Abstract
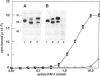
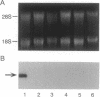
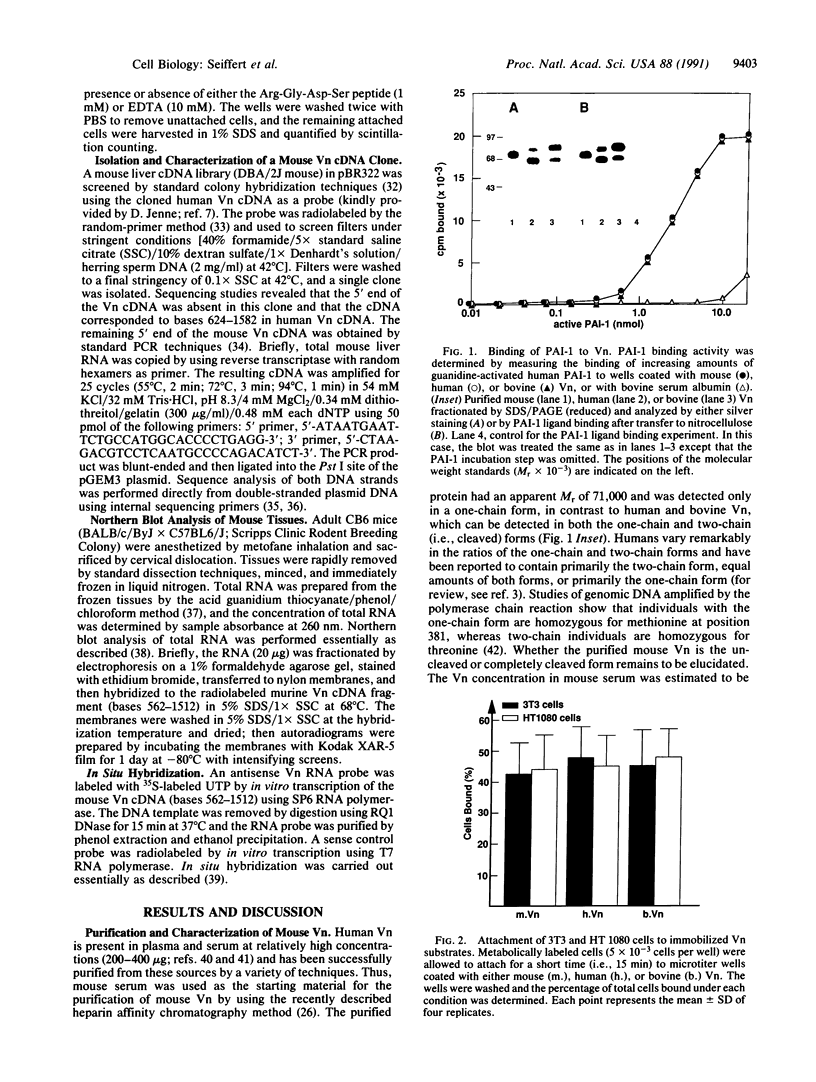
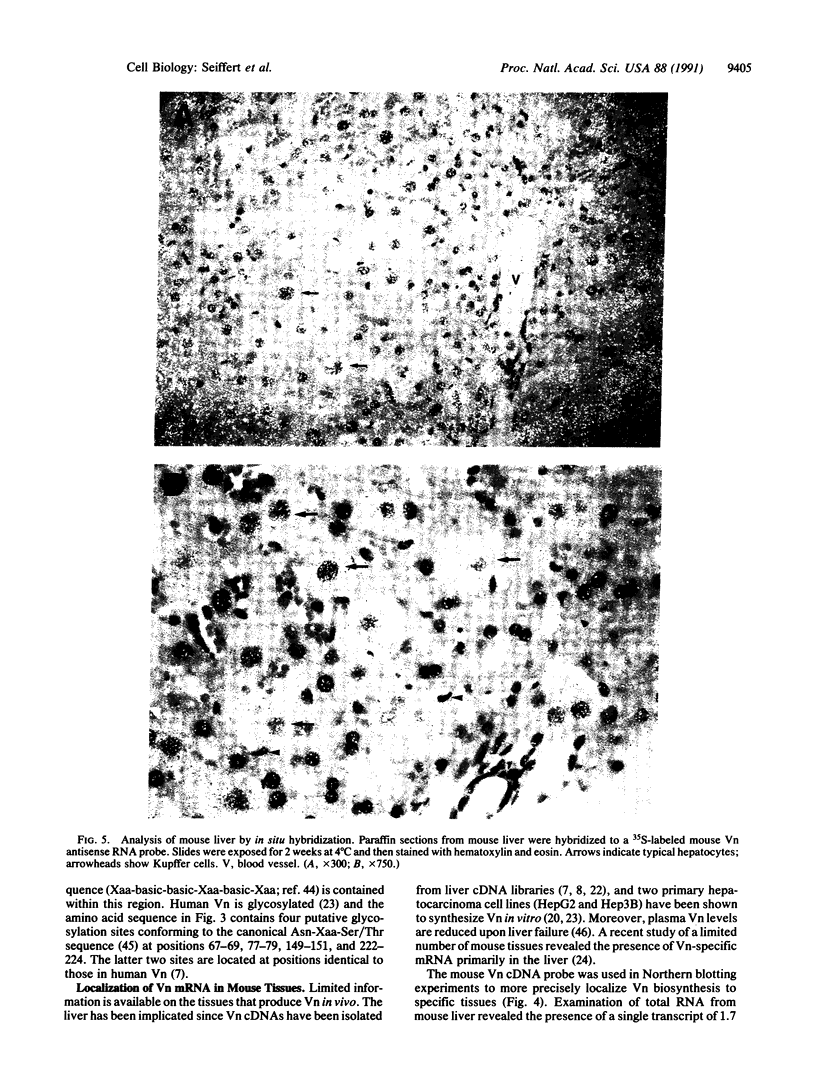
Mouse vitronectin (Vn) was isolated from serum by heparin affinity chromatography. The purified protein (Mr 71,000) supported adhesion of mouse and human cells in an Arg-Gly-Asp-dependent manner and bound to type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor with kinetics similar to those observed using human and bovine Vn. To further characterize murine Vn and its biosynthesis in vivo, a mouse Vn cDNA was isolated from a liver cDNA library. The amino acid sequence of mouse Vn was deduced from the cDNA and was aligned with that of human Vn. Based on this alignment, mouse Vn was inferred to be 457 amino acids long and to have extensive (82%) homology with human Vn. Northern blot hybridization analysis of RNA from mouse tissues, using the mouse Vn cDNA as a hybridization probe, revealed the presence of a single transcript of 1.7 kilobases in mouse liver. Vn mRNA was not detectable in heart, lung, kidney, spleen, muscle, brain, thymus, testes, uterus, skin, adipose tissue, and aorta. The cellular localization of liver Vn mRNA was studied by in situ hybridization. Strong staining was observed only in hepatocytes, suggesting that these cells are the primary source of Vn in vivo.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes D. W., Reing J. Human spreading factor: synthesis and response by HepG2 hepatoma cells in culture. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Nov;125(2):207–214. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041250206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes D. W., Silnutzer J. Isolation of human serum spreading factor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12548–12552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardin A. D., Weintraub H. J. Molecular modeling of protein-glycosaminoglycan interactions. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Jan-Feb;9(1):21–32. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheresh D. A. Human endothelial cells synthesize and express an Arg-Gly-Asp-directed adhesion receptor involved in attachment to fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6471–6475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlan M. G., Tomasini B. R., Schultz R. L., Mosher D. F. Plasma vitronectin polymorphism in normal subjects and patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation. Blood. 1988 Jul;72(1):185–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck K., Löfberg H., Alumets J., Dahlbäck B. Immunohistochemical demonstration of age-related deposition of vitronectin (S-protein of complement) and terminal complement complex on dermal elastic fibers. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 May;92(5):727–733. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12721619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Declerck P. J., De Mol M., Alessi M. C., Baudner S., Pâques E. P., Preissner K. T., Müller-Berghaus G., Collen D. Purification and characterization of a plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 binding protein from human plasma. Identification as a multimeric form of S protein (vitronectin). J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15454–15461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich H. J., Gebbink R. K., Keijer J., Linders M., Preissner K. T., Pannekoek H. Alteration of serpin specificity by a protein cofactor. Vitronectin endows plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 with thrombin inhibitory properties. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13029–13035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guettier C., Hinglais N., Bruneval P., Kazatchkine M., Bariety J., Camilleri J. P. Immunohistochemical localization of S protein/vitronectin in human atherosclerotic versus arteriosclerotic arteries. