Abstract
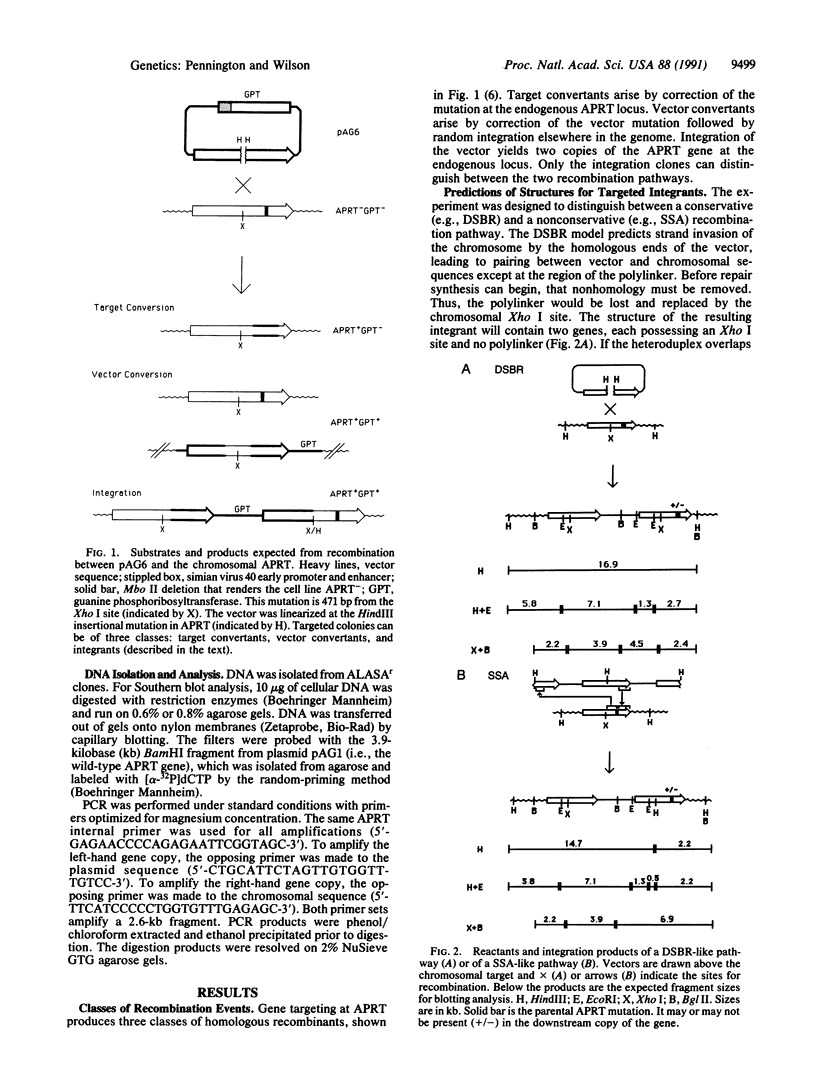
Two fundamentally different pathways for homologous recombination have been identified in mammalian cells. For most chromosomal recombination events, two copies of a homologous sequence recombine to yield two copies in the products; such events are said to be conservative because the number of copies is preserved. By contrast, virtually all extrachromosomal recombination events are nonconservative; two copies recombine to give a product containing a single intact copy (the other copy is destroyed in the mechanism). Since gene targeting involves an introduced (extrachromosomal) plasmid and a chromosomal target, it was not clear which pathway would apply. We used a marked vector to determine whether targeted integrants were products of recombination events that involved two copies (the conservative pathway) or three copies (the nonconservative pathway) of the homologous sequence. Among 51 gene targeting events, we identified 17 homologous integrants and analyzed their structures. All match the predictions for a conservative pathway. We conclude that the principal pathway for gene targeting in mammalian cells is conservative.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adair G. M., Nairn R. S., Wilson J. H., Scheerer J. B., Brotherman K. A. Targeted gene replacement at the endogenous APRT locus in CHO cells. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1990 Sep;16(5):437–441. doi: 10.1007/BF01233193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adair G. M., Nairn R. S., Wilson J. H., Seidman M. M., Brotherman K. A., MacKinnon C., Scheerer J. B. Targeted homologous recombination at the endogenous adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus in Chinese hamster cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4574–4578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollag R. J., Liskay R. M. Conservative intrachromosomal recombination between inverted repeats in mouse cells: association between reciprocal exchange and gene conversion. Genetics. 1988 May;119(1):161–169. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Hayakawa H., Berg P. Electroporation for the efficient transfection of mammalian cells with DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1311–1326. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetschman T., Maeda N., Smithies O. Targeted mutation of the Hprt gene in mouse embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8583–8587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasin M., Berg P. Homologous integration in mammalian cells without target gene selection. Genes Dev. 1988 Nov;2(11):1353–1363. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.11.1353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Intermolecular recombination between DNAs introduced into mouse L cells is mediated by a nonconservative pathway that leads to crossover products. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):103–112. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Model for homologous recombination during transfer of DNA into mouse L cells: role for DNA ends in the recombination process. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1020–1034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Disruption of the proto-oncogene int-2 in mouse embryo-derived stem cells: a general strategy for targeting mutations to non-selectable genes. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):348–352. doi: 10.1038/336348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn R. S., Humphrey R. M., Adair G. M. Transformation of UV-hypersensitive Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants with UV-irradiated plasmids. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1988 Feb;53(2):249–260. doi: 10.1080/09553008814550601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickoloff J. A., Chen E. Y., Heffron F. A 24-base-pair DNA sequence from the MAT locus stimulates intergenic recombination in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7831–7835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Nicolas A., Szostak J. W. Gene conversion adjacent to regions of double-strand break repair. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5292–5298. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W. Yeast recombination: the association between double-strand gap repair and crossing-over. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4417–4421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter T., Pennington S. L., Adair G. M., Nairn R. S., Wilson J. H. A novel selection system for recombinational and mutational events within an intron of a eucaryotic gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5173–5180. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommerskirch W., Graeber I., Grässmann M., Grässmann A. Homologous recombination of SV40 DNA in COS7 cells occurs with high frequency in a gene dose independent fashion. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):941–952. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Chang X. B., Wilson J. H. Comparison of filler DNA at immune, nonimmune, and oncogenic rearrangements suggests multiple mechanisms of formation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3049–3057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Wilson J. H. Nonhomologous recombination in mammalian cells: role for short sequence homologies in the joining reaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4295–4304. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman M. M. Intermolecular homologous recombination between transfected sequences in mammalian cells is primarily nonconservative. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3561–3565. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Gregg R. G., Boggs S. S., Koralewski M. A., Kucherlapati R. S. Insertion of DNA sequences into the human chromosomal beta-globin locus by homologous recombination. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):230–234. doi: 10.1038/317230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramani S., Rubnitz J. Recombination events after transient infection and stable integration of DNA into mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):659–666. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun H., Treco D., Szostak J. W. Extensive 3'-overhanging, single-stranded DNA associated with the meiosis-specific double-strand breaks at the ARG4 recombination initiation site. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1155–1161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90270-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Orr-Weaver T. L., Rothstein R. J., Stahl F. W. The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by gene targeting in mouse embryo-derived stem cells. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Folger K. R., Capecchi M. R. High frequency targeting of genes to specific sites in the mammalian genome. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):419–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90463-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S., Clarke A. R., Pow A. M., Hooper M. L., Melton D. W. Germ line transmission and expression of a corrected HPRT gene produced by gene targeting in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):313–321. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90905-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Vernaleone F., Wilson J. H. Topological requirements for homologous recombination among DNA molecules transfected into mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2080–2089. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng H., Chang X. B., Wilson J. H. Primary cells and established cell lines join DNA ends with the same efficiency relative to homologous recombination. Plasmid. 1989 Sep;22(2):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(89)90019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zijlstra M., Li E., Sajjadi F., Subramani S., Jaenisch R. Germ-line transmission of a disrupted beta 2-microglobulin gene produced by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):435–438. doi: 10.1038/342435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer A., Gruss P. Production of chimaeric mice containing embryonic stem (ES) cells carrying a homoeobox Hox 1.1 allele mutated by homologous recombination. Nature. 1989 Mar 9;338(6211):150–153. doi: 10.1038/338150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]