Abstract
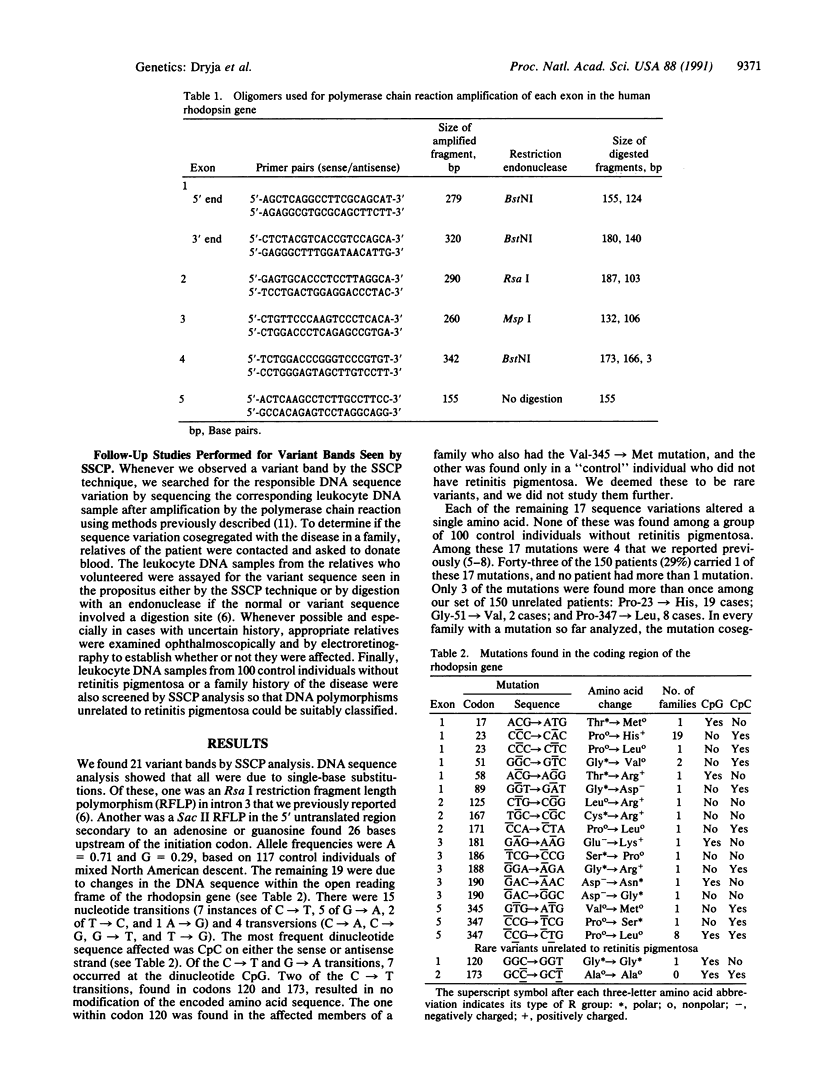
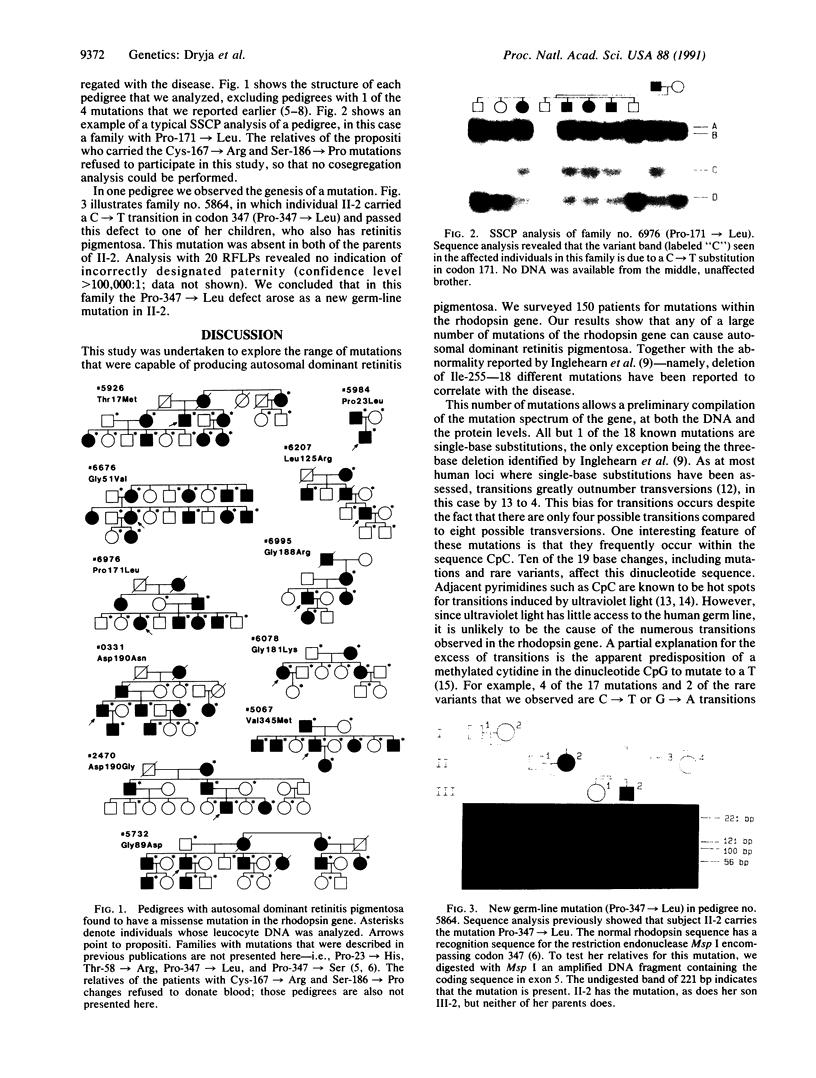
We searched for point mutations in every exon of the rhodopsin gene in 150 patients from separate families with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Including the 4 mutations we reported previously, we found a total of 17 different mutations that correlate with the disease. Each of these mutations is a single-base substitution corresponding to a single amino acid substitution. Based on current models for the structure of rhodopsin, 3 of the 17 mutant amino acids are normally located on the cytoplasmic side of the protein, 6 in transmembrane domains, and 8 on the intradiscal side. Forty-three of the 150 patients (29%) carry 1 of these mutations, and no patient has more than 1 mutation. In every family with a mutation so far analyzed, the mutation cosegregates with the disease. We found one instance of a mutation in an affected patient that was absent in both unaffected parents (i.e., a new germ-line mutation), indicating that some "isolate" cases of retinitis pigmentosa carry a mutation of the rhodopsin gene.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berson E. L., Rosner B., Sandberg M. A., Dryja T. P. Ocular findings in patients with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa and a rhodopsin gene defect (Pro-23-His). Arch Ophthalmol. 1991 Jan;109(1):92–101. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1991.01080010094039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berson E. L., Rosner B., Sandberg M. A., Weigel-DiFranco C., Dryja T. P. Ocular findings in patients with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa and rhodopsin, proline-347-leucine. Am J Ophthalmol. 1991 May 15;111(5):614–623. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)73708-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boughman J. A., Conneally P. M., Nance W. E. Population genetic studies of retinitis pigmentosa. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 Mar;32(2):223–235. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brash D. E., Seetharam S., Kraemer K. H., Seidman M. M., Bredberg A. Photoproduct frequency is not the major determinant of UV base substitution hot spots or cold spots in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3782–3786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunker C. H., Berson E. L., Bromley W. C., Hayes R. P., Roderick T. H. Prevalence of retinitis pigmentosa in Maine. Am J Ophthalmol. 