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1989;414(4):309–313. doi: 10.1007/BF00734084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman E. G., Pierschbacher M. D., Ohgren Y., Ruoslahti E. Serum spreading factor (vitronectin) is present at the cell surface and in tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4003–4007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman E. G., Pierschbacher M. D., Suzuki S., Ruoslahti E. Vitronectin--a major cell attachment-promoting protein in fetal bovine serum. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Oct;160(2):245–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90173-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekman C. M., Loskutoff D. J. Bovine plasminogen activator inhibitor 1: specificity determinations and comparison of the active, latent, and guanidine-activated forms. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2911–2918. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekman C. M., Loskutoff D. J. Endothelial cells produce a latent inhibitor of plasminogen activators that can be activated by denaturants. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11581–11587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ill C. R., Ruoslahti E. Association of thrombin-antithrombin III complex with vitronectin in serum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15610–15615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D., Stanley K. K. Molecular cloning of S-protein, a link between complement, coagulation and cell-substrate adhesion. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3153–3157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04058.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota K., Hayashi M., Oishi N., Sakaki Y. Polymorphism of the human vitronectin gene causes vitronectin blood type. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 30;167(3):1355–1360. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90672-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. D. The nature and metabolism of the carbohydrate-peptide linkages of glycoproteins. Biochem Soc Symp. 1974;(40):17–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimuro J., Loskutoff D. J. Purification of a protein from bovine plasma that binds to type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor and prevents its interaction with extracellular matrix. Evidence that the protein is vitronectin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):936–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niculescu F., Rus H. G., Poruţiu D., Ghiurca V., Vlaicu R. Immunoelectron-microscopic localization of S-protein/vitronectin in human atherosclerotic wall. Atherosclerosis. 1989 Aug;78(2-3):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(89)90223-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Loftus J. C., Levin E. G., Fair D. S., Dixon D., Forsyth J., Ginsberg M. H. Immunologic relationship between platelet membrane glycoprotein GPIIb/IIIa and cell surface molecules expressed by a variety of cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6002–6006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E., Marguerie G., Ginsberg M. H. Arginyl-glycyl-aspartic acid sequences and fibrinogen binding to platelets. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):110–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preissner K. T., Grulich-Henn J., Ehrlich H. J., Declerck P., Justus C., Collen D., Pannekoek H., Müller-Berghaus G. Structural requirements for the extracellular interaction of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 with endothelial cell matrix-associated vitronectin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18490–18498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preissner K. T., Heimburger N., Anders E., Müller-Berghaus G. Physicochemical, immunochemical and functional comparison of human S-protein and vitronectin. Evidence for the identity of both plasma proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 29;134(2):951–956. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preissner K. T., Müller-Berghaus G. Neutralization and binding of heparin by S protein/vitronectin in the inhibition of factor Xa by antithrombin III. Involvement of an inducible heparin-binding domain of S protein/vitronectin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12247–12253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preissner K. T., Wassmuth R., Müller-Berghaus G. Physicochemical characterization of human S-protein and its function in the blood coagulation system. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 15;231(2):349–355. doi: 10.1042/bj2310349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):491–497. doi: 10.1126/science.2821619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela O., Rifkin D. B. Cell-associated plasminogen activation: regulation and physiological functions. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:93–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato R., Komine Y., Imanaka T., Takano T. Monoclonal antibody EMR1a/212D recognizing site of deposition of extracellular lipid in atherosclerosis. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone for the antigen. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21232–21236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiffert D., Loskutoff D. J. Evidence that type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor binds to the somatomedin B domain of vitronectin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2824–2830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiffert D., Wagner N. N., Loskutoff D. J. Serum-derived vitronectin influences the pericellular distribution of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1283–1291. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solem M., Helmrich A., Collodi P., Barnes D. Human and mouse S-protein mRNA detected in northern blot experiments and evidence for the gene encoding S-protein in mammals by Southern blot analysis. Mol Cell Biochem. 1991 Feb 2;100(2):141–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00234163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Oldberg A., Hayman E. G., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Complete amino acid sequence of human vitronectin deduced from cDNA. Similarity of cell attachment sites in vitronectin and fibronectin. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2519–2524. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03965.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasini B. R., Mosher D. F. On the identity of vitronectin and S-protein: immunological crossreactivity and functional studies. Blood. 1986 Sep;68(3):737–742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virca G. D., Northemann W., Shiels B. R., Widera G., Broome S. Simplified northern blot hybridization using 5% sodium dodecyl sulfate. Biotechniques. 1990 Apr;8(4):370–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox J. N., Smith K. M., Schwartz S. M., Gordon D. Localization of tissue factor in the normal vessel wall and in the atherosclerotic plaque. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2839–2843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Almquist A., Sigurdardottir O., Lindahl T. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI) is bound to vitronectin in plasma. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 19;242(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80999-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatohgo T., Izumi M., Kashiwagi H., Hayashi M. Novel purification of vitronectin from human plasma by heparin affinity chromatography. Cell Struct Funct. 1988 Aug;13(4):281–292. doi: 10.1247/csf.13.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Mourik J. A., Lawrence D. A., Loskutoff D. J. Purification of an inhibitor of plasminogen activator (antiactivator) synthesized by endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14914–14921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]