Abstract
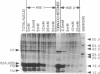
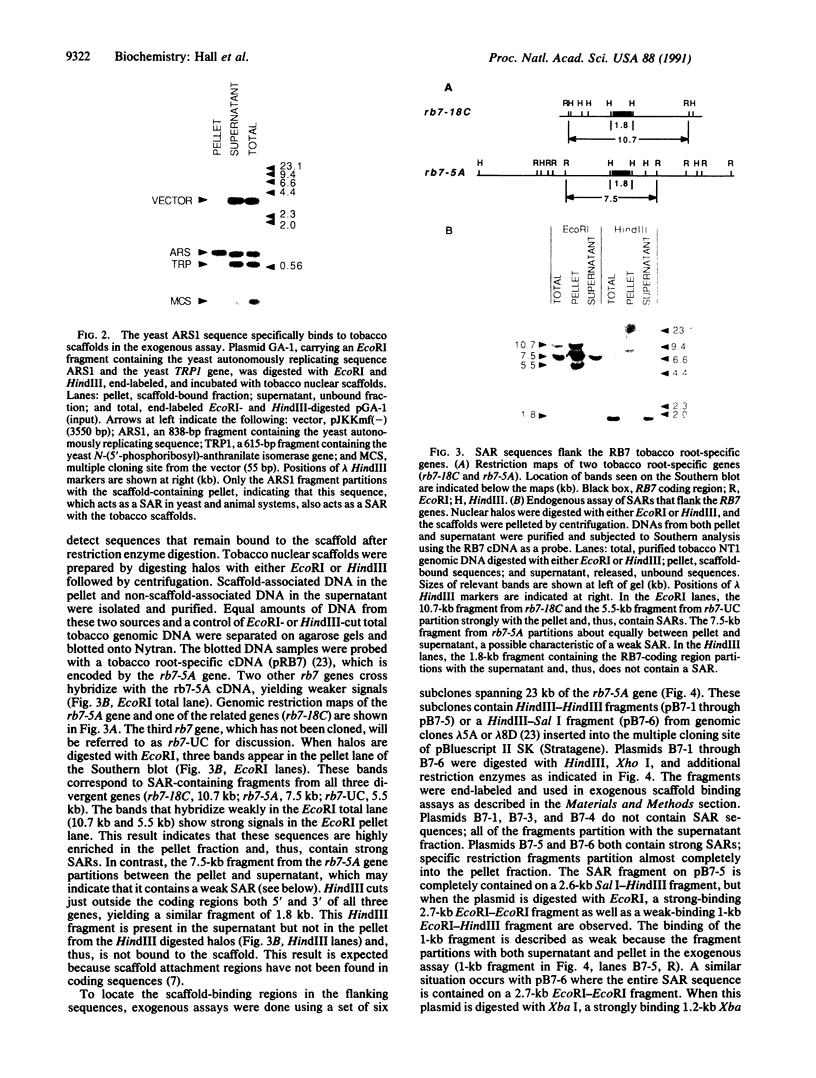
DNA in the nuclei of eukaryotic organisms undergoes a hierarchy of folding to be packaged into interphase and metaphase chromosomes. The first level of packaging is the 11-nm nucleosome fiber, which is further coiled into a 30-nm fiber. Evidence from fungal and animal systems reveals the existence of higher order packaging consisting of loops of the 30-nm fibers attached to a proteinaceous nuclear scaffold by an interaction between the scaffold and specific DNA sequences called scaffold-attachment regions (SARs). Support for the ubiquitous nature of such higher order packaging of DNA is presented here by our work with plants. We have isolated scaffolds from tobacco nuclei using buffers containing lithium diiodosalicylate to remove histones and then using restriction enzymes to remove the DNA not closely associated with the scaffold. We have used Southern hybridization to show that the DNA remaining bound to the scaffolds after nuclease digestion includes SARs flanking three root-specific tobacco genes. This assay for SARs is termed the endogenous assay because it identifies genomic sequences as SARs by their endogenous association with the scaffold. Another assay, the exogenous assay, depends upon the ability of scaffolds to specifically bind exogenously added DNA fragments containing SARs. The tobacco scaffolds specifically bind a well-characterized yeast SAR, and cloned DNA fragments derived from the 3'-flanking regions of the root-specific genes are confirmed to contain SARs by this exogenous assay.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amati B. B., Gasser S. M. Chromosomal ARS and CEN elements bind specifically to the yeast nuclear scaffold. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):967–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90111-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- An G. High efficiency transformation of cultured tobacco cells. Plant Physiol. 1985 Oct;79(2):568–570. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.2.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Worcel A. Isolation, characterization, and structure of the folded interphase genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):393–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode J., Maass K. Chromatin domain surrounding the human interferon-beta gene as defined by scaffold-attached regions. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 28;27(13):4706–4711. doi: 10.1021/bi00413a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifer C., Vidal M., Grosveld F., Sippel A. E. Tissue specific and position independent expression of the complete gene domain for chicken lysozyme in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2843–2848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07473.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Garrard W. T. Chromosomal loop anchorage of the kappa immunoglobulin gene occurs next to the enhancer in a region containing topoisomerase II sites. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90761-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Yuen M. H., Garrard W. T. The enhancer of the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus is flanked by presumptive chromosomal loop anchorage elements. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5394–5397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conkling M. A., Cheng C. L., Yamamoto Y. T., Goodman H. M. Isolation of transcriptionally regulated root-specific genes from tobacco. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jul;93(3):1203–1211. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.3.1203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R., Brazell I. A. Conformational constraints in nuclear DNA. J Cell Sci. 1976 Nov;22(2):287–302. doi: 10.1242/jcs.22.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R., Brazell I. A. Supercoils in human DNA. J Cell Sci. 1975 Nov;19(2):261–279. doi: 10.1242/jcs.19.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean C., Jones J., Favreau M., Dunsmuir P., Bedbrook J. Influence of flanking sequences on variability in expression levels of an introduced gene in transgenic tobacco plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9267–9283. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. Chromatin structure and gene activity. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;2(3):437–445. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90125-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Amati B. B., Cardenas M. E., Hofmann J. F. Studies on scaffold attachment sites and their relation to genome function. Int Rev Cytol. 1989;119:57–96. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60649-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laemmli U. K. The organisation of chromatin loops: characterization of a scaffold attachment site. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):511–518. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04240.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs S. L., Kpodar P., DeLong C. M. The effect of T-DNA copy number, position and methylation on reporter gene expression in tobacco transformants. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Dec;15(6):851–864. doi: 10.1007/BF00039425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaurralde E., Mirkovitch J., Laemmli U. K. Interaction of DNA with nuclear scaffolds in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1988 Mar 5;200(1):111–125. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90337-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarman A. P., Higgs D. R. Nuclear scaffold attachment sites in the human globin gene complexes. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3337–3344. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03205.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschman J. A., Cramer J. H. Two new tools: multi-purpose cloning vectors that carry kanamycin or spectinomycin/streptomycin resistance markers. Gene. 1988 Aug 15;68(1):163–165. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90609-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loc P. V., Strätling W. H. The matrix attachment regions of the chicken lysozyme gene co-map with the boundaries of the chromatin domain. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):655–664. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02860.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. A view of interphase chromosomes. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1533–1540. doi: 10.1126/science.2274784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mielke C., Kohwi Y., Kohwi-Shigematsu T., Bode J. Hierarchical binding of DNA fragments derived from scaffold-attached regions: correlation of properties in vitro and function in vivo. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 14;29(32):7475–7485. doi: 10.1021/bi00484a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Mirault M. E., Laemmli U. K. Organization of the higher-order chromatin loop: specific DNA attachment sites on nuclear scaffold. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. R., Laemmli U. K. The structure of histone-depleted metaphase chromosomes. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):817–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. C., Ochs R. L., Lin D., Chinault A. C. Ultrastructural and biochemical comparisons of nuclear matrices prepared by high salt or LIS extraction. Mol Cell Biochem. 1987 Sep;77(1):49–61. doi: 10.1007/BF00230150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder J., Larsen A., Engel J. D., Dolan M., Groudine M., Weintraub H. Tissue-specific DNA cleavages in the globin chromatin domain introduced by DNAase I. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90631-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stief A., Winter D. M., Strätling W. H., Sippel A. E. A nuclear DNA attachment element mediates elevated and position-independent gene activity. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):343–345. doi: 10.1038/341343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. C., Lin D., Hwang S. J., Framson P. E., Chinault A. C. Yeast ARS function and nuclear matrix association coincide in a short sequence from the human HPRT locus. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 May;212(2):301–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00334700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. An octamer of histones in chromatin and free in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2626–2630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschumper G., Carbon J. Sequence of a yeast DNA fragment containing a chromosomal replicator and the TRP1 gene. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitz W., Loidl P. In situ preparation of the nuclear matrix of Physarum polycephalum: ultrastructural and biochemical analysis of different matrix isolation procedures. J Cell Sci. 1988 Aug;90(Pt 4):621–628. doi: 10.1242/jcs.90.4.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kries J. P., Buhrmester H., Strätling W. H. A matrix/scaffold attachment region binding protein: identification, purification, and mode of binding. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):123–135. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90214-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]