1984 Mar;97(3):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(84)90636-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulondre C., Miller J. H., Farabaugh P. J., Gilbert W. Molecular basis of base substitution hotspots in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):775–780. doi: 10.1038/274775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defoe D. M., Besharse J. C., Fliesler S. J. Tunicamycin-induced dysgenesis of retinal rod outer segment membranes. II. Quantitative freeze-fracture analysis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1986 Nov;27(11):1595–1601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryja T. P., McGee T. L., Hahn L. B., Cowley G. S., Olsson J. E., Reichel E., Sandberg M. A., Berson E. L. Mutations within the rhodopsin gene in patients with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. N Engl J Med. 1990 Nov 8;323(19):1302–1307. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199011083231903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryja T. P., McGee T. L., Reichel E., Hahn L. B., Cowley G. S., Yandell D. W., Sandberg M. A., Berson E. L. A point mutation of the rhodopsin gene in one form of retinitis pigmentosa. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):364–366. doi: 10.1038/343364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliesler S. J., Rayborn M. E., Hollyfield J. G. Membrane morphogenesis in retinal rod outer segments: inhibition by tunicamycin. J Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;100(2):574–587. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.2.574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglehearn C. F., Bashir R., Lester D. H., Jay M., Bird A. C., Bhattacharya S. S. A 3-bp deletion in the rhodopsin gene in a family with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jan;48(1):26–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippke J. A., Gordon L. K., Brash D. E., Haseltine W. A. Distribution of UV light-induced damage in a defined sequence of human DNA: detection of alkaline-sensitive lesions at pyrimidine nucleoside-cytidine sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3388–3392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Davenport C. M., Maumenee I. H., Lewis R. A., Hejtmancik J. F., Litt M., Lovrien E., Weleber R., Bachynski B., Zwas F. Molecular genetics of human blue cone monochromacy. Science. 1989 Aug 25;245(4920):831–838. doi: 10.1126/science.2788922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita M., Suzuki Y., Sekiya T., Hayashi K. Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):874–879. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulshafer R. J., Allen C. B., Fliesler S. J. Tunicamycin-induced dysgenesis of retinal rod outer segment membranes. I. A scanning electron microscopy study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1986 Nov;27(11):1587–1594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel F., Rathenberg R. Spontaneous mutation in man. Adv Hum Genet. 1975;5:223–318. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9068-2_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





