Abstract
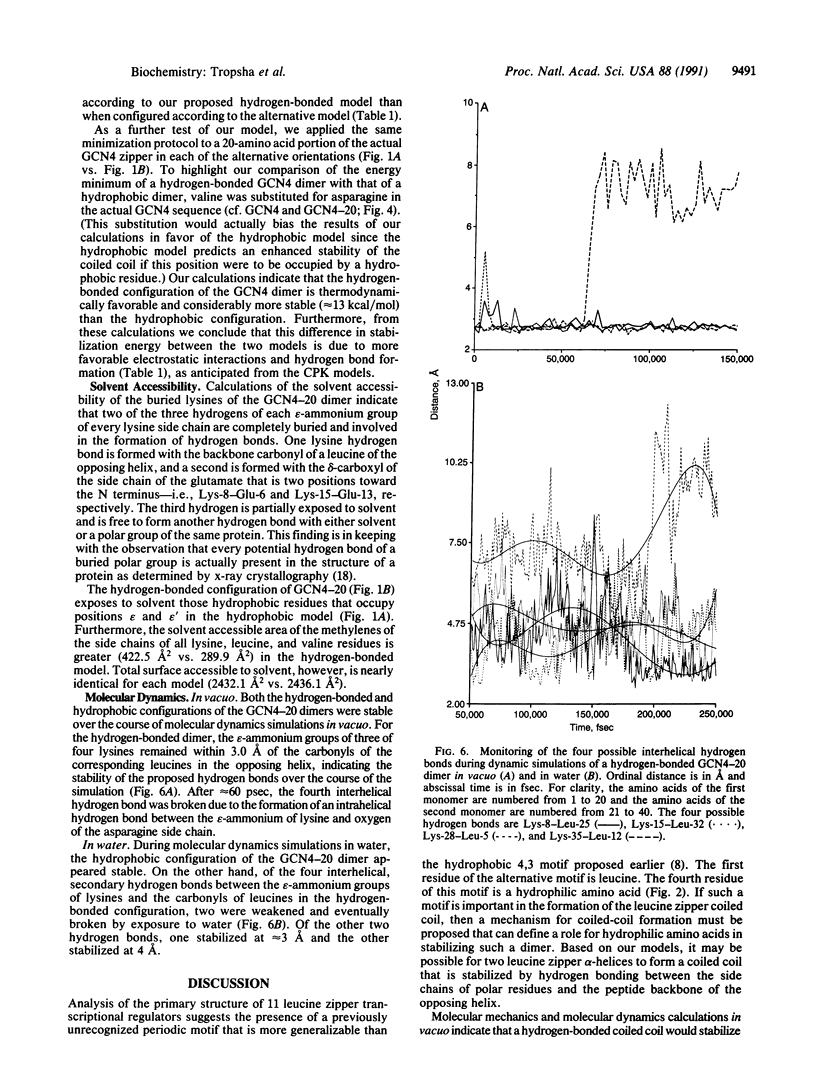
The leucine zipper proteins are a group of transcriptional regulators that dimerize to form a DNA binding domain. It has been proposed that this dimerization results from the hydrophobic association of the alpha-helices of two leucine zipper monomers into a coiled coil. We propose a model for a coiled coil based on a periodic hydrophobic-hydrophilic amino acid motif found in the leucine zipper regions of 11 transcriptional regulatory proteins. This model predicts the symmetrical formation of secondary hydrogen bonds between the polar side chains of one helix and the peptide carbonyls of the opposite chain, supplementing the interactions between hydrophobic side chains. Physical modeling (CPK) and in vacuo molecular mechanics calculations of the stability of the GCN4 leucine zipper coiled coil configured in accordance with this model demonstrate a greater stability for this conformer than for a conformer configured according to a current hydrophobic model. Molecular dynamics simulations show similar stability of the two models in vacuo but a higher stability of the hydrophobic model in water.
