorne D. J. Phosphorylation of smooth muscle myosin and myosin light chains. Fed Proc. 1980 Apr;39(5):1564–1568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura J., Kolber M., van Breemen C. Norepinephrine and GTP-gamma-S increase myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity in alpha-toxin permeabilized arterial smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):677–683. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rembold C. M., Murphy R. A. Myoplasmic [Ca2+] determines myosin phosphorylation in agonist-stimulated swine arterial smooth muscle. Circ Res. 1988 Sep;63(3):593–603. doi: 10.1161/01.res.63.3.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Ozaki H., Karaki H. Changes in cytosolic calcium level in vascular smooth muscle strip measured simultaneously with contraction using fluorescent calcium indicator fura 2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Jul;246(1):294–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V., Kitazawa T., Horiuti K., Kobayashi S., Trentham D., Somlyo A. P. Heparin-sensitive inositol trisphosphate signaling and the role of G-proteins in Ca2(+)-release and contractile regulation in smooth muscle. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990;327:167–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull J. T., Hsu L. C., Tansey M. G., Kamm K. E. Myosin light chain kinase phosphorylation in tracheal smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16683–16690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



