Abstract
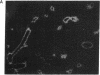
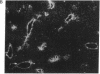
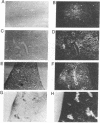
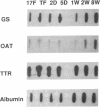
In situ hybridization showed that the mRNA for ornithine aminotransferase (OAT; ornithine-oxo-acid aminotransferase; L-ornithine: 2-oxo-acid aminotransferase, EC 2.6.1.13) colocalized with glutamine synthetase [GS; glutamate-ammonia ligase; L-glutamate: ammonia ligase (ADP-forming), EC 6.3.1.2] in pericentral hepatocytes of the adult mouse liver. In addition to an identical distribution in adult hepatocytes, OAT and GS have very similar expression patterns in fetal and neonatal liver. As was earlier described for GS, there is a low level of OAT mRNA in fetal cells and increasing pericentral levels in neonates that reach adult patterns within 2 weeks. These results suggest that the transcriptional regulation of the two genes is similar in the liver. However, there was a lack of colocalization of the mRNAs for the two enzymes in cells of the kidney, intestine, and brain, suggesting different regulatory decisions for the OAT and GS genes in the cells of these different tissues. The metabolic consequences of these localized expression patterns favor ammonia clearance from the blood by the liver and urea synthesis by the kidney.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett A. L., Paulson K. E., Miller R. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Acquisition of antigens characteristic of adult pericentral hepatocytes by differentiating fetal hepatoblasts in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1073–1085. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming G. A., Steel G., Valle D., Granger A. S., Phang J. M. The aqueous humor of rabbit contains high concentrations of pyrroline-5-carboxylate. Metabolism. 1986 Oct;35(10):933–937. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(86)90057-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaasbeek Janzen J. W., Lamers W. H., Moorman A. F., de Graaf A., Los J. A., Charles R. Immunohistochemical localization of carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase (ammonia) in adult rat liver; evidence for a heterogeneous distribution. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Jun;32(6):557–564. doi: 10.1177/32.6.6373912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt R., Mecke D. Heterogeneous distribution of glutamine synthetase among rat liver parenchymal cells in situ and in primary culture. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):567–570. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotta Y., Kato T. Ornithine aminotransferase distribution in ocular tissues and retinas of cat and mouse. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1989 Jun;30(6):1173–1177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. E. Conversion of glutamate to ornithine and proline: pyrroline-5-carboxylate, a possible modulator of arginine requirements. J Nutr. 1985 Apr;115(4):509–515. doi: 10.1093/jn/115.4.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungermann K., Katz N. Functional hepatocellular heterogeneity. Hepatology. 1982 May-Jun;2(3):385–395. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara M., Matsuzawa T., Kokubo M., Gushiken Y., Tashiro K., Koide T., Watanabe H., Katunuma N. Immunohistochemical localization of ornithine aminotransferase in normal rat tissues by Fab'-horseradish peroxidase conjugates. J Histochem Cytochem. 1986 Nov;34(11):1385–1388. doi: 10.1177/34.11.3534076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. F., Darnell J. E., Jr Mouse glutamine synthetase is encoded by a single gene that can be expressed in a localized fashion. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jul 5;208(1):45–56. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. F., Paulson K. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Positional and developmental regulation of glutamine synthetase expression in mouse liver. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4966–4971. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell G. A., Looney J. E., Brody L. C., Steel G., Suchanek M., Engelhardt J. F., Willard H. F., Valle D. Human ornithine-delta-aminotransferase. cDNA cloning and analysis of the structural gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14288–14295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison M., Steele W., Danner D. J. The reaction of benzoquinone with amines and proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Nov;134(2):515–523. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90313-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPPAPORT A. M., BOROWY Z. J., LOUGHEED W. M., LOTTO W. N. Subdivision of hexagonal liver lobules into a structural and functional unit; role in hepatic physiology and pathology. Anat Rec. 1954 May;119(1):11–33. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091190103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHANK R. E., MORRISON G., CHENG C. H., KARL I., SCHWARTZ R. Cell heterogeneity within the hepatic lobule: quantitative histochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1959 Jul;7(4):237–239. doi: 10.1177/7.4.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi O., Ishiguro S., Mito T., Hayasaka S., Shiono T., Mizuno K., Ohura T., Tada K. Immunocytochemical localization of ornithine aminotransferase in rat ocular tissues. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1987 Sep;28(9):1617–1619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windmueller H. G., Spaeth A. E. Respiratory fuels and nitrogen metabolism in vivo in small intestine of fed rats. Quantitative importance of glutamine, glutamate, and aspartate. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):107–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]