Abstract
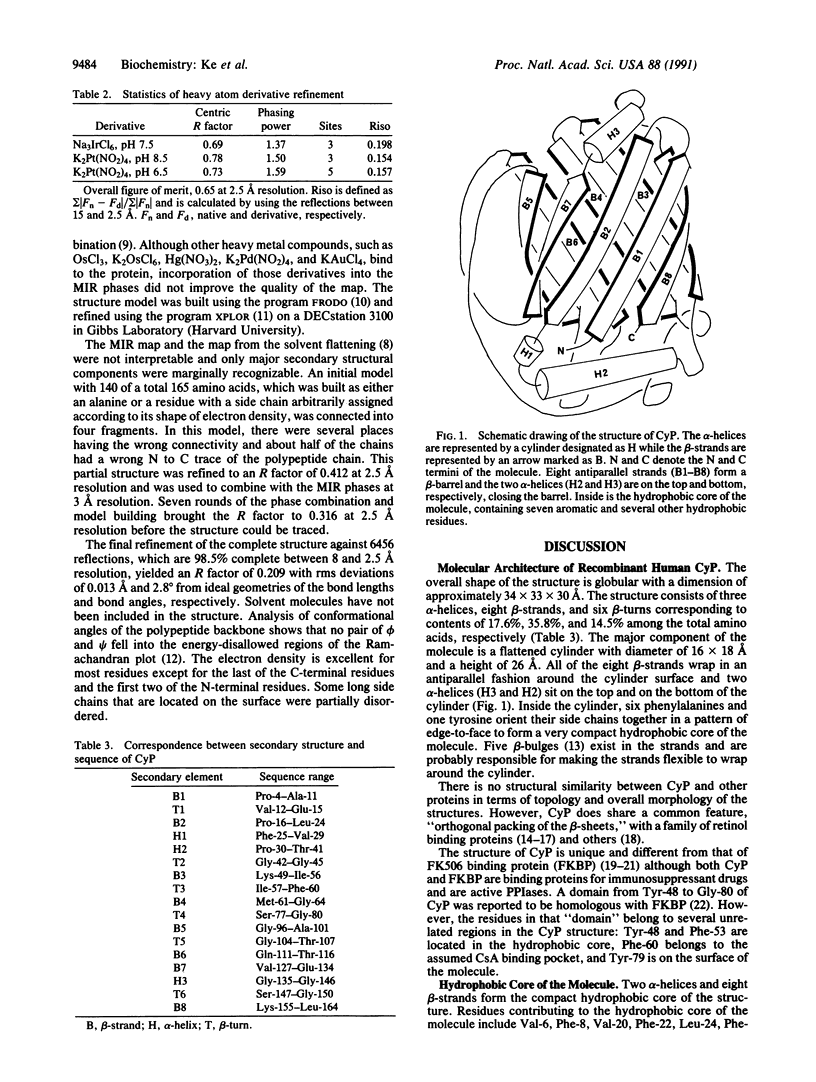
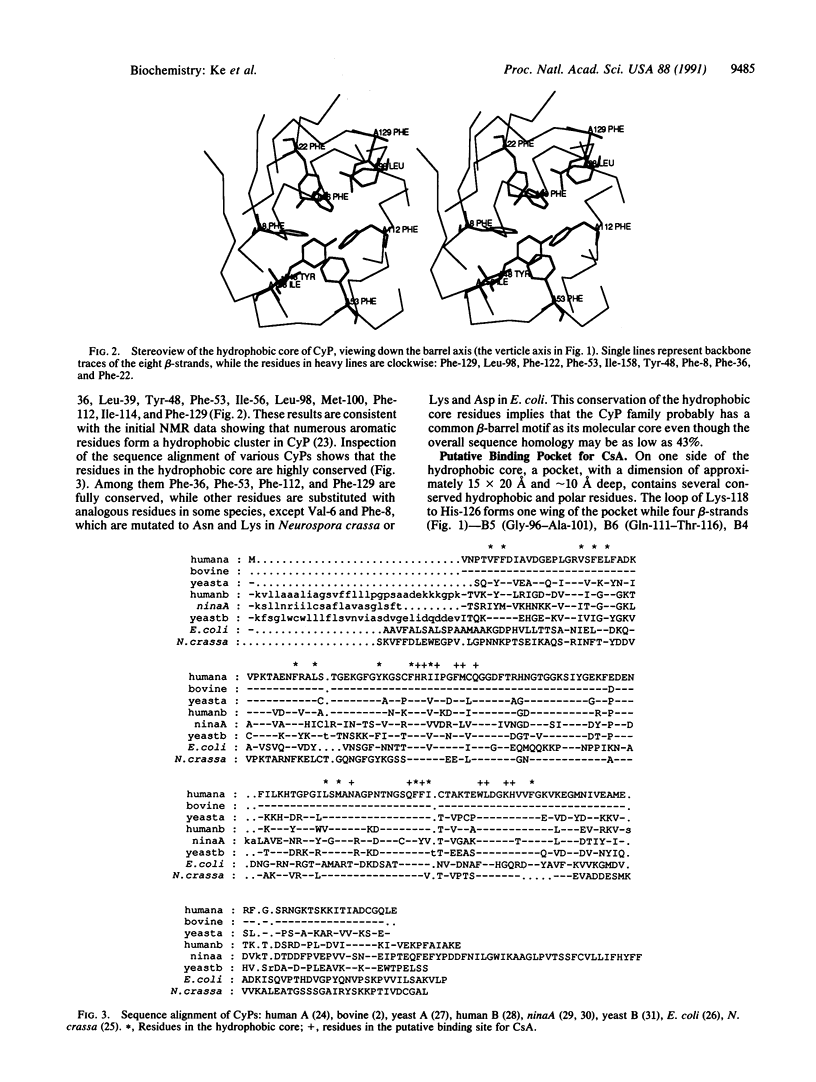
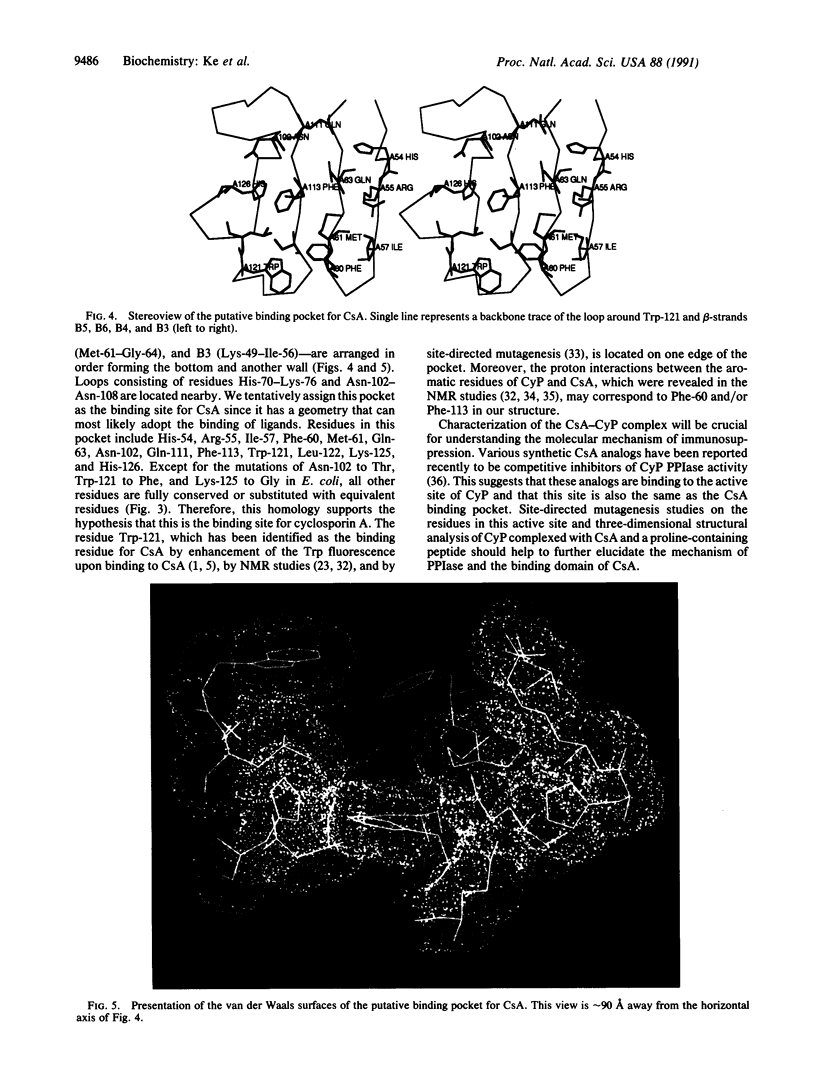
The structure of the unligated human T-cell recombinant cyclophilin has been determined at 3 A resolution by multipole isomorphous replacement methods and refined at 2.5 A resolution to an R factor of 0.209. The root-mean-square errors of the bond lengths and bond angles are 0.013 A and 2.8 degrees from ideal geometry, respectively. The overall structure is a beta-barrel, consisting of eight antiparallel beta-strands wrapping around the barrel surface and two alpha-helices sitting on the top and the bottom closing the barrel. Inside the barrel, seven aromatic and other hydrophobic residues form a compact hydrophobic core. A loop of Lys-118 to His-126 and four beta-strands (B3-B6) constitute a pocket we speculate to be the binding site of cyclosporin A.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brünger A. T., Kuriyan J., Karplus M. Crystallographic R factor refinement by molecular dynamics. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):458–460. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4787.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Janin J. Orthogonal packing of beta-pleated sheets in proteins. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 17;21(17):3955–3965. doi: 10.1021/bi00260a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgarno D. C., Harding M. W., Lazarides A., Handschumacher R. E., Armitage I. M. 1H NMR studies on bovine cyclophilin: preliminary structural characterization of this specific cyclosporin A binding protein. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):6778–6784. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesik S. W., Gampe R. T., Jr, Eaton H. L., Gemmecker G., Olejniczak E. T., Neri P., Holzman T. F., Egan D. A., Edalji R., Simmer R. NMR studies of [U-13C]cyclosporin A bound to cyclophilin: bound conformation and portions of cyclosporin involved in binding. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 2;30(26):6574–6583. doi: 10.1021/bi00240a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesik S. W., Gampe R. T., Jr, Holzman T. F., Egan D. A., Edalji R., Luly J. R., Simmer R., Helfrich R., Kishore V., Rich D. H. Isotope-edited NMR of cyclosporin A bound to cyclophilin: evidence for a trans 9,10 amide bond. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1406–1409. doi: 10.1126/science.2255910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G., Wittmann-Liebold B., Lang K., Kiefhaber T., Schmid F. X. Cyclophilin and peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase are probably identical proteins. