Abstract
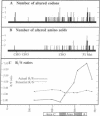
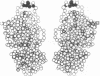
The murine alpha 1-protease inhibitors (alpha 1-PI) are encoded by a small gene family on chromosome 12. Studies of alpha 1-PI and other serine protease inhibitor genes have revealed an unusually high rate of mutation of the reactive centers of the inhibitors. Using a modification of the PCR technique, we have previously identified five distinct alpha 1 PI reactive site sequences present in the genome of C57BL/6 mice. In this report, we use cDNA cloning techniques to demonstrate that all five genes are expressed in the adult mouse liver. DNA sequence analysis shows that three of the five mRNAs expressed have a substitution for methionine-353, which is essential for normal activity of the homologous human protein, alpha 1-antitrypsin (alpha 1-AT). Comparison of the DNA sequences of the five cDNAs indicates a higher degree of polymorphism in the carboxyl-terminal half of the protein and an extraordinarily replacement/silent ratio of nucleotide changes in a narrow region surrounding the reactive site. The clustering of polymorphisms near the reactive site combined with the high replacement/silent ratio suggest an evolutionary mechanism that apparently selects for functional diversity of the alpha 1-PI genes. Finally, modeling of the three-dimensional positions of the alpha 1-PI polymorphic residues into the homologous positions of the crystallographic structure of ovalbumin, a member of the alpha 1-PI supergene family, predicts that many of these amino acids are on the surfaces, which are likely to interact with the protease targets.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blank R. D., Campbell G. R., Calabro A., D'Eustachio P. A linkage map of mouse chromosome 12: localization of Igh and effects of sex and interference on recombination. Genetics. 1988 Dec;120(4):1073–1083. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.4.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borriello F., Krauter K. S. Reactive site polymorphism in the murine protease inhibitor gene family is delineated using a modification of the PCR reaction (PCR + 1). Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5481–5487. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrell R. W., Jeppsson J. O., Laurell C. B., Brennan S. O., Owen M. C., Vaughan L., Boswell D. R. Structure and variation of human alpha 1-antitrypsin. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):329–334. doi: 10.1038/298329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman E., Krauter K., Walling L., Weinberger C., Ray M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control in the production of liver-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):731–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Angiotensinogen is related to the antitrypsin-antithrombin-ovalbumin family. Science. 1983 Oct 28;222(4622):417–419. doi: 10.1126/science.6604942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. E., Hastie N. D. Accelerated evolution in the reactive centre regions of serine protease inhibitors. Nature. 1987 Mar 5;326(6108):96–99. doi: 10.1038/326096a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. E., Shaw P. H., Barth R. K., Hastie N. D. A genetic locus closely linked to a protease inhibitor gene complex controls the level of multiple RNA transcripts. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2114–2122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. E., Shaw P. H., Boyd P. A., Baumann H., Hastie N. D. Plasma protease inhibitors in mouse and man: divergence within the reactive centre regions. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):175–177. doi: 10.1038/311175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jukes T. H., King J. L. Evolutionary nucleotide replacements in DNA. Nature. 1979 Oct 18;281(5732):605–606. doi: 10.1038/281605a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Figueroa F. Evolution of the major histocompatibility complex. Crit Rev Immunol. 1986;6(4):295–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft R., Tardiff J., Krauter K. S., Leinwand L. A. Using mini-prep plasmid DNA for sequencing double stranded templates with Sequenase. Biotechniques. 1988 Jun;6(6):544-6, 549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauter K. S., Citron B. A., Hsu M. T., Powell D., Darnell J. E., Jr Isolation and characterization of the alpha 1-antitrypsin gene of mice. DNA. 1986 Feb;5(1):29–36. doi: 10.1089/dna.1986.5.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latimer J. J., Berger F. G., Baumann H. Highly conserved upstream regions of the alpha 1-antitrypsin gene in two mouse species govern liver-specific expression by different mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):760–769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leicht M., Long G. L., Chandra T., Kurachi K., Kidd V. J., Mace M., Jr, Davie E. W., Woo S. L. Sequence homology and structural comparison between the chromosomal human alpha 1-antitrypsin and chicken ovalbumin genes. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):655–659. doi: 10.1038/297655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loebermann H., Tokuoka R., Deisenhofer J., Huber R. Human alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. Crystal structure analysis of two crystal modifications, molecular model and preliminary analysis of the implications for function. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 15;177(3):531–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery K. T., Tardiff J., Reid L. M., Krauter K. S. Negative and positive cis-acting elements control the expression of murine alpha 1-protease inhibitor genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2625–2637. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton P. A., Stein P. E., Pepys M. B., Potter J. M., Carrell R. W. Hormone binding globulins undergo serpin conformational change in inflammation. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):257–258. doi: 10.1038/336257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perler F., Efstratiadis A., Lomedico P., Gilbert W., Kolodner R., Dodgson J. The evolution of genes: the chicken preproinsulin gene. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90641-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potempa J., Shieh B. H., Travis J. Alpha-2-antiplasmin: a serpin with two separate but overlapping reactive sites. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):699–700. doi: 10.1126/science.2456616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlomchik M. J., Marshak-Rothstein A., Wolfowicz C. B., Rothstein T. L., Weigert M. G. The role of clonal selection and somatic mutation in autoimmunity. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):805–811. doi: 10.1038/328805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sifers R. N., Rogers B. B., Hawkins H. K., Finegold M. J., Woo S. L. Elevated synthesis of human alpha 1-antitrypsin hinders the secretion of murine alpha 1-antitrypsin from hepatocytes of transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15696–15700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver G., Krauter K. S. Expression of cytochromes P-450c and P-450d mRNAs in cultured rat hepatocytes. 3-Methylcholanthrene induction is regulated primarily at the post-transcriptional level. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11802–11807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein P. E., Leslie A. G., Finch J. T., Turnell W. G., McLaughlin P. J., Carrell R. W. Crystal structure of ovalbumin as a model for the reactive centre of serpins. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):99–102. doi: 10.1038/347099a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J., Salvesen G. S. Human plasma proteinase inhibitors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:655–709. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]