Full text
PDF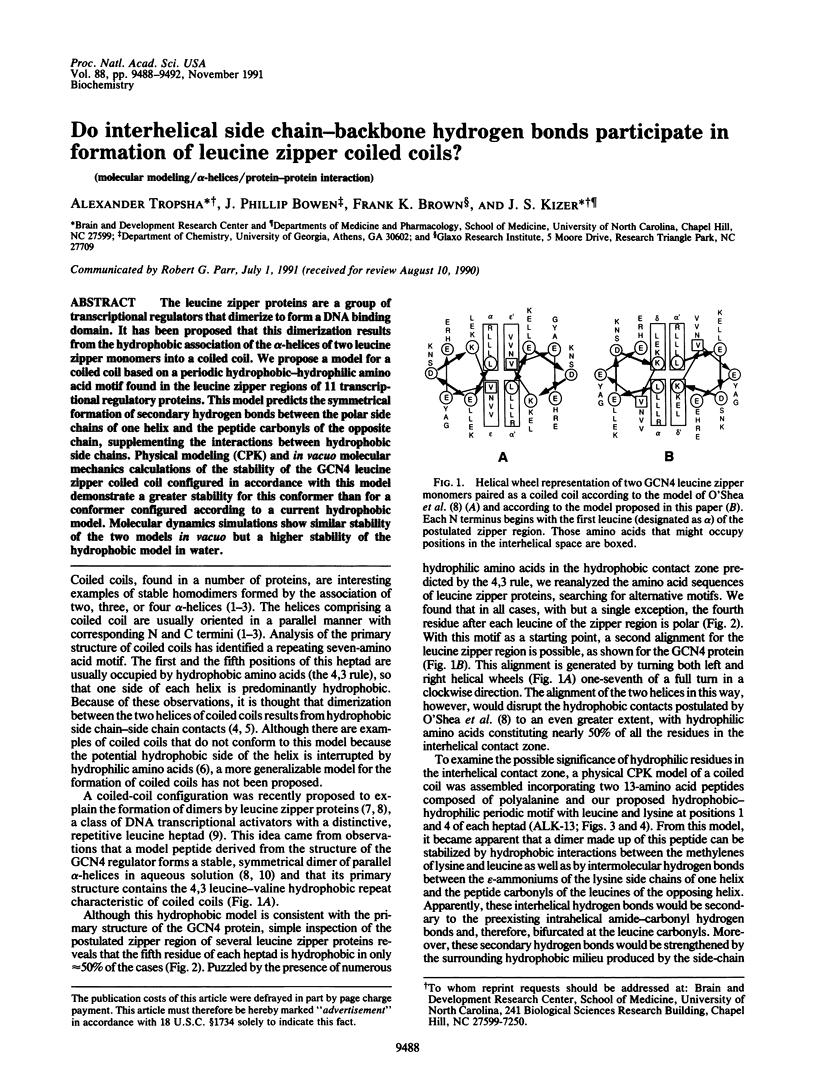


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker E. N., Hubbard R. E. Hydrogen bonding in globular proteins. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1984;44(2):97–179. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(84)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burley S. K., Petsko G. A. Weakly polar interactions in proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1988;39:125–189. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60376-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christophe D., Cabrer B., Bacolla A., Targovnik H., Pohl V., Vassart G. An unusually long poly(purine)-poly(pyrimidine) sequence is located upstream from the human thyroglobulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5127–5144. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C., Parry D. A. Alpha-helical coiled coils and bundles: how to design an alpha-helical protein. Proteins. 1990;7(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/prot.340070102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coll M., Frederick C. A., Wang A. H., Rich A. A bifurcated hydrogen-bonded conformation in the d(A.T) base pairs of the DNA dodecamer d(CGCAAATTTGCG) and its complex with distamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8385–8389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanvey J. C., Shimizu M., Wells R. D. Intramolecular DNA triplexes in supercoiled plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6292–6296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau S. Y., Taneja A. K., Hodges R. S. Synthesis of a model protein of defined secondary and quaternary structure. Effect of chain length on the stabilization and formation of two-stranded alpha-helical coiled-coils. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13253–13261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Richards F. M. The interpretation of protein structures: estimation of static accessibility. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 14;55(3):379–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liou H. C., Boothby M. R., Finn P. W., Davidon R., Nabavi N., Zeleznik-Le N. J., Ting J. P., Glimcher L. H. A new member of the leucine zipper class of proteins that binds to the HLA DR alpha promoter. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1581–1584. doi: 10.1126/science.2321018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyamichev V. I., Mirkin S. M., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Structures of homopurine-homopyrimidine tract in superhelical DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Feb;3(4):667–669. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10508454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D., Karn J. Periodic features in the amino acid sequence of nematode myosin rod. J Mol Biol. 1983 Mar 15;164(4):605–626. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Rutkowski R., Kim P. S. Evidence that the leucine zipper is a coiled coil. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):538–542. doi: 10.1126/science.2911757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Rutkowski R., Stafford W. F., 3rd, Kim P. S. Preferential heterodimer formation by isolated leucine zippers from fos and jun. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):646–648. doi: 10.1126/science.2503872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
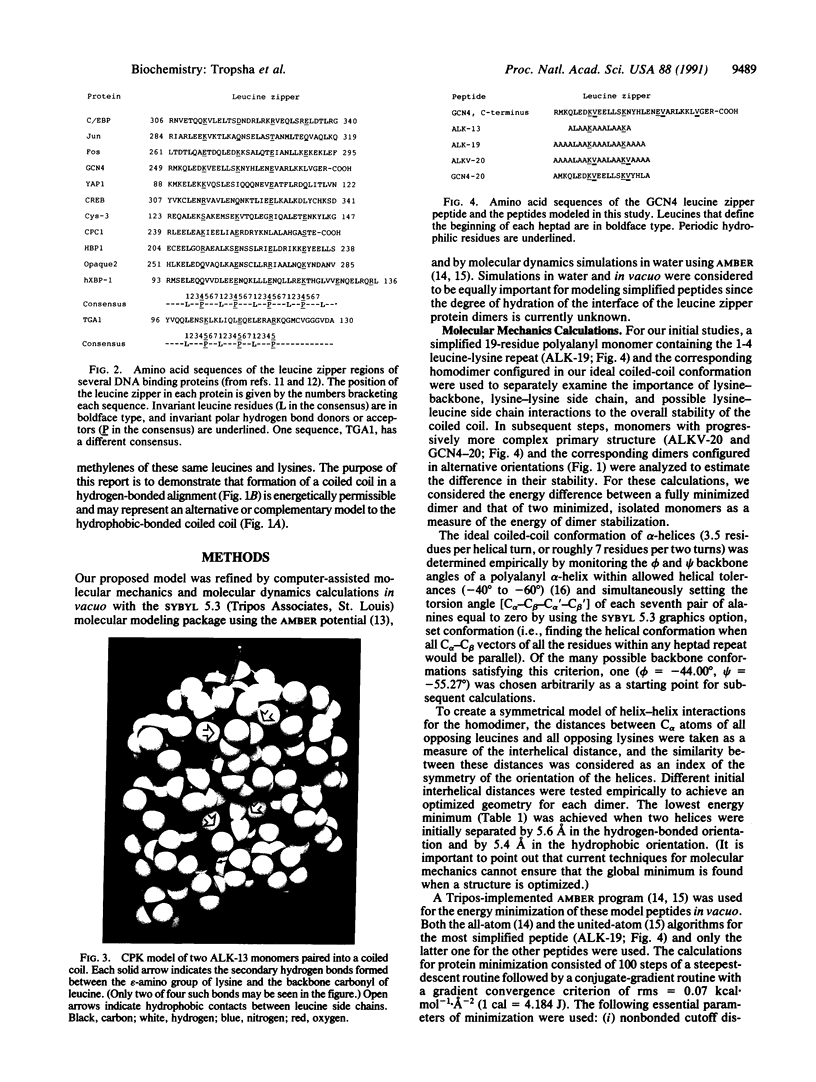
- Oas T. G., McIntosh L. P., O'Shea E. K., Dahlquist F. W., Kim P. S. Secondary structure of a leucine zipper determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 27;29(12):2891–2894. doi: 10.1021/bi00464a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presta L. G., Rose G. D. Helix signals in proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 17;240(4859):1632–1641. doi: 10.1126/science.2837824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran G. N., Sasisekharan V. Conformation of polypeptides and proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1968;23:283–438. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60402-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S., Richardson D. C. Amino acid preferences for specific locations at the ends of alpha helices. Science. 1988 Jun 17;240(4859):1648–1652. doi: 10.1126/science.3381086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S. Schematic drawings of protein structures. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:359–380. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segrest J. P., De Loof H., Dohlman J. G., Brouillette C. G., Anantharamaiah G. M. Amphipathic helix motif: classes and properties. Proteins. 1990;8(2):103–117. doi: 10.1002/prot.340080202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]