Abstract
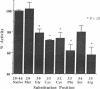
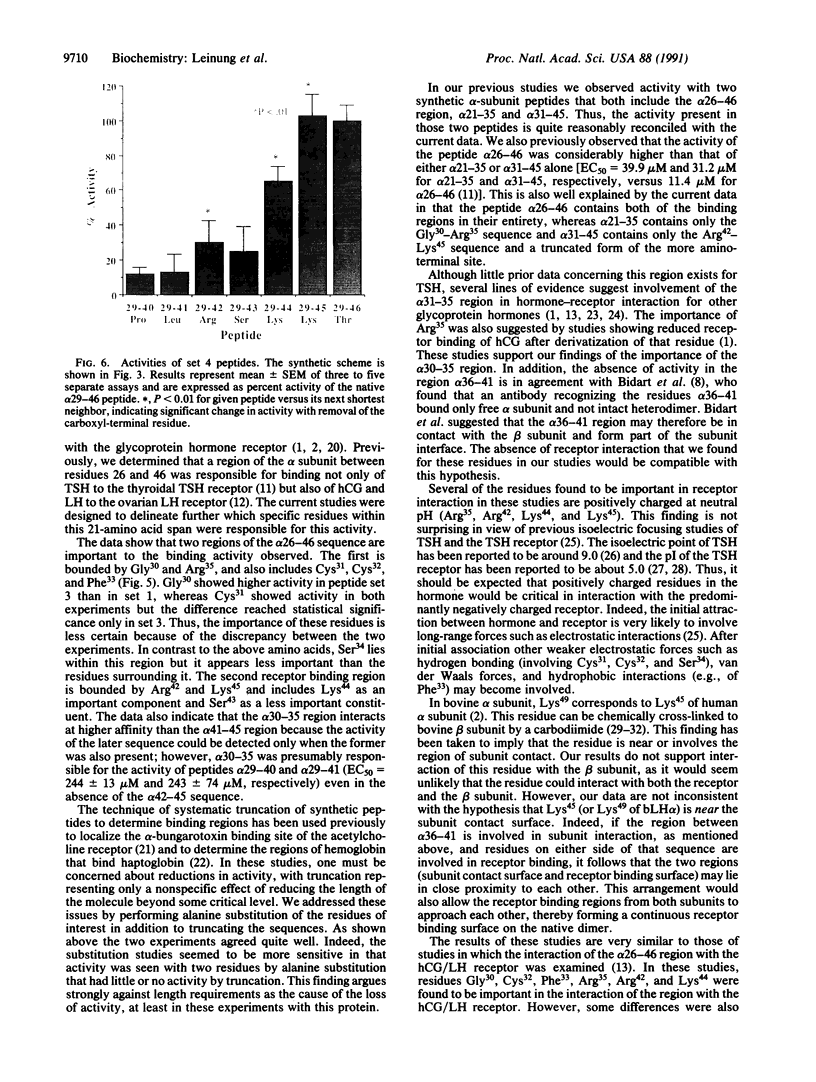
Previously, using a synthetic peptide strategy, we determined that the region of the common glycoprotein hormone alpha subunit between residues 26 and 46 is a site of interaction of the hormone with the thyroid membrane-bound receptor for thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). We have undertaken to identify further the specific residues within this 21-amino acid span that are critical in hormone receptor binding. We synthesized three nested sets of peptide, two in which we systematically truncated the amino-terminal region of the sequence and another in which we truncated the carboxyl-terminal region, and we synthesized a fourth nested set in which we systematically substituted alanine for the native residues from the region of highest activity. Each peptide was tested in a TSH radioreceptor assay for its ability to inhibit binding of 125I-labeled bovine TSH to porcine thyroid membranes. Removal either by truncation or alanine substitution, of several specific residues resulted in a significant reduction in the ability of the sequence to interact with receptor; these residues included Cys31, Cys32, Phe33, Arg35, Arg42, Lys44, and Lys45, suggesting that they are crucial for binding activity. Loss of activity also occurred with substitution for Gly30 and Ser34, but the reduction was less pronounced. Amino-terminal truncation of the sequence through Arg35 (leaving the alpha-subunit peptide 36-46) resulted in greater than 98% loss of activity of the sequence. We conclude that two distinct receptor binding regions lie within the alpha-subunit 26-46 sequence. The first lies between residues Gly30 and Arg35 and includes Cys31, Cys32, and Phe33 as important constituents, and the second region lies between residues Arg42 and Lys45 and includes Lys44 as an important residue and Ser43 as a less important component.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso-Whipple C., Couet M. L., Doss R., Koziarz J., Ogunro E. A., Crowley W. F., Jr Epitope mapping of human luteinizing hormone using monoclonal antibodies. Endocrinology. 1988 Oct;123(4):1854–1860. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-4-1854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidart J. M., Troalen F., Bousfield G. R., Birken S., Bellet D. H. Antigenic determinants on human choriogonadotropin alpha-subunit. I. Characterization of topographic sites recognized by monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10364–10369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burleigh B. D., Liu W. K., Ward D. N. Photocoupling of the subunits of ovine lutropin using a specific aryl azide derivative of the beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7179–7185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth M. C., McCormick D. J., Madden B., Ryan R. J. Inhibition of human choriotropin binding to receptor by human choriotropin alpha peptides. A comprehensive synthetic approach. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13409–13416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combarnous Y., Hennen G. Luteinizing hormone derivatives with covalently-linked subunits. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 25;44(2):224–228. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80730-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costagliola S., Madec A. M., Benkirane M. M., Orgiazzi J., Carayon P. Monoclonal antibody approach to the relationship between immunological structure and biological activity of thyrotropin. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Jul;2(7):613–618. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-7-613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creagh F. M., Howells R. D., Williams S., Didcote S., Hashim F. A., Petersen V. B., Rees Smith B. IgG thyrotrophin receptor antibody activity in Graves' disease; a study of TSH agonist and antagonist activities by isoelectric focusing. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1986 Jan;24(1):79–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1986.tb03257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson L. D., Rizza S. A., Bergert E. R., Charlesworth M. C., McCormick D. J., Ryan R. J. Synthetic alpha-subunit peptides stimulate testosterone production in vitro by rat Leydig cells. Endocrinology. 1990 May;126(5):2555–2560. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-5-2555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. C., Machin K. J., Evin G. M., Morgan F. J., Isaacs N. W. Preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of human chorionic gonadotropin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6705–6706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashim F. A., Davies Jones E., Howells R. D., Reees Smith B. Isoelectric focusing of the human TSH receptor A subunit. Biosci Rep. 1986 Jul;6(7):685–689. doi: 10.1007/BF01114764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrikson R. L., Meredith S. C. Amino acid analysis by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography: precolumn derivatization with phenylisothiocyanate. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A. General method for the rapid solid-phase synthesis of large numbers of peptides: specificity of antigen-antibody interaction at the level of individual amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5131–5135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustbader J. W., Birken S., Pileggi N. F., Kolks M. A., Pollak S., Cuff M. E., Yang W., Hendrickson W. A., Canfield R. E. Crystallization and characterization of human chorionic gonadotropin in chemically deglycosylated and enzymatically desialylated states. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 28;28(24):9239–9243. doi: 10.1021/bi00450a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick D. J., Atassi M. Z. Hemoglobin binding with haptoglobin: delineation of the haptoglobin binding site on the alpha-chain of human hemoglobin. J Protein Chem. 1990 Dec;9(6):735–742. doi: 10.1007/BF01024768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson A., Koszelak S., Axelrod H., Day J., Williams R., Robinson L., McGrath M., Cascio D. An experiment regarding crystallization of soluble proteins in the presence of beta-octyl glucoside. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1969–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. C., 3rd, Jiang N. S., Charlesworth M. C., McCormick D. J., Ryan R. J. The effects of synthetic alpha-subunit peptides on thyrotropin interaction with its receptor. Endocrinology. 1988 Jul;123(1):456–462. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-1-456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. C., McCormick D. J., Ryan R. J. Inhibition of thyrotropin binding to receptor by synthetic human thyrotropin beta peptides. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):1881–1884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons T. F., Pierce J. G. Biologically active covalently cross-linked glycoprotein hormones and the effects of modification of the COOH-terminal region of their alpha subunits. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6010–6015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. G., Parsons T. F. Glycoprotein hormones: structure and function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:465–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed D. K., Ryan R. J., McCormick D. J. Residues in the alpha subunit of human choriotropin that are important for interaction with the lutropin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14251–14255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan R. J., Charlesworth M. C., McCormick D. J., Milius R. P., Keutmann H. T. The glycoprotein hormones: recent studies of structure-function relationships. FASEB J. 1988 Aug;2(11):2661–2669. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.11.2456242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan R. J., Keutmann H. T., Charlesworth M. C., McCormick D. J., Milius R. P., Calvo F. O., Vutyavanich T. Structure-function relationships of gonadotropins. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1987;43:383–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Jiang N. S., Gorman C. A., Lee C. Y. Thyrotropin receptors in normal and pathological human thyroid tissues. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Oct;47(4):870–876. doi: 10.1210/jcem-47-4-870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troalen F., Bellet D. H., Ghillani P., Puisieux A., Bohuon C. J., Bidart J. M. Antigenic determinants on human choriogonadotropin alpha-subunit. II. Immunochemical mapping by a monoclonal antipeptide antibody. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10370–10376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Remoundos M. S. Fine localization of the major alpha-bungarotoxin binding site to residues alpha 189-195 of the Torpedo acetylcholine receptor. Residues 189, 190, and 195 are indispensable for binding. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21462–21467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weare J. A., Reichert L. E., Jr Studies with carbodiimide-cross-linked derivatives of bovine lutropin. II. Location of the cross-link and implication for interaction with the receptors in testes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):6972–6979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner R. S., Andersen T. T., Dias J. A. Topographic analysis of the alpha-subunit of human follicle-stimulating hormone using site-specific antipeptide antisera. Endocrinology. 1990 Aug;127(2):573–579. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-2-573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner R. S., Dias J. A., Andersen T. T. Epitope mapping of human follicle stimulating hormone-alpha using monoclonal antibody 3A identifies a potential receptor binding sequence. Endocrinology. 1991 Mar;128(3):1485–1495. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-3-1485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]