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):476–478. doi: 10.1038/337476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haendler B., Hofer-Warbinek R., Hofer E. Complementary DNA for human T-cell cyclophilin. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):947–950. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04843.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haendler B., Keller R., Hiestand P. C., Kocher H. P., Wegmann G., Movva N. R. Yeast cyclophilin: isolation and characterization of the protein, cDNA and gene. Gene. 1989 Nov 15;83(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90401-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handschumacher R. E., Harding M. W., Rice J., Drugge R. J., Speicher D. W. Cyclophilin: a specific cytosolic binding protein for cyclosporin A. Science. 1984 Nov 2;226(4674):544–547. doi: 10.1126/science.6238408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding M. W., Handschumacher R. E., Speicher D. W. Isolation and amino acid sequence of cyclophilin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8547–8555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden H. M., Rypniewski W. R., Law J. H., Rayment I. The molecular structure of insecticyanin from the tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta L. at 2.6 A resolution. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1565–1570. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02401.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Bergfors T., Sedzik J., Unge T. The three-dimensional structure of P2 myelin protein. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1597–1604. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02985.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamukai M., Matsuda H., Fujii W., Utsumi R., Komano T. Nucleotide sequences of fic and fic-1 genes involved in cell filamentation induced by cyclic AMP in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4525–4529. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4525-4529.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kofron J. L., Kuzmic P., Kishore V., Colón-Bonilla E., Rich D. H. Determination of kinetic constants for peptidyl prolyl cis-trans isomerases by an improved spectrophotometric assay. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 25;30(25):6127–6134. doi: 10.1021/bi00239a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koser P. L., Sylvester D., Livi G. P., Bergsma D. J. A second cyclophilin-related gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1643–1643. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.6.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Albers M. W., Chen C. M., Schreiber S. L., Walsh C. T. Cloning, expression, and purification of human cyclophilin in Escherichia coli and assessment of the catalytic role of cysteines by site-directed mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2304–2308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Chen C. M., Walsh C. T. Human and Escherichia coli cyclophilins: sensitivity to inhibition by the immunosuppressant cyclosporin A correlates with a specific tryptophan residue. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 5;30(9):2306–2310. doi: 10.1021/bi00223a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michnick S. W., Rosen M. K., Wandless T. J., Karplus M., Schreiber S. L. Solution structure of FKBP, a rotamase enzyme and receptor for FK506 and rapamycin. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):836–839. doi: 10.1126/science.1709301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. M., Peattie D. A., Fitzgibbon M. J., Thomson J. A. Solution structure of the major binding protein for the immunosuppressant FK506. Nature. 1991 May 16;351(6323):248–250. doi: 10.1038/351248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomer M. E., Jones T. A., Aqvist J., Sundelin J., Eriksson U., Rask L., Peterson P. A. The three-dimensional structure of retinol-binding protein. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1451–1454. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01995.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papiz M. Z., Sawyer L., Eliopoulos E. E., North A. C., Findlay J. B., Sivaprasadarao R., Jones T. A., Newcomer M. E., Kraulis P. J. The structure of beta-lactoglobulin and its similarity to plasma retinol-binding protein. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):383–385. doi: 10.1038/324383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price E. R., Zydowsky L. D., Jin M. J., Baker C. H., McKeon F. D., Walsh C. T. Human cyclophilin B: a second cyclophilin gene encodes a peptidyl-prolyl isomerase with a signal sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1903–1907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran G. N., Sasisekharan V. Conformation of polypeptides and proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1968;23:283–438. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60402-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S. The anatomy and taxonomy of protein structure. Adv Protein Chem. 1981;34:167–339. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60520-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneuwly S., Shortridge R. D., Larrivee D. C., Ono T., Ozaki M., Pak W. L. Drosophila ninaA gene encodes an eye-specific cyclophilin (cyclosporine A binding protein). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5390–5394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh B. H., Stamnes M. A., Seavello S., Harris G. L., Zuker C. S. The ninaA gene required for visual transduction in Drosophila encodes a homologue of cyclosporin A-binding protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):67–70. doi: 10.1038/338067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Hayano T., Suzuki M. Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase is the cyclosporin A-binding protein cyclophilin. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):473–475. doi: 10.1038/337473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tropschug M., Nicholson D. W., Hartl F. U., Köhler H., Pfanner N., Wachter E., Neupert W. Cyclosporin A-binding protein (cyclophilin) of Neurospora crassa. One gene codes for both the cytosolic and mitochondrial forms. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14433–14440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Duyne G. D., Standaert R. F., Karplus P. A., Schreiber S. L., Clardy J. Atomic structure of FKBP-FK506, an immunophilin-immunosuppressant complex. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):839–842. doi: 10.1126/science.1709302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B. C. Resolution of phase ambiguity in macromolecular crystallography. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:90–112. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber C., Wider G., von Freyberg B., Traber R., Braun W., Widmer H., Wüthrich K. The NMR structure of cyclosporin A bound to cyclophilin in aqueous solution. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 2;30(26):6563–6574. doi: 10.1021/bi00240a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederrecht G., Brizuela L., Elliston K., Sigal N. H., Siekierka J. J. FKB1 encodes a nonessential FK 506-binding protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and contains regions suggesting homology to the cyclophilins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):1029–